How to Manage Risk in New Business Strategies
Launching a new business strategy is exciting, but it also comes with uncertainty. Every decision, whether it’s entering a new market, adopting an emerging technology, or forming partnerships, carries potential risks that could affect performance, reputation, and growth. Understanding how to manage risk from a new business perspective is not about avoiding challenges altogether; it’s about identifying them early, evaluating their potential impact, and creating strategies to minimize disruptions.
Risk management is more than a defensive exercise. For modern enterprises, it serves as a foundation for sustainable growth and smarter decision-making. Organizations that embed risk awareness into their business strategy are better positioned to turn uncertainties into opportunities, build resilience, and maintain stakeholder trust.
In this blog, we’ll explore the fundamentals of risk management, the types of risks businesses typically face, the process for managing them effectively, and how enterprise-wide frameworks can make risk management a strategic advantage.
Overview
New businesses face unique risks like over-dependence on suppliers, compliance gaps, and cybersecurity challenges.
A structured risk management process ensures risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated early.
Building a risk-aware culture is as critical as having formal systems in place.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) offers a holistic, integrated approach aligned with strategic goals.
Auditive enhances this framework with automation, a Trust Center, and advanced vendor risk management capabilities.
Understanding Risk Management and Its Importance
Risk management is the discipline of anticipating, assessing, and responding to potential threats before they escalate into serious challenges. At its core, it is a structured process that involves:
Identifying risks that could affect business operations or objectives
Evaluating and prioritizing those risks based on likelihood and impact
Designing and implementing mitigation strategies to minimize exposure
Far from being just a defensive mechanism, risk management is a strategic enabler. It equips organizations with the insight needed to make better decisions, safeguard resources, and sustain long-term growth. By systematically analyzing uncertainties, leaders can prepare for disruptions while still pursuing ambitious opportunities.
When applied effectively, risk management helps organizations:
Reduce financial and operational losses
Protect their brand reputation and customer trust
Safeguard employees and stakeholders
Enhance agility when responding to unforeseen events
