Comprehensive Guide to Integrated Risk Management
Risk comes in many forms, like financial, operational, cyber, regulatory, and reputational. Managing these risks in isolation is no longer enough. Organizations need a holistic framework that not only identifies and mitigates threats but also aligns risk management with strategic objectives. This is where integrated risk management (IRM) comes in.
A comprehensive guide to integrated risk management equips leaders with the knowledge to unify fragmented risk practices into a single, coordinated approach. Unlike traditional methods that treat risks separately, IRM fosters cross-functional collaboration, enhances visibility, and supports informed decision-making. By embedding risk management into daily operations, businesses can anticipate challenges, build resilience, and unlock opportunities for growth.
This blog explores the fundamentals of IRM, its benefits, and the practical steps to implement it effectively, offering a clear roadmap for organizations looking to transform risk into a strategic advantage.
Key Highlights:
Integrated Risk Management (IRM) unifies risk processes across finance, operations, compliance, cybersecurity, and strategy.
It delivers benefits like proactive decision-making, cost savings, regulatory alignment, and improved resilience.
Vendor risk management is a core element, ensuring third-party risks don’t undermine enterprise security.
Auditive’s Trust Center provides a scalable, transparent, and intelligent solution for managing risk and building trust.
Moving towards IRM strengthens compliance and creates a foundation for long-term growth and stakeholder confidence.
What is Integrated Risk Management?
Integrated Risk Management (IRM) is a strategic, organisation-wide approach that unifies all risk-related activities into a single, coordinated framework. Rather than treating risks in silos, such as financial, operational, or cybersecurity risks, IRM brings together insights from multiple functions, including compliance, IT, security, and business units, to create a holistic view of risk.
The goal of IRM is not just to identify and mitigate risks but to align risk management practices directly with business objectives. This ensures that the most critical assets, those that drive core operations and long-term growth, are prioritized and protected.
Unlike traditional compliance-driven models, IRM emphasizes agility, automation, and cross-departmental collaboration. By embedding risk awareness into company culture and using real-time data to assess and respond to threats, IRM helps organizations make better, faster, and more informed decisions. In essence, it transforms risk management from a defensive necessity into a proactive enabler of resilience and strategic advantage.
Why is Integrated Risk Management Important?
Integrated Risk Management (IRM) plays a vital role in helping organizations align compliance, security, and operational objectives into a unified strategy. Instead of treating compliance as a separate task, IRM ensures it becomes an extension of business and security goals.
Here’s why IRM is so important:
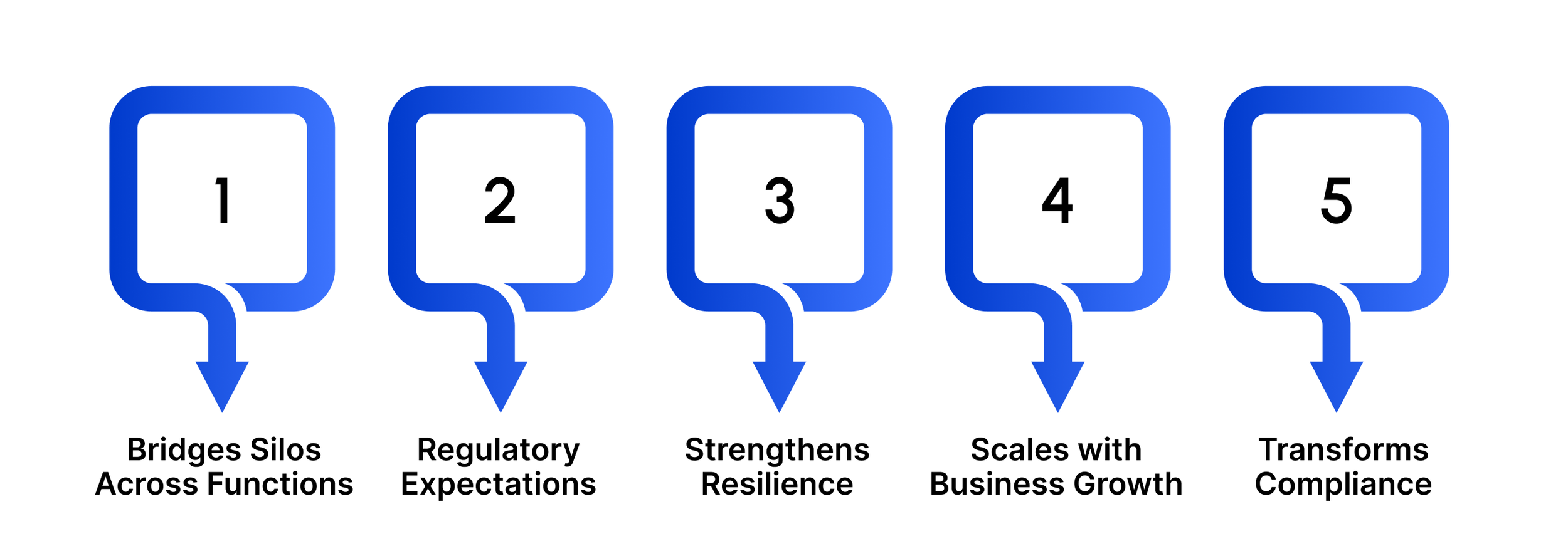
Bridges silos across functions
Compliance, security, and risk management often overlap. IRM connects these activities, reducing duplication and ensuring teams work towards shared objectives.
