What is Ongoing Monitoring in AML and Vendor Risk Management
The ongoing monitoring process allows organizations to stay ahead of potential risks, detect suspicious activities early, and comply with regulatory standards. Be it tracking financial transactions, vendor performance, or customer behavior, real-time risk management ensures that businesses can act promptly when issues arise.
In this article, we’ll explore effective strategies for real-time vendor risk management, its applications, challenges, and best practices for successful implementation.
Key Takeaways
Ongoing monitoring enables businesses to identify and address financial crimes like money laundering and fraud as they occur, preventing long-term damage.
Continuous monitoring helps organizations remain compliant with changing AML/CFT regulations, ensuring timely reporting and avoiding legal penalties.
Incorporating machine learning and AI into monitoring systems enhances accuracy, identifies hidden risks, and automates real-time decision-making for better risk mitigation.
Ongoing monitoring allows businesses to stay ahead of emerging risks, ensuring continuous compliance and safeguarding reputations by addressing vulnerabilities before they escalate.
Real-time monitoring tracks third-party vendors, ensuring their security and compliance practices meet your standards, reducing exposure to operational, financial, and reputational risks.
What Is Ongoing Monitoring in AML and Vendor Risk Management?
Ongoing monitoring in AML and vendor risk management refers to the continuous and dynamic process of assessing and evaluating risk across various touchpoints in your business operations. This includes tracking the behavior of customers, transactions, and vendors in real time to detect potential threats before they escalate into significant problems.
This approach moves beyond periodic checks, allowing businesses to maintain constant vigilance and proactive risk mitigation. By using automated tools, AI-driven analysis, and regulatory compliance checks, ongoing monitoring ensures that any deviations from expected behavior are addressed immediately.
Auditive’s Supply Chain Continuous Monitoring can track real-time incidents across your supply chain, from data breaches to financial instability. This feature keeps you informed of any changes, allowing for timely responses and proactive risk mitigation.
