What Is Operational Risk Management? Definition, Framework & Tools
Every organization faces risks, but not all risks are strategic or financial. Some are embedded in the day-to-day running of a business. These are operational risks, failures in processes, systems, people, or external events that interrupt normal workflows. And in a time when business continuity and resilience are at the forefront, managing these risks isn’t just a precaution; it’s a necessity.
Operational risk management is a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and controlling potential threats that arise from routine operations. Whether it's a supply chain failure, system downtime, or employee error, operational risk management (ORM) helps businesses safeguard performance, maintain compliance, and protect their reputation.
This blog unpacks the operational risk management meaning, explores why it matters across industries, and outlines how to apply it effectively using modern strategies and tools, especially in complex environments where visibility and control are crucial.
Overview
Operational risk stems from failures in people, processes, systems, or external events, and it’s embedded in everyday business activities.
Effective Operational Risk Management (ORM) helps organizations reduce disruptions, meet compliance standards, and maintain customer trust.
A strong ORM framework includes identification, assessment, mitigation, control implementation, monitoring, and continuous improvement.
Auditive enhances ORM with real-time vendor monitoring, AI-powered verification, automated workflows, and a collaborative Trust Center network.
Investing in ORM isn’t optional, it’s essential for resilience, efficiency, and long-term competitive advantage in today’s complex risk landscape.
What Is Operational Risk Management?
Operational risk management refers to the processes and tools organizations use to manage risks arising from internal operations. Unlike strategic risks (which relate to long-term goals) or financial risks (like market fluctuations), operational risks are tied to the systems and procedures businesses rely on daily.
Common sources of operational risk include:
People: Human error, insufficient training, insider fraud
Processes: Poorly designed workflows, lack of standardization, manual dependencies
Systems: Technology outages, cyberattacks, outdated platforms
External events: Natural disasters, regulatory changes, geopolitical issues
What makes operational risk unique is that it is everywhere, embedded in your HR policies, vendor onboarding process, or even how employees handle data. Left unmanaged, these risks can lead to loss of productivity, fines, reputational damage, or even shutdowns.