Meets customer and regulatory expectations
Protecting data privacy, ensuring product/service availability, and adopting safeguards across IT, HR, legal, and vendor management are not just compliance tasks; they’re also key to maintaining customer trust.
Learn more about: Vendor Onboarding
Strengthens resilience
By embedding risk management into daily operations, organizations are better prepared to respond to disruptions, cyber threats, and regulatory audits.
Scales with business growth
As compliance requirements expand (e.g., GDPR, ISO, SOC 2), IRM leverages existing processes instead of creating new systems, making it cost-effective and adaptable.
Transforms compliance into a by-product
Rather than being a burden, compliance becomes a natural outcome of robust security and operational processes.
In essence, integrated risk management ensures that compliance, security, and business continuity reinforce each other, making the organisation both resilient and trustworthy.
What are the benefits of IRM?
Adopting Integrated Risk Management (IRM) is more than just a compliance exercise; it’s a way to strengthen organizational resilience and create long-term value. By consolidating risk practices into one coordinated framework, businesses can unlock several advantages:
1. A complete view of risk
Traditional risk programs often operate in silos, which means certain threats go unnoticed until it’s too late. IRM breaks down these barriers, offering a 360-degree perspective on how different risks cybersecurity, financial, operational, or regulatory, interact and influence one another. This broader understanding enables organizations to address vulnerabilities in a more connected and proactive manner.
2. Alignment with strategic objectives
Instead of treating risks as standalone issues, IRM ties them directly to business goals. This ensures that every risk management effort supports the organisation’s vision and strategy, making risk management a driver of growth rather than just a defensive mechanism.
3. Smarter, data-driven decisions
Decision-making is only as strong as the information behind it. With IRM, leadership has access to consolidated and reliable insights across all domains of risk. This empowers executives to make faster, evidence-based decisions while reducing the chances of blind spots or overlooked threats.
4. Cost efficiency and risk-to-revenue opportunities
Disruptions, compliance penalties, or unmanaged risks can drain financial resources. IRM helps prevent these losses by identifying threats early and applying corrective measures before they escalate. Beyond cost savings, an integrated approach can even uncover new opportunities by turning risk insights into competitive advantages.
In short, IRM doesn’t just protect the organisation; it makes the business smarter, more agile, and better positioned to thrive in a challenging risk environment.
To fully realize these benefits, organizations need the right tools to unify risk monitoring and decision-making. This is where Auditive adds value by providing a trust-driven platform that simplifies complex risk management, enhances vendor risk visibility, and aligns security practices with business objectives.
Essential Elements of Integrated Risk Management
Every effective integrated risk management (IRM) framework rests on a strong foundation. This base ensures that risks are not just identified but also assessed, prioritized, and addressed in ways that strengthen organizational resilience. For global enterprises navigating complex markets, getting these fundamentals right is what turns risk from a liability into a source of competitive advantage.