Now, let’s explore why companies are increasingly adopting ongoing monitoring in vendor risk management.
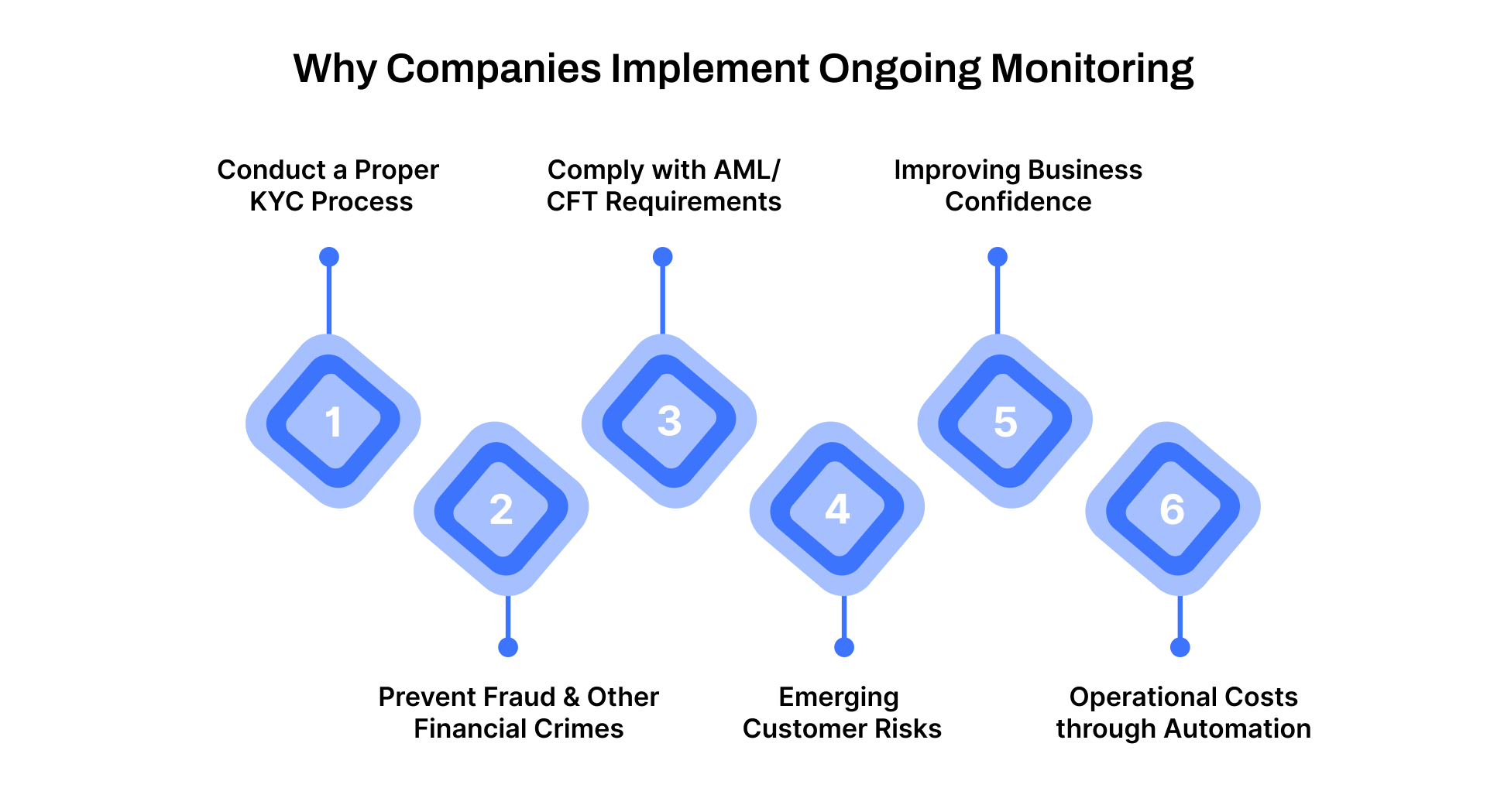
Why Companies Implement Ongoing Monitoring
Many organizations in financial services, healthcare, and education sectors adopt ongoing monitoring to manage risks effectively. Here’s why it’s critical:
1. Conduct a Proper KYC Process
Ongoing monitoring ensures that Know Your Customer (KYC) practices are continuously followed. By verifying customer identities in real-time, businesses can prevent fraudulent activities and comply with regulations like FinCEN and KYC guidelines.
2. Prevent Fraud and Other Financial Crimes
With real-time monitoring, businesses can quickly identify fraudulent activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing. By monitoring transactions continuously, suspicious activities can be flagged and investigated immediately, reducing financial crime exposure.
3. Comply with AML/CFT Requirements
Regulatory bodies demand that businesses comply with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter Financing of Terrorism (CFT) standards. Ongoing monitoring helps businesses track transactions, customers, and vendors, ensuring they meet compliance standards and avoid legal penalties.
4. Adapting to Emerging Customer Risks
Customer risks adapt with changing behaviors, market conditions, and financial activities. Ongoing monitoring helps businesses quickly adapt to these changes and ensures continuous compliance with shifting regulatory requirements.
5. Improving Business Confidence and Credibility
By adopting ongoing monitoring, businesses signal to stakeholders, such as customers, regulators, and partners, that they are committed to transparency and risk mitigation.
6. Reducing Operational Costs through Automation
With real-time monitoring systems in place, businesses can automate many aspects of AML and vendor risk management. This reduces manual intervention, minimizes human error, and lowers operational costs, all while maintaining high levels of compliance and risk detection.
Also Read: Supplier Information Validation Methods You Need to Know
With clear reasons for implementation, let's look at the key components that make the ongoing monitoring process effective.