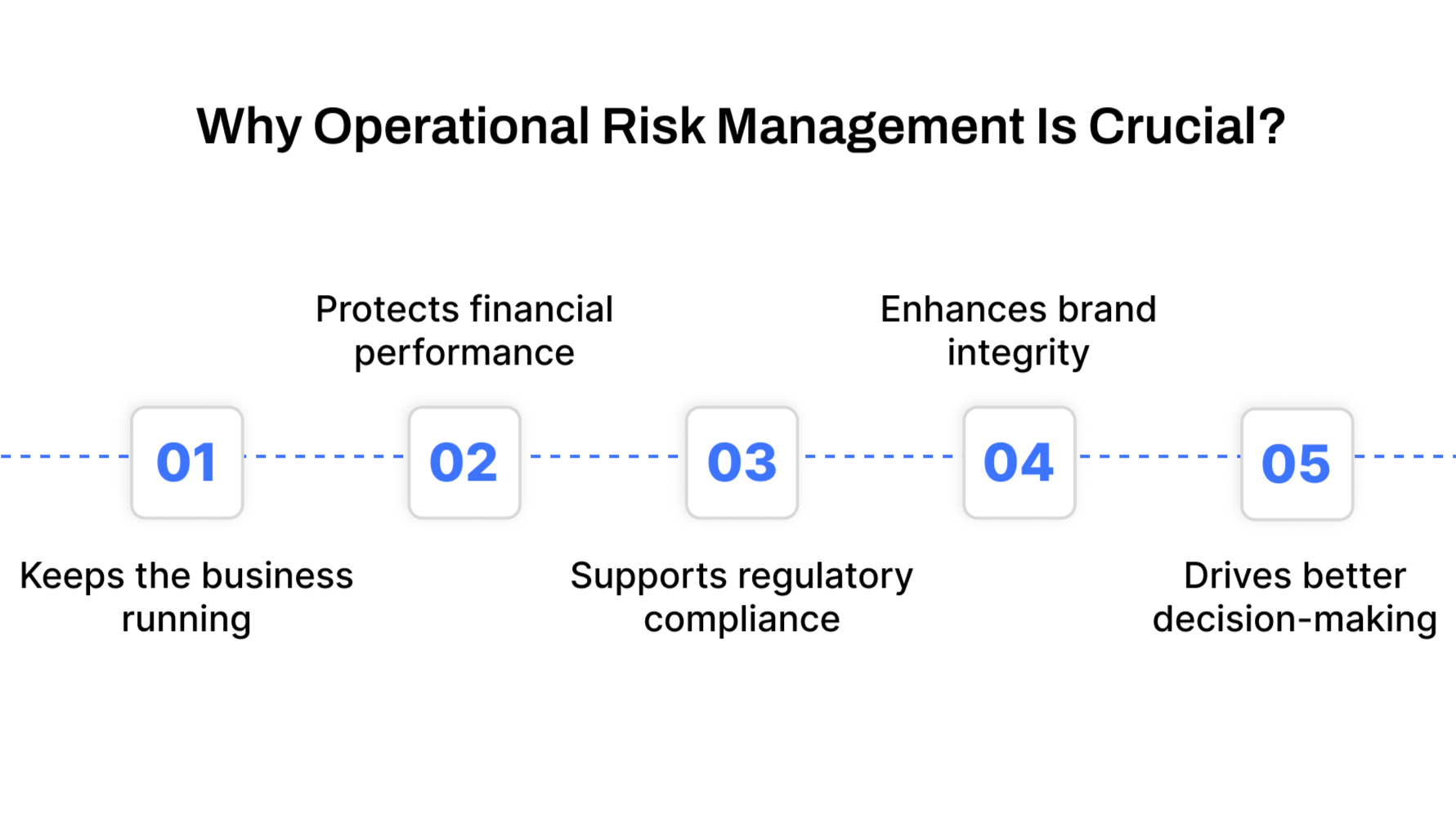
Why Operational Risk Management Is Crucial Today?
Operational risk management isn’t just about preventing things from going wrong; it’s about making your business stronger, faster, and more adaptable in the face of change.
Here’s why it matters:
Keeps the business running
ORM ensures that essential operations continue, even when disruptions occur. It reduces downtime and helps businesses recover quickly from incidents.
Protects financial performance
Operational disruptions can be expensive. By controlling these risks, organizations prevent revenue loss and reduce unexpected costs.
Supports regulatory compliance
Regulatory bodies across finance, healthcare, and technology demand proof of risk control. ORM helps organizations meet audit and legal requirements.
Enhances trust and brand integrity
Customers and partners are more confident in companies that demonstrate strong risk controls and transparency.
Drives better decision-making
ORM feeds real-time risk insights to leadership, enabling smarter, more proactive planning.
Platforms like Auditive provide continuous monitoring and AI-powered insights into operational vulnerabilities, helping companies reduce uncertainty and stay compliant without added overhead.
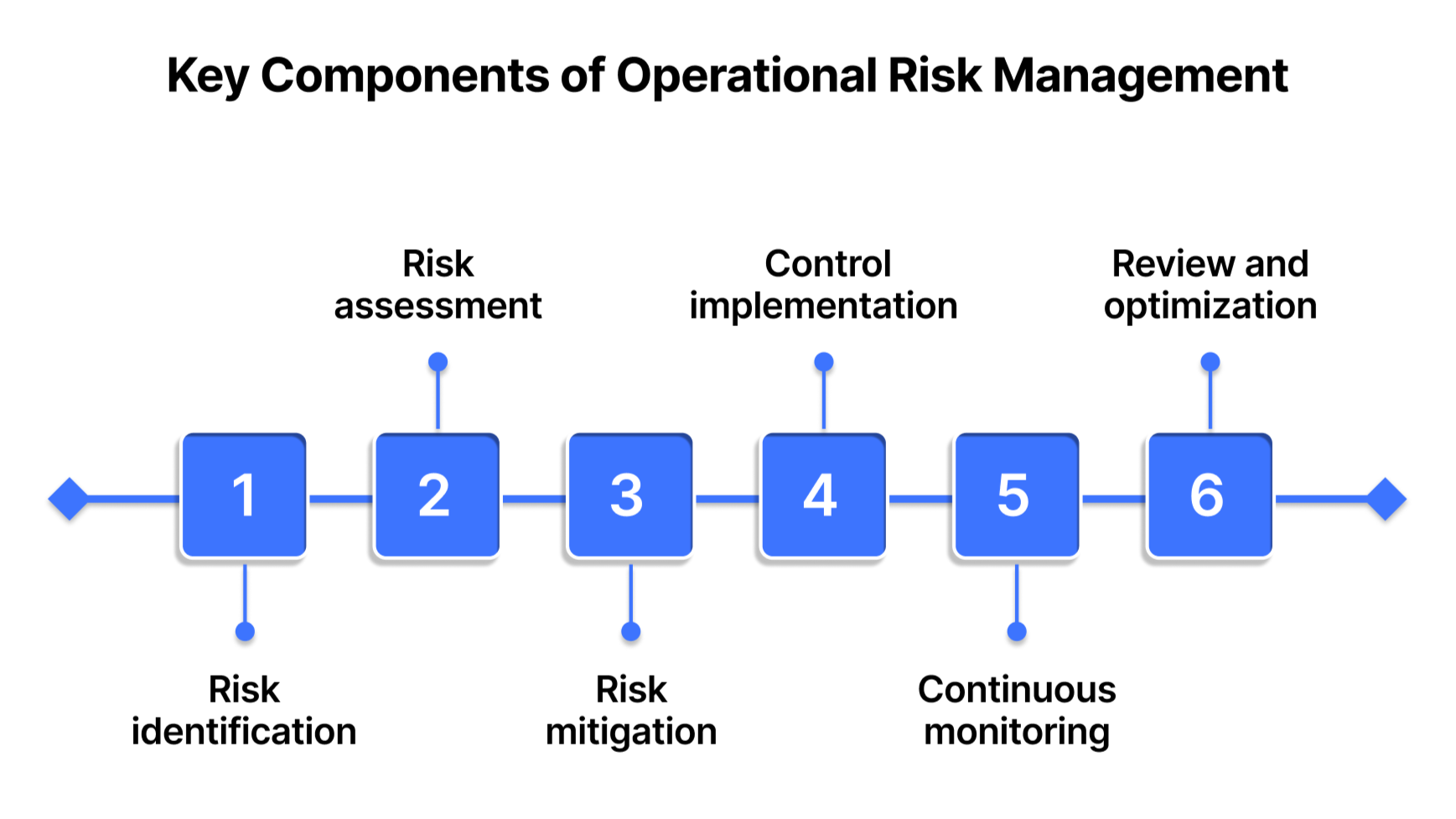
6 Key Components of an Effective Operational Risk Management Framework
A strong ORM program follows a cycle of identification, assessment, mitigation, monitoring, and continuous improvement. Let’s break down each stage in detail:
1. Risk identification
The first step is recognizing where operational risks exist within your organization.
Areas to evaluate:
Vendor relationships and supply chain dependencies
Internal processes across departments (e.g., finance, IT, compliance)
Employee actions and access controls
Legacy systems, manual tasks, and automation gaps
Environmental and geopolitical events
Auditive’s TPRM platform can highlight third-party risks automatically, helping you map out where vendors may introduce vulnerabilities into your operations.
2. Risk assessment and prioritization
Not all risks carry the same weight. Once identified, they must be evaluated based on:
Likelihood: How probable is the risk?
Impact: What’s the potential damage, financial, reputational, or operational?
Velocity: How quickly could the risk materialize and cause disruption?
Procurement and security teams can use tools like risk heatmaps, key risk indicators (KRIs), and scenario analysis to quantify risks and determine which ones require immediate action.