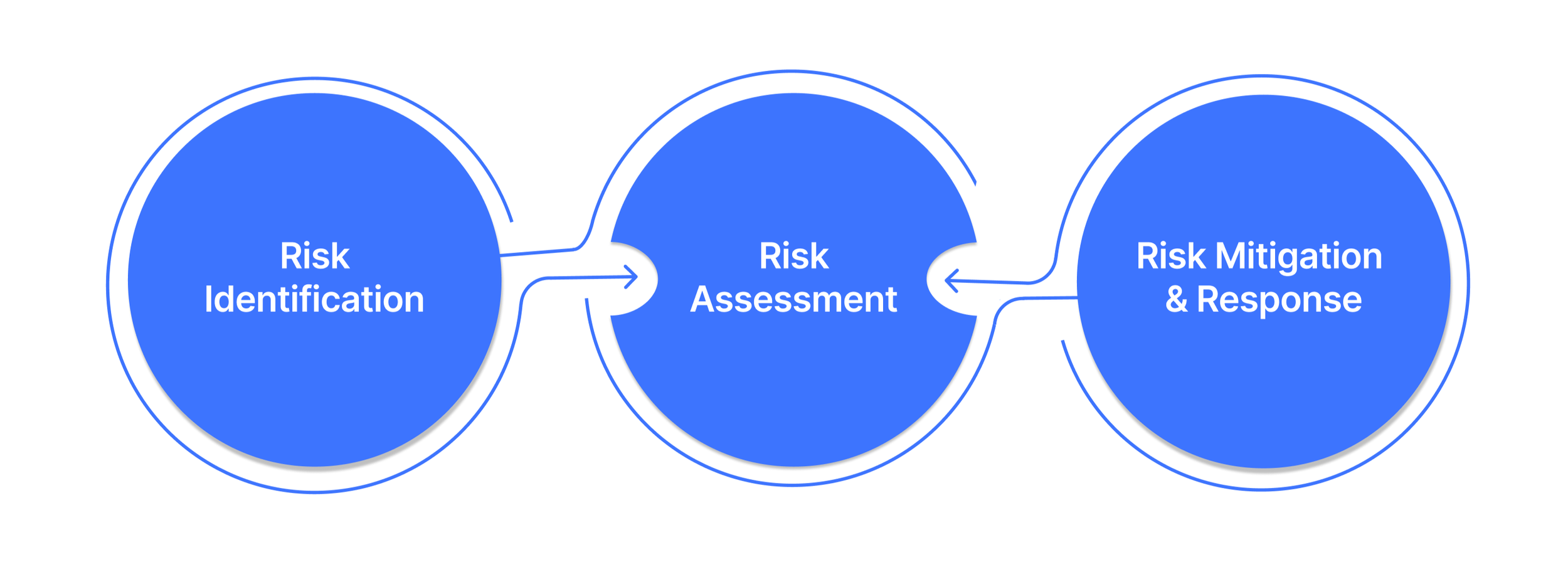
1. Risk Identification
The starting point of IRM is a systematic approach to identifying risks and opportunities that could affect business objectives. This involves scanning both internal operations and external environments to create a comprehensive risk register. Common tools include:
Risk assessment checklists to ensure no critical area is overlooked.
SWOT analysis to weigh strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Root cause analysis to trace vulnerabilities back to their origins.
For instance, many organizations document emerging cybersecurity risks in their risk registers, ensuring that potential threats are captured early and evaluated consistently.
2. Risk Assessment
Once risks are identified, the next step is to measure and evaluate them. Risk assessment has two dimensions:
Qualitative methods (e.g., probability-impact matrix, Bow-Tie analysis, Delphi technique) that help rank risks based on likelihood and severity.
Quantitative methods (e.g., decision trees, Monte Carlo simulations, Expected Monetary Value) that assign numerical values to potential outcomes, offering a clearer view of exposure.
Often, a hybrid approach, combining both qualitative and quantitative techniques, provides the most accurate picture. For example, industries like construction or agriculture frequently use these methods to anticipate weather-related delays and prepare contingency plans.
3. Risk Mitigation and Response
After risks are identified and assessed, organizations must decide how to respond. Typical strategies include:
Avoidance – altering plans to eliminate exposure.
Transfer – shifting risk to another party, such as through insurance.
Mitigation – implementing measures to reduce impact or likelihood.