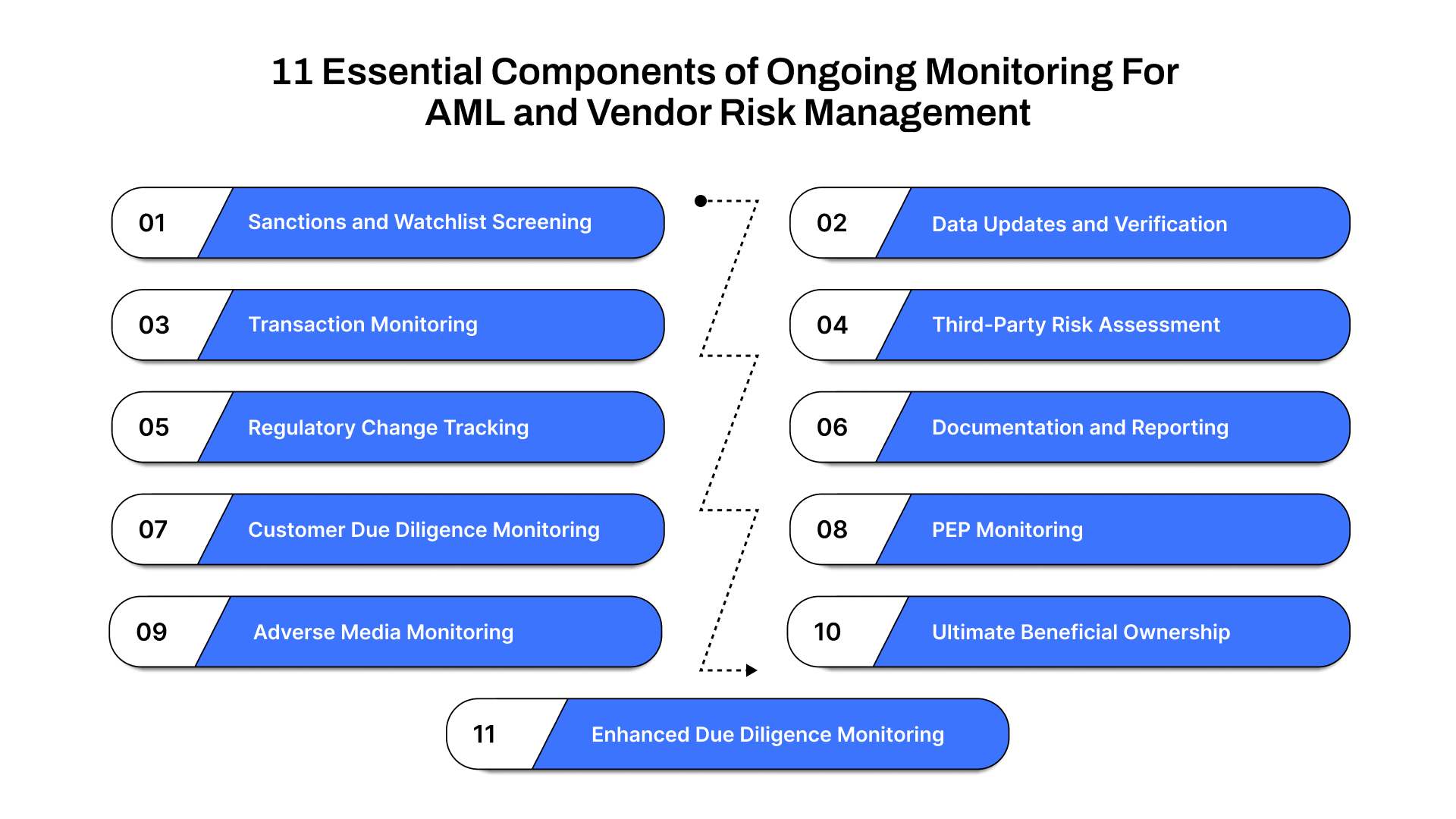
11 Essential Components of Ongoing Monitoring For AML and Vendor Risk Management
Implementing an effective ongoing monitoring process involves integrating various key components to track and assess risks dynamically. These components help ensure compliance and reduce potential threats from customers and vendors.
1. Sanctions and Watchlist Screening
Regular screening of customers and vendors against sanctions lists and watchlists is a core component of ongoing monitoring. This ensures you avoid engaging with individuals or entities involved in illegal activities.
2. Data Updates and Verification
For accurate monitoring, continuous verification of data is necessary. This includes updating customer profiles, financial transactions, and vendor information to ensure they align with regulatory standards and organizational policies.
3. Transaction Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of financial transactions helps identify suspicious patterns, such as large, unexpected payments or transactions involving high-risk regions. Automated systems help track and flag irregularities for further investigation.
4. Third-Party Risk Assessment
Ongoing monitoring of third-party vendors involves assessing their security practices, financial stability, and regulatory compliance. This ensures they remain a secure and reliable partner throughout the course of the business relationship.