3. Risk mitigation strategies
Once risks are prioritized, you need to decide how to handle them.
Common risk treatment strategies:
Avoid: Discontinue or redesign the risky activity
Reduce: Implement controls to minimize impact
Transfer: Outsource or insure against the risk
Accept: Acknowledge the risk, but monitor closely
Mitigation plans must be realistic, cost-effective, and tailored to the business environment. Auditive supports this phase with intelligent dashboards that track mitigation efforts across your vendor ecosystem.
4. Control implementation
After planning, it’s time to act. Controls are safeguards that reduce the chance or impact of a risk.
Examples of operational controls:
Segregation of duties
Approval workflows and dual sign-offs
Automated compliance alerts
Regular access and permissions audits
Incident response playbooks
The right controls should integrate into daily operations without slowing teams down, especially in fast-moving industries like FinTech or HealthTech.
5. Continuous monitoring and reporting
Risks evolve. That’s why monitoring is essential.
ORM monitoring includes:
Real-time alerts on vendor status changes
Regular KRI tracking and threshold breaches
Audit trails for all mitigation and control activities
Reports for internal stakeholders and regulators
With Auditive, procurement and security leaders get a unified view of risk across all third-party relationships, updated continuously, allowing faster response times and stronger compliance posture.
6. Review and optimization
An ORM framework must evolve. After every incident, audit, or major change, review what worked and what didn’t.
Conduct post-event analyses
Update controls and documentation
Train staff based on lessons learned
Improve collaboration across departments
Operational risk isn’t a one-time project. It’s an ongoing cycle of learning, adapting, and strengthening your business.
Real-World Examples of Operational Risks
Operational risk shows up in unexpected ways. Some examples across industries include:
Banking: IT system outages preventing transaction processing
Healthcare: Mishandling of sensitive patient data leading to compliance fines
Manufacturing: Single-source vendor failure delaying production
EdTech: Platform downtime during high-traffic exam periods
Retail: Supply chain disruptions due to external strikes or weather events
These incidents don’t just cause immediate losses, they often expose gaps in planning and controls that could have been prevented with stronger operational risk management.