In short, managing risk isn’t just about avoiding harm, it’s about creating resilience. Businesses that prioritize it are better positioned to thrive in competitive markets, adapt to evolving conditions, and turn uncertainty into an advantage.
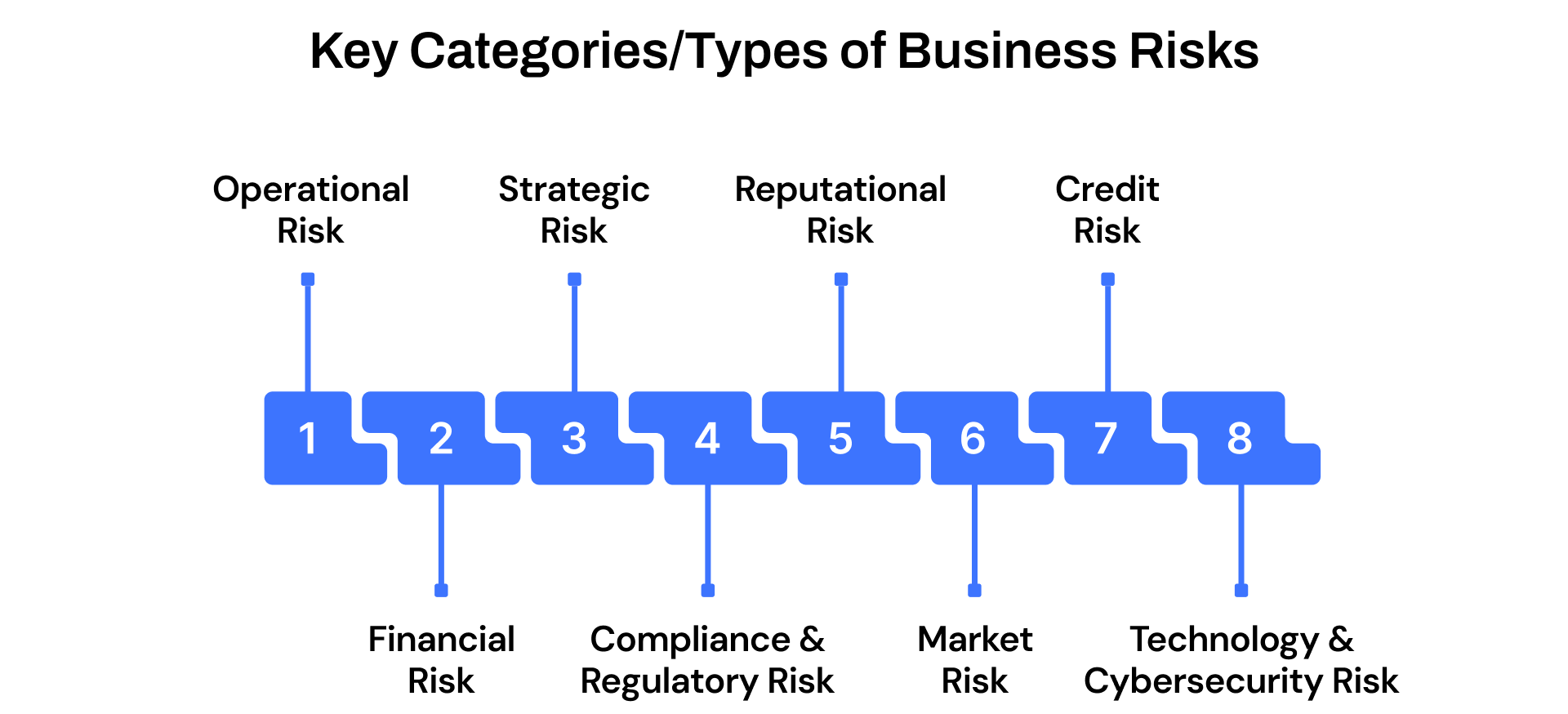
Key Categories/Types of Business Risks
For leaders shaping new business strategies, understanding the different types of risks is critical. Each risk category carries unique challenges that can impact performance, profitability, and long-term sustainability. Recognizing them upfront allows organizations to design stronger mitigation plans and avoid costly surprises. Below are some of the most significant types of risks businesses must navigate:
1. Operational Risk
These risks emerge from within the organization’s day-to-day activities, flaws in processes, human errors, supply chain disruptions, or system inefficiencies. Even well-structured businesses can face setbacks if their internal operations aren’t resilient or adaptable to unexpected circumstances.
2. Financial Risk
Every organization is vulnerable to risks tied to financial activities such as liquidity, cash flow management, currency fluctuations, or rising interest rates. Poor financial planning or exposure to volatile markets can threaten both short-term stability and long-term viability.
3. Strategic Risk
When business strategies fail to align with market realities or competitive pressures, organizations face strategic risks. For instance, expanding into the wrong market, misjudging consumer demand, or neglecting innovation can quickly erode a company’s competitive edge.
4. Compliance and Regulatory Risk
Changing regulations and legal frameworks pose significant challenges. Non-compliance, whether in data privacy, labor laws, or industry-specific requirements, can lead to hefty fines, reputational damage, and loss of stakeholder confidence.
5. Reputational Risk
A company’s reputation can be tarnished overnight. Negative publicity, poor customer experiences, or mishandled crises can undermine trust, which is often more difficult to rebuild than to maintain.
6. Market Risk
External forces such as fluctuating commodity prices, shifting customer preferences, or global economic downturns fall under this category. Market risk is particularly challenging because it’s often outside an organization’s direct control, requiring proactive monitoring and adaptive strategies.
7. Credit Risk
When customers, partners, or borrowers fail to meet financial obligations, businesses encounter credit risk. This risk is especially relevant in industries reliant on lending or extended credit terms, where defaults can cause serious financial strain.