5. Regulatory Change Tracking
Ongoing monitoring includes tracking regulatory changes that may affect your AML and vendor risk management practices, ensuring that your systems and processes remain compliant.
6. Documentation and Reporting
Maintaining proper documentation and generating timely reports is a vital part of ongoing monitoring. Accurate, real-time records ensure compliance and provide an audit trail for regulators.
7. Customer Due Diligence Monitoring
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) should be continuously monitored to track changes in a customer’s risk profile. This ensures that any change in behavior or transaction patterns is addressed quickly.
8. PEP Monitoring
Monitoring Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) is crucial in identifying potential risks related to corruption, bribery, or money laundering. Ongoing monitoring allows you to track any changes in PEP status and adapt your risk management approach accordingly.
9. Adverse Media Monitoring
Regular monitoring of media outlets for any adverse news related to your customers or vendors helps identify reputational risks early, such as involvement in criminal activities or other financial crimes.
10. Ultimate Beneficial Ownership (UBO) Monitoring
Ongoing monitoring ensures that you can track the true ownership of entities involved in financial transactions, preventing hidden ownership or connections to illegal activities.
11. Enhanced Due Diligence Monitoring
For high-risk customers or vendors, enhanced due diligence (EDD) should be continuously conducted. This involves collecting and analyzing additional information to assess the risks involved in these relationships.
Also Read: Optimizing Third-Party Healthcare Risk Management Strategies
Now that we've covered the components, let’s look at how you can implement an effective ongoing monitoring process.
6 Steps to Implement Ongoing Monitoring For AML and Vendor Risk Management
Implementing an effective ongoing monitoring process requires a structured approach. Below are the steps to ensure a smooth and efficient implementation:
1. Risk Assessment
Begin by conducting a comprehensive risk assessment to understand the specific threats and vulnerabilities associated with your customers, vendors, and business operations. This will guide your ongoing monitoring strategy.
2. Internal Controls
Establish strong internal controls to validate customer identities before transactions occur. These include implementing identity verification systems, setting policies for transaction monitoring, and creating escalation procedures for flagging suspicious activities.
3. Transaction Monitoring
Monitor transactions in real time, looking for red flags such as large, unusual transactions or activity from high-risk jurisdictions. Automated systems can help spot these anomalies quickly, reducing the chance of overlooking serious issues.
4. Reporting Suspicious Activities
Set up clear reporting procedures for suspicious activities. These reports should be automatically flagged and escalated to the compliance team, who will then investigate further and report to authorities if necessary.
5. Audits and Reviews
Regular audits and reviews help ensure that your ongoing monitoring process is functioning as intended. This includes verifying the effectiveness of monitoring tools and reviewing compliance reports to confirm adherence to policies.
6. Continuous Training
Ongoing training for employees ensures they stay updated on the latest regulatory requirements, emerging threats, and how to use monitoring tools effectively. This enables them to identify and address risks more efficiently.
Also Read: Top Vendor Security and Privacy Assessment Software for 2025
Once the implementation steps are clear, understanding the frequency of ongoing monitoring is essential to maintaining effectiveness.
When and How Often Should You Conduct Ongoing Monitoring?
The frequency and timing of ongoing monitoring depend on the risk profile of your organization and the nature of your vendor or customer relationships. Here’s a breakdown of how often and when you should conduct real-time risk management:
1. For High-Risk Customers and Vendors
High-risk entities, such as Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs), customers from high-risk jurisdictions, or vendors with complex ownership structures, should be monitored continuously in real time. Regular updates, along with automated alerts, ensure that changes in their risk profile are detected immediately.
2. For Regular Customers and Vendors
Customers or vendors with a stable risk profile may require less frequent but still regular monitoring. In this case, monthly or quarterly reviews combined with real-time transaction monitoring can help keep risks at bay.
3. For Transactions
Transaction monitoring should occur in real time for every transaction, especially for financial institutions or organizations handling large sums. This ensures compliance with AML/CFT regulations and reduces the chances of fraudulent transactions.
4. When Regulatory Changes Occur
Whenever there is a change in the regulatory conditions, immediate updates to the monitoring process are required. This ensures compliance with new requirements and adjusts risk levels accordingly.