Preparedness – ensuring response plans are in place to act quickly when risks materialise.
A practical example is manufacturers diversifying their supplier base to avoid disruptions if a primary vendor fails to deliver. With clear response strategies, businesses not only minimize risks but also improve their ability to adapt in real time.
Building this foundation is only the first step; the real challenge lies in sustaining it across departments, vendors, and evolving risks. This is where technology and intelligent platforms make a difference. Auditive helps organizations strengthen their IRM foundations by centralizing risk data, automating assessments, and ensuring continuous monitoring through its Trust Centre, turning strategy into execution with real-time clarity.
Must read: How to Manage Risk in New Business Strategies
Integrated Risk Management (IRM) Solutions
Shifting to an integrated risk management (IRM) model requires more than technology; it calls for cultural alignment, cross-department collaboration, and continuous improvement. The right solutions bring together people, processes, and tools to embed risk awareness into the DNA of an organisation.
1. Align risk strategy with business goals
For IRM to succeed, security and compliance efforts must be directly linked to business objectives. This alignment helps leadership and security teams pull in the same direction, cultivating a culture where risk management is seen as a driver of resilience and business value, not just a regulatory requirement.
2. Make risk management a shared responsibility
Effective risk management isn’t confined to compliance teams. Every department, from engineering and HR to finance and sales, plays a role in identifying and managing risks. Establishing a shared responsibility culture ensures that risks are considered at every level, with executives endorsing and reinforcing accountability across teams.
3. Improve visibility of risk activities
To avoid siloed approaches, IRM solutions must make risk activities transparent and accessible. Documenting internal controls, assigning clear ownership, and storing evidence in one central repository allows stakeholders to see responsibilities, track progress, and respond quickly when issues arise.
4. Automate repetitive tasks
Manual, repetitive work like control testing, audit evidence collection, and compliance tracking drains resources. Automation helps reduce these inefficiencies, freeing teams to focus on higher-value strategic initiatives such as strengthening risk posture and driving innovation.
5. Continuously refine and adapt
Risk management isn’t static. As organizations launch new products, expand into new markets, or adopt new technologies, new risks inevitably emerge. A robust IRM solution supports iterative improvements through real-time monitoring, automated reporting, and proactive updates to controls that evolve with business needs.