8. Technology and Cybersecurity Risk
As digital transformation accelerates, businesses face increasing exposure to cyberattacks, data breaches, and IT system failures. Technology risks can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive data, and lead to both financial and reputational losses.
By identifying these diverse risks, organizations can move beyond reactive firefighting and adopt proactive strategies that safeguard their operations, strengthen resilience, and foster long-term growth.
While identifying financial, operational, and compliance risks is essential, the real challenge lies in continuously tracking them across complex vendor ecosystems. This is where Auditive steps in, offering businesses a unified Trust Center that helps monitor vendor risk exposure, spot compliance gaps, and flag emerging threats before they escalate.
How to Develop and Implement a Risk Management Plan
Risk management involves a structured approach that enables organizations to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks. Following standard frameworks, such as those outlined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), helps create consistency and reliability in managing risks. A comprehensive plan doesn’t just map risks but also ensures effective implementation, accountability, and continuous improvement.
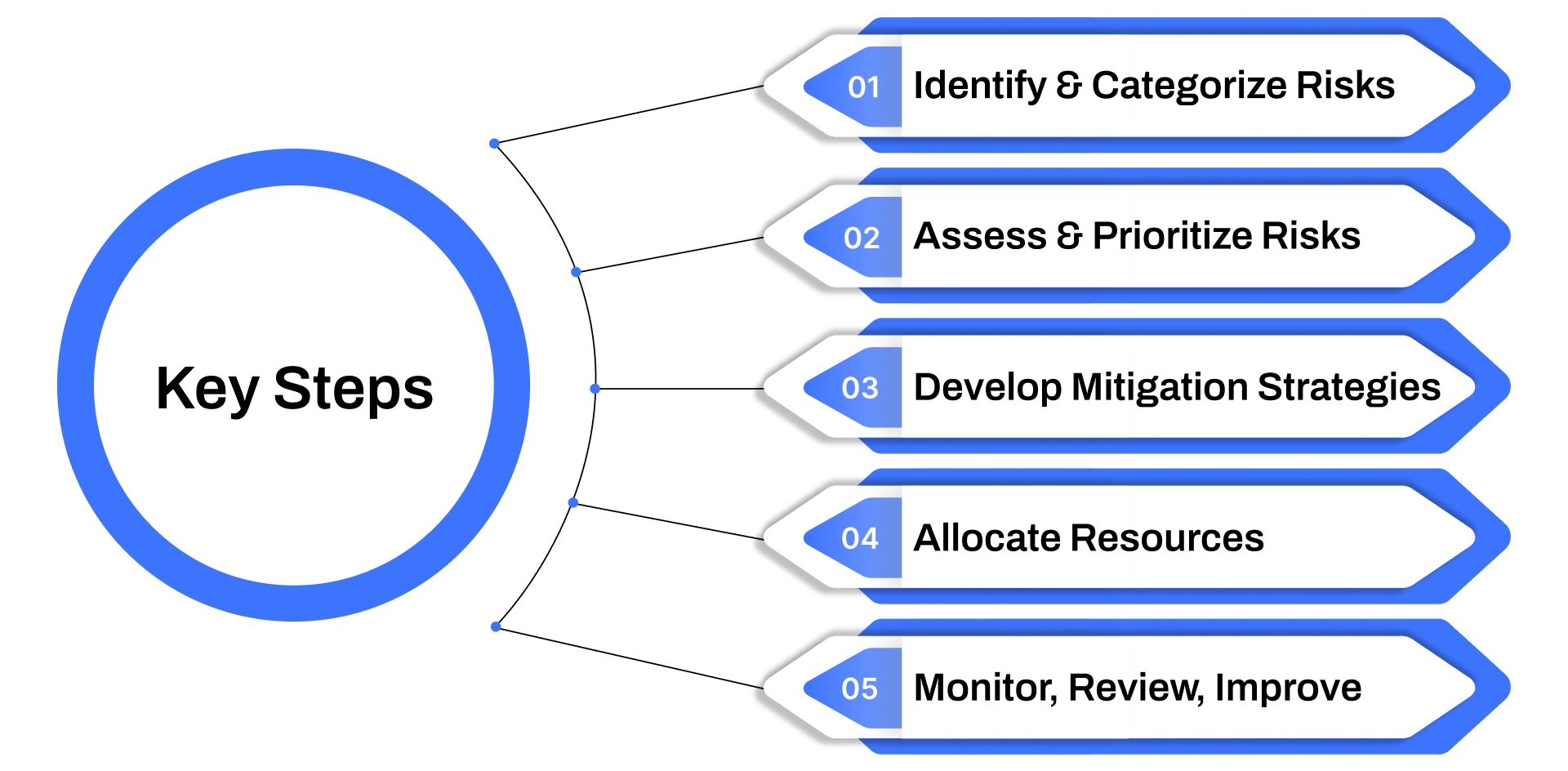
Here are the key steps:
1. Identify and Categorize Risks
The first step is to recognize all possible risks that might affect the organization, whether operational, financial, technological, reputational, or regulatory.
Techniques for risk identification include:
SWOT analysis to evaluate strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Historical data analysis to learn from past incidents.
Stakeholder interviews and workshops for multiple perspectives.
Expert consultations for industry-specific risks.
Once identified, categorize risks into groups such as strategic, operational, financial, compliance, or environmental. Categorization ensures a structured approach and highlights areas of greatest vulnerability.
Example: A retail company may flag cybersecurity breaches as a key risk due to the sensitive nature of customer data.
2. Assess and Prioritize Risks
Not all risks carry the same weight. After identification, evaluate risks based on their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact.