When managing AML and vendor risk, it’s important to monitor contract compliance continuously. Auditive’s Contract Monitor tracks vendor adherence, flags discrepancies, and ensures key clauses remain compliant. By automating this process, you can stay ahead of potential risks, maintaining strong vendor relationships and compliance at all times.
Also Read: CCPA Compliance Tools in 2025
Let’s now explore the legal and regulatory aspects that shape ongoing monitoring in vendor risk management.
AML Regulations and Requirements for Ongoing Monitoring and Vendor Risk Management
Understanding the regulations governing ongoing monitoring is essential for staying compliant with AML standards. Both the U.S. and Canada enforce strict requirements for continuous monitoring in AML and vendor risk management.
1. Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN)
The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) in the US enforces ongoing monitoring to identify and report suspicious transactions as part of its customer due diligence (CDD) rule. Businesses must continuously assess their customers and transactions to detect any illicit activity.
Penalties for Non-Compliance:
Civil Penalties: Companies that fail to comply with FinCEN regulations can face significant civil fines. These fines are typically based on the severity of the violation, ranging from thousands to millions of dollars.
Criminal Charges: In some cases, non-compliance can lead to criminal charges, particularly if the failure to monitor or report suspicious activity is deemed intentional.
2. Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Financing Act (PCMLTFA)
In Canada, the Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Financing Act (PCMLTFA) mandates that all reporting entities comply with ongoing monitoring requirements. These regulations came into effect in 2021, and businesses are expected to maintain continuous vigilance over financial transactions to detect and prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.
Penalties for Non-Compliance:
Fines: Entities that fail to comply with PCMLTFA regulations can face hefty financial penalties, which can range from thousands to millions of dollars.
Reputational Damage: Businesses found in violation of AML laws risk significant reputational damage and loss of customer trust. This can lead to reduced business opportunities and a damaged public image.
Now, let’s look at practical examples of how ongoing monitoring works in real-world scenarios.
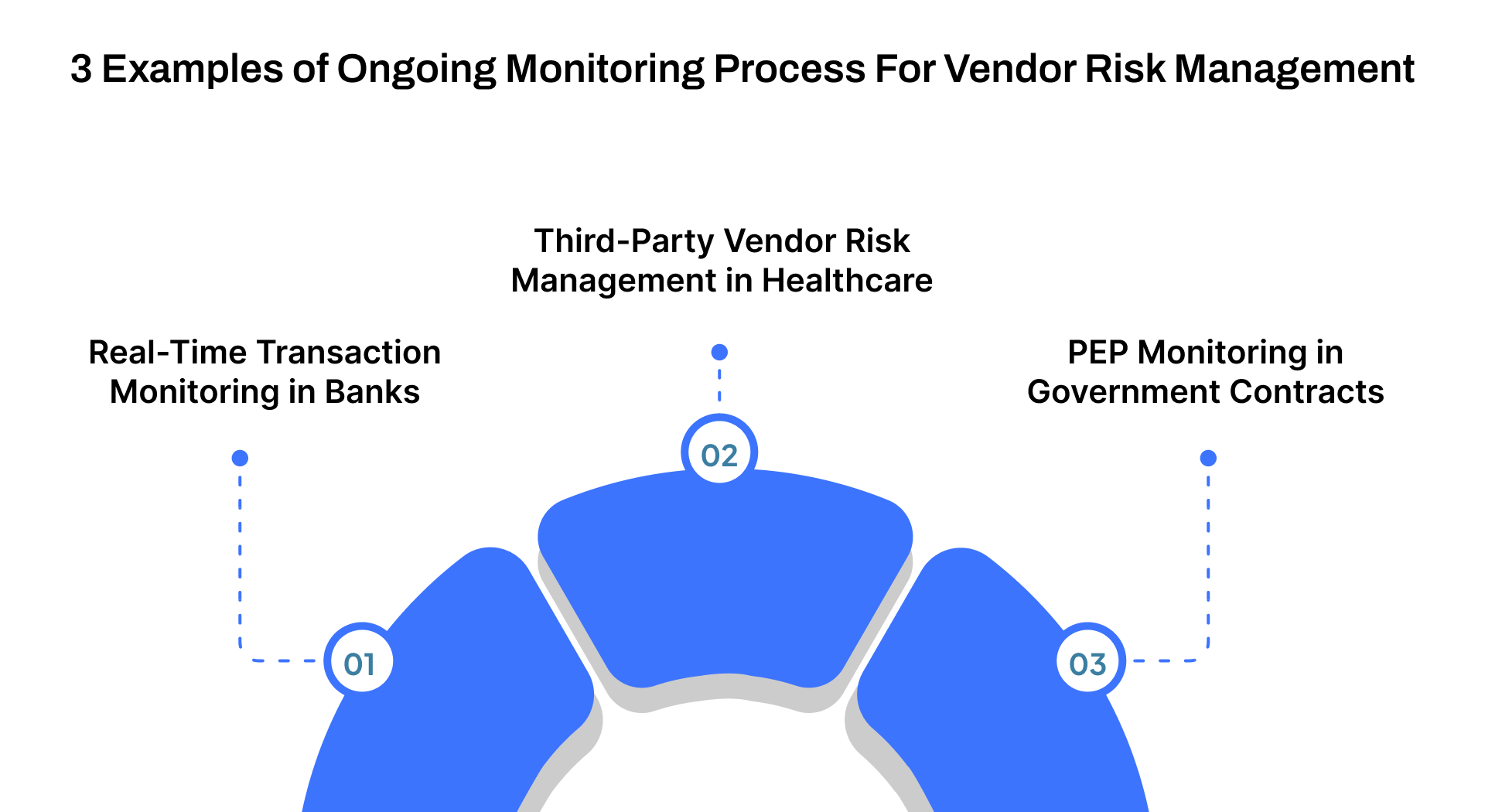