6. Use the right IRM tools
While traditional GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) platforms attempt to support integrated risk management, many fall short due to complexity and poor usability. Modern IRM tools, on the other hand, are designed for ease of use and engagement. They enable seamless participation from stakeholders, simplify compliance evidence gathering, and keep an organized record of risk activities, making audits and regulatory reviews far more efficient.
By combining cultural change with the right technology, IRM solutions move organizations away from ad hoc, fragmented practices and toward a proactive, business-driven risk management strategy.
How to Execute and Implement Integrated Risk Management
As risks evolve in scale and complexity, companies can no longer afford to treat risk management as an isolated or one-off exercise. An effective integrated risk management (IRM) framework requires deliberate planning, structured execution, and continuous adaptation. Here are five essential steps to successfully implement IRM in your organisation:
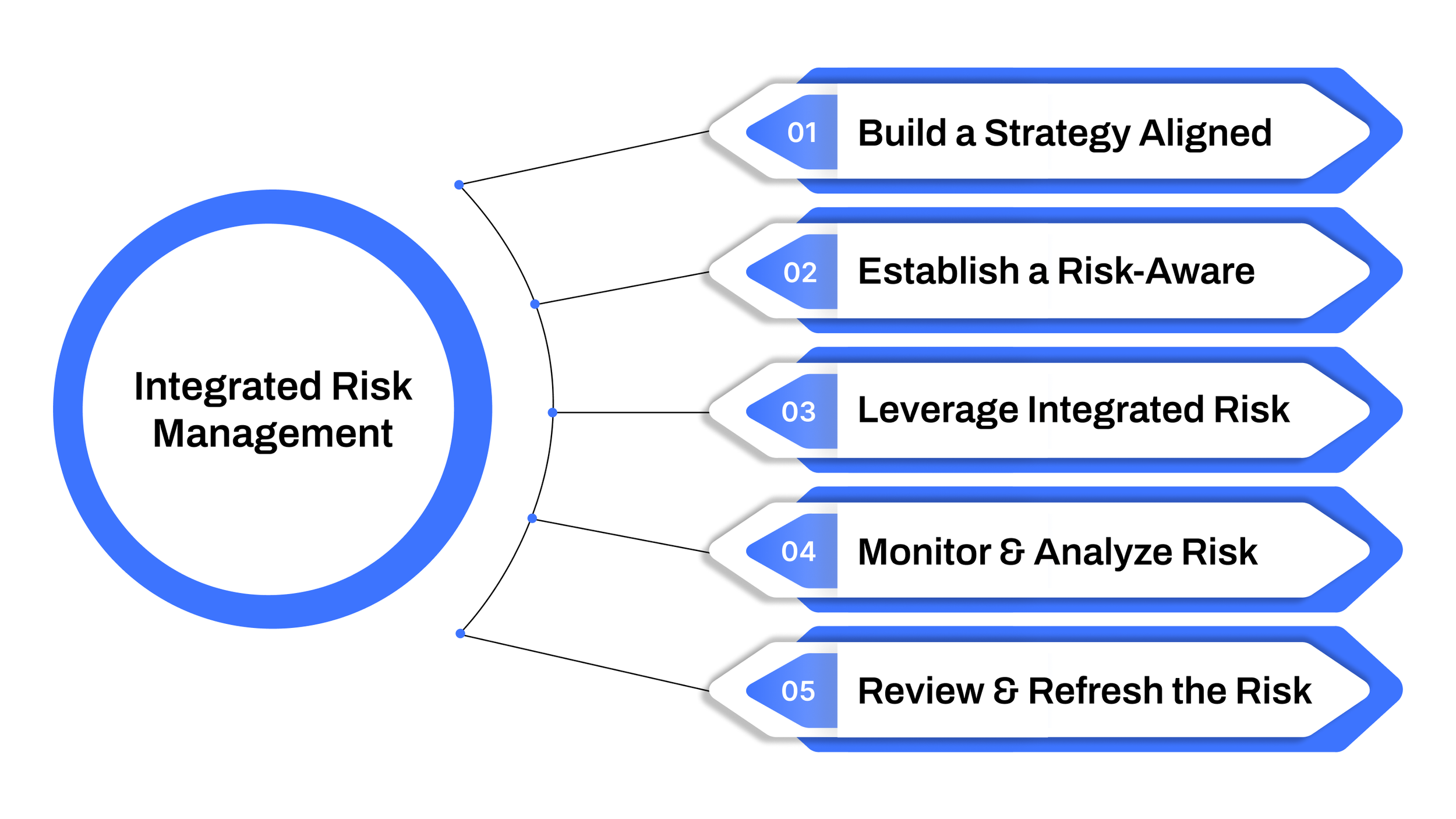
1. Build a Strategy Aligned with Business Goals
The foundation of IRM begins with a strategy tailored to your business type, size, and unique risk exposures. A manufacturing enterprise may prioritize supply chain continuity, while a retail organisation might focus more on consumer data protection and compliance.
Learn more about: Supply chain vulnerability
Start by identifying the risks most relevant to your operations, financial, compliance, cyber, operational, or reputational, and rank them by likelihood and potential impact. From there, develop clear risk-handling strategies, such as:
Avoidance – eliminating risky activities altogether.
Mitigation – reducing exposure by diversifying suppliers, introducing safeguards, or strengthening controls.
Transfer – shifting risk through insurance, outsourcing, or third-party partnerships.
Acceptance – acknowledging certain low-impact risks as tolerable.
When your IRM strategy is anchored in business objectives, it not only strengthens resilience but also supports sustainable performance.
2. Establish a Risk-Aware Culture Through Training
Even the most well-designed risk strategies can falter if employees are unaware of their role in managing risks. Training ensures staff across all levels can identify, respond to, and escalate risks effectively.
Key steps include:
Defining what risk management means in your organisation and why it matters.
Teaching employees how to spot risks in their roles, from operational errors to third-party failures.
Sharing clear policies and escalation procedures for risk reporting.
Encouraging open communication so potential threats are raised early.
Embedding a culture of risk awareness transforms your workforce into a frontline defense system, ensuring small issues don’t grow into major disruptions.