How Auditive Helps You Manage Operational Risk
Operational risks often stem from external relationships, particularly suppliers and vendors. Whether it’s a security lapse, compliance failure, or unreliable documentation, third-party vulnerabilities can have a direct impact on your internal workflows. That’s where Auditive steps in, not just as a tool, but as a partner in building operational resilience.
Here’s how Auditive strengthens your operational risk management efforts across the board:
1. Real-time risk monitoring
Auditive continuously tracks your vendors’ risk posture, scanning for changes in security status, compliance issues, or newly surfaced threats.
Instant alerts help teams act before disruptions occur
Ongoing monitoring replaces outdated, point-in-time assessments
Supports business continuity by keeping procurement and risk aligned in real time
2. AI-Powered information verification
Manually reviewing vendor documents is slow and prone to oversight. Auditive uses AI to verify security audits, certifications, and policy documents provided by vendors.
Cuts down review time and human error
Ensures you're working with current, validated data
Builds trust in supplier-provided risk data without relying on self-reporting alone
3. Centralized risk profiles for every vendor
Auditive creates a single source of truth for each supplier, pulling in all relevant risk, compliance, and performance data.
Helps security, procurement, and compliance teams collaborate more effectively
Reduces confusion caused by fragmented systems or duplicate records
Enables faster, better-informed decisions
4. Auditive Trust Center network
With its Trust Center, Auditive facilitates transparent, secure data exchange between buyers and suppliers.
Encourages mutual accountability and compliance readiness
Makes risk communication clearer and more structured
Strengthens long-term vendor relationships by promoting openness
5. Automated workflows and reporting
From onboarding to audits, Auditive automates risk assessments, document collection, and compliance reporting.
Saves time while standardizing data gathering
Keeps audit trails consistent and accessible
Reduces the burden of manual paperwork and follow-ups
6. Scalable risk oversight
Whether you're managing ten suppliers or ten thousand, Auditive scales with you.
Supports growing procurement ecosystems without increasing workload
Maintains oversight even as vendor complexity grows
Ideal for multi-regional, high-regulation industries like FinTech, EdTech, or HealthTech
7. Seamless integration with workflows
Auditive fits directly into your existing procurement and productivity workflows.
Enables teams to onboard vendors 4x faster
Allows easy invitation and onboarding of sellers to the Auditive network
Ensures continuous risk visibility without requiring a change in daily operations
By bringing these capabilities together, Auditive transforms operational risk management from a reactive checklist into a proactive, intelligence-driven discipline. Whether you’re securing your supply chain, improving audit readiness, or aligning risk insights with strategic planning, Auditive gives your team the tools to lead with confidence.
Conclusion
Understanding the operational risk management meaning is more than a definition, it’s about embedding a mindset of vigilance, clarity, and control into your operations. When risks are managed effectively, businesses gain more than stability, they gain the confidence to grow, adapt, and lead.
With Auditive’s cutting-edge Vendor Risk Management and Trust Center tools, your procurement and risk teams gain the visibility, automation, and intelligence needed to thrive in today’s fast-moving, risk-heavy environment.
Ready to strengthen your operational risk strategy?
Book a free demo today and take control of your operational resilience with Auditive.
FAQs
Q1. What is the main goal of operational risk management?
A1. The primary goal of operational risk management is to identify, assess, and mitigate risks that arise from internal processes, systems, people, or external events, ensuring the organization can operate smoothly, maintain compliance, and reduce losses.
Q2. How is operational risk different from other types of risk?
A2. Operational risk focuses on failures in day-to-day business functions, like process breakdowns, cyber incidents, or human error. In contrast, financial risk deals with market fluctuations, and strategic risk relates to long-term business goals or competitive positioning.
Q3. What are examples of operational risks in a business?
A3. Common examples include:
IT system outages
Data breaches due to weak security controls
Supplier non-compliance or failure
Fraud or unauthorized transactions
Inaccurate reporting due to manual errors
Q4. How can technology improve operational risk management?
A4. Technology platforms like Auditive automate risk detection, centralize vendor data, provide real-time monitoring, and use AI for intelligent verification. This enhances accuracy, speeds up assessments, and ensures better oversight across operations.
Q5. Why should organizations invest in operational risk management now?
A5. Marked by regulatory pressure, cybersecurity threats, and global supply chain disruptions, ignoring operational risk can lead to costly failures. ORM not only protects the business but also builds resilience, trust, and long-term value.