3 Examples of Ongoing Monitoring Process For Vendor Risk Management
To better understand how ongoing monitoring is applied in real-world scenarios, here are three examples of its key role in AML and vendor risk management.
1. Real-Time Transaction Monitoring in Banks
Banks monitor every financial transaction in real time, using automated systems to flag any suspicious activity, such as high-value transfers or activities linked to high-risk countries.
2. Third-Party Vendor Risk Management in Healthcare
In healthcare, continuous monitoring of third-party vendors ensures compliance with HIPAA regulations and assesses their cybersecurity practices, protecting patient data from breaches.
3. PEP Monitoring in Government Contracts
Governments monitor vendors for politically exposed persons (PEPs) to prevent corruption and illegal activities in public contracts, ensuring compliance with anti-bribery laws.
Also Read: Complete Guide to SOC 2 Compliance and Audits
While ongoing monitoring is vital, it's not without its challenges.
Limitations of Ongoing Monitoring in AML and Vendor Risk Management
While ongoing monitoring is vital, there are limitations that can impact its effectiveness. Let’s explore the challenges organizations face when implementing these systems in AML and vendor risk management.
1. High Implementation Costs
Setting up continuous monitoring systems requires significant investment in technology, staff, and training, making it cost-prohibitive for smaller businesses.
2. Overwhelming False Positives
Automated systems can generate a high volume of false positives, leading to unnecessary investigations and administrative burden.
3. Regulatory and Jurisdictional Complexity
Different regions have varying AML regulations, making it challenging to maintain compliance across global operations. This increases the complexity of monitoring systems.
4. Data Management Issues
Managing large volumes of data from multiple sources can be overwhelming, leading to potential data overload and the risk of missing information.
5. Risk of Over-Reliance on Technology
While technology is essential for effective monitoring, over-reliance on automated systems can overlook nuances that human oversight would catch, such as context or emerging threats.
6. Growing Threats
Fraudsters continuously modify their tactics. Staying ahead of these threats requires constant system updates and adjustments to monitoring protocols.
To overcome these challenges, adopting best practices can ensure more efficient monitoring.