3. Leverage Integrated Risk Management Technology
Manual risk tracking is both inefficient and prone to gaps. Modern IRM platforms automate risk detection, centralize reporting, and provide real-time dashboards for leadership visibility.
An effective IRM solution should:
Identify, track, and assess risks across departments.
Provide alerts for emerging risks and compliance gaps.
Integrate seamlessly with other enterprise systems like ERP or procurement tools.
Investing in such software not only improves accuracy and efficiency but also ensures risks are proactively addressed before they escalate.
4. Monitor and Analyze Risk Reports Continuously
IRM reports offer leadership a holistic view of both financial risks (credit, liquidity, market) and non-financial risks (IT, strategic, reputational). By analyzing these regularly, organizations can adjust their priorities, refine mitigation measures, and recalibrate their risk appetite.
Comprehensive dashboards and analytics also make it easier to demonstrate compliance to regulators and stakeholders, an increasingly important requirement in today’s regulatory climate.
5. Review and Refresh the Risk Strategy Regularly
The risk environment is never static. New threats emerge as technology, regulations, and market conditions change. Periodic reviews of your IRM program ensure that your organisation remains agile and prepared.
Key considerations include:
Has the risk landscape shifted?
Are mitigation strategies still effective?
Do current practices align with updated business goals?
Is the defined risk tolerance still appropriate?
Regular evaluations and updates transform IRM from a static framework into a dynamic tool that evolves alongside your organisation.
How Auditive Enhances Integrated Risk Management
Executing an integrated risk management strategy requires more than frameworks and policies; it demands visibility, automation, and accountability across the vendor and partner ecosystem. This is where Auditive adds value.
Also read: Risk Management strategy for businesses
Centralized Risk Insights via the Trust Center
Auditive’s Trust Center provides a unified view of risks across your vendors, suppliers, and third parties. This centralization eliminates silos and ensures decision-makers see the full risk picture in real time.
Automated Vendor Risk Management
Instead of relying on manual assessments, Auditive automates due diligence, risk scoring, and continuous monitoring. High-risk vendors are flagged instantly, reducing exposure and allowing faster intervention.
Ongoing Compliance Tracking
Regulations evolve quickly, and so do risks. Auditive keeps your compliance posture updated by monitoring vendor performance against global frameworks and internal policies.
By combining automation with real-time intelligence, Auditive transforms integrated risk management from a reactive process into a proactive, business-aligned strategy.
Conclusion
Integrated Risk Management is no longer an optional framework, it’s a critical enabler of resilience, compliance, and strategic growth. By embedding IRM practices into your operations, you not only safeguard against financial, reputational, and operational risks but also establish a strong foundation for trust.
For organizations working with multiple partners and suppliers, vendor risk management plays an especially vital role. Auditive’s Trust Center provides a centralized hub where businesses can streamline risk assessments, monitor third-party compliance, and enhance transparency with stakeholders. With automation, analytics, and real-time visibility, you can move beyond reactive responses and embrace proactive governance.
If you are ready to move from fragmented risk frameworks to a unified, intelligent, and scalable approach, now is the time to explore how IRM can transform your business strategy.
Don’t wait for risk to become disruption. Partner with Auditive and experience how our Trust Center makes risk management transparent, scalable, and efficient.
FAQs
Q1. What is the main difference between traditional risk management and integrated risk management?
Traditional risk management often works in silos, focusing on isolated risks, while integrated risk management connects risks across the enterprise, aligning them with strategy and decision-making.
Q2. Why is vendor risk management important in IRM?
Vendors and third parties can expose businesses to compliance, cybersecurity, and operational risks. Vendor risk management ensures these risks are identified, monitored, and mitigated as part of the wider IRM framework.
Q3. Can small and mid-sized businesses benefit from integrated risk management?
Yes. IRM is scalable and flexible, making it suitable for organizations of all sizes. SMBs especially benefit from greater visibility and efficiency in compliance and risk oversight.
Q4. How does a Trust Center improve transparency?
A Trust Center acts as a digital hub where organizations can share compliance reports, security certifications, and policies, creating transparency with clients, partners, and regulators.
Q5. What are the first steps to implementing integrated risk management?
Start with risk identification, assess maturity across functions, define governance structures, and adopt an IRM solution that aligns with your business objectives.