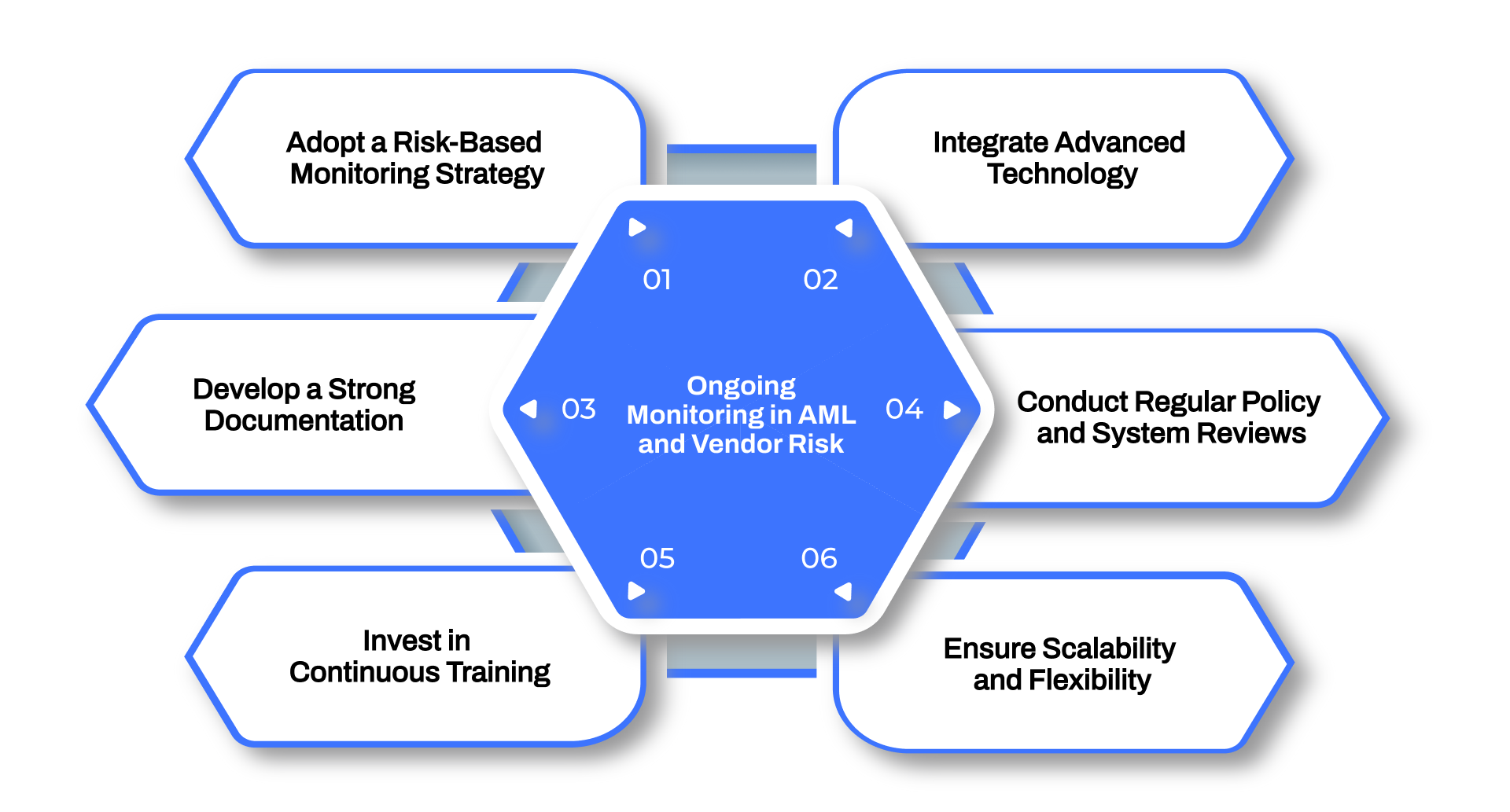
6 Best Practices For Ongoing Monitoring in AML and Vendor Risk Management
To ensure the success of an ongoing monitoring process, adopting best practices is essential. Here are key strategies that organizations can implement to optimize AML and vendor risk management efforts.
1. Adopt a Risk-Based Monitoring Strategy
Focus on high-risk areas, dynamically adjust risk scoring, and prioritize monitoring based on customer profiles, transaction volume, or vendor location.
2. Integrate Advanced Technology
Utilize machine learning and AI to enhance monitoring accuracy, automate screening, and predict future risks based on historical data patterns.
3. Develop a Strong Documentation Framework
Ensure real-time record-keeping, automated reporting, and regulatory alignment to support audits and ensure compliance during regulatory reviews.
4. Conduct Regular Policy and System Reviews
Regularly update policies and test system resilience to ensure that your monitoring process can handle new challenges and changing regulatory requirements.
5. Invest in Continuous Training
Provide role-specific training for staff on the latest regulatory updates and how to manage risk effectively, using real-life scenarios for practical learning.
6. Ensure Scalability and Flexibility
Choose scalable platforms that grow with your business and adapt to changing regulations. Modular systems can help integrate new features as risks grow.
Also Read: Vendor Offboarding Best Practices and Checklist
To implement these best practices effectively, using the right tools is important for real-time risk monitoring.
Simplify Your Vendor Risk Management with Auditive's Monitoring Solutions
When it comes to ensuring continuous AML compliance and managing third-party risk, Auditive provides real-time monitoring and actionable insights to strengthen your risk management processes. Here's how Auditive's ongoing monitoring features enhance your AML and third-party risk management strategy:
Contract Monitor: Auditive’s Contract Monitor continuously tracks your vendor's adherence to contracts, flagging any discrepancies, missed SLAs, or hidden risks in real time.
Partner Trust Exchange: With Partner Trust Exchange, Auditive keeps you updated with real-time data from your entire vendor network, creating transparency and strengthening your ongoing vendor risk management process.
Accelerated Intake Form: The Accelerated Intake Form automates third-party onboarding and provides immediate insights into a new vendor's inherent risks. This ongoing monitoring ensures that you understand the potential risks associated with a vendor right from the start, streamlining your AML compliance efforts.
Questionnaire Copilot: Questionnaire Copilot uses AI to complete risk assessments, questionnaires, and RFPs in minutes, saving time and improving accuracy. By automating this process, Auditive ensures that your vendor risk evaluations are continuously updated and aligned with AML standards.
Supplier Risk Assessment Agent: Auditive’s Supplier Risk Assessment Agent continuously monitors third-party risks and evaluates vendors 80% faster. Analyzing large sets of vendor data, including certifications and policies, provides real-time insights and recommendations to mitigate AML-related risks.
Supply Chain Continuous Monitoring: Supply Chain Continuous Monitoring enables you to track your vendors’ security and compliance posture at all times.
Learn how Pelago achieved significant ROI with Auditive, streamlining workflows and saving valuable time; explore the full case study now.
By incorporating these ongoing monitoring solutions, Auditive ensures that your AML compliance and vendor risk management processes are continuously updated and aligned with your security requirements.
Wrapping Up
Continuously tracking and assessing risks in real time can mitigate potential threats before they escalate. Automated monitoring tools and AI-driven technologies improve efficiency, while ongoing training and system updates ensure that organizations are always prepared for emerging risks.
For effective AML and vendor risk management, Auditive enables continuous evaluation of vendors through automated risk assessments and streamlined onboarding processes. This ensures timely identification of risks, keeping your business compliant and secure at all times.
Get in touch with Auditive and take control of your ongoing monitoring process to safeguard your business.
FAQs
1. How does ongoing monitoring help detect money laundering activities in cross-border transactions?
Ongoing monitoring detects unusual transaction patterns, such as large cross-border transfers, ensuring compliance with regulations and preventing money laundering through real-time alerts.
2. What role does machine learning play in real-time monitoring of vendor risks?
Machine learning enhances real-time risk monitoring by analyzing patterns in transaction data, detecting anomalies, and predicting potential risks, improving the accuracy of alerts.
3. How does ongoing monitoring contribute to meeting AML regulations like FATF’s Recommendation 10?
Ongoing monitoring helps ensure compliance with FATF’s Recommendation 10 by continuously tracking and reporting suspicious activities, maintaining real-time records, and updating risk assessments regularly.
4. What are the challenges of monitoring third-party vendors for financial crimes in high-risk regions?
Monitoring vendors in high-risk regions requires constant data updates, complex geopolitical risk assessments, and regulatory compliance checks, making continuous monitoring crucial to minimize exposure.
5. How can ongoing monitoring improve the detection of financial crimes in healthcare transactions?
Continuous monitoring in healthcare tracks billing patterns, flagging unusual charges or fraud attempts, ensuring compliance with HIPAA, and preventing financial crimes in real-time.