A risk assessment matrix is commonly used to visually map risks into categories like low, medium, and high priority. Additionally, classify risks by time horizon, immediate, short-term, or long-term, to ensure timely focus.
Modern approaches to assessment also leverage AI, machine learning, and data analytics to detect patterns, predict risk probability, and quantify impacts with more accuracy.
Example: A financial institution might determine that fraud risk has a high likelihood and high impact due to gaps in fraud detection systems, making it a top priority.
3. Develop and Implement Mitigation Strategies
Once high-priority risks are clear, the next step is to design targeted strategies to address them. The goal is either to eliminate the risk, reduce its likelihood, or minimize its consequences.
Common mitigation strategies include:
Risk avoidance: Eliminating activities that create risk (e.g., exiting a high-risk market).
Risk reduction: Introducing safeguards to lower the probability or severity (e.g., implementing stronger cybersecurity protocols).
Risk transfer: Shifting financial or operational burden to a third party, often through insurance or contractual agreements.
Risk acceptance: Acknowledging the risk and preparing for potential consequences when mitigation is not feasible.
Every strategy should have clear, actionable steps, timelines, and contingencies. It’s equally important to align these actions with organizational objectives so the risk response strengthens, rather than disrupts, business goals.
Example: A healthcare provider might mitigate cyberattack risks by enhancing encryption, training staff on phishing awareness, and purchasing cyber insurance.
4. Allocate Resources and Assign Ownership
Mitigation strategies are only as strong as their execution. Allocate the necessary resources, budget, personnel, and tools, to carry them out effectively. Each risk should have a designated owner responsible for tracking, reporting, and ensuring timely interventions.
For risks that span multiple functions, cross-departmental teams can foster collaboration and ensure that no blind spots are overlooked. Clear accountability prevents delays and creates organizational discipline in managing threats.
5. Monitor, Review, and Continuously Improve
Risk management is not a one-time activity, it’s an ongoing cycle. Monitoring ensures that risk responses remain relevant as circumstances evolve.
Best practices for monitoring include:
Risk dashboards for real-time updates on key risk indicators.
Regular audits to confirm compliance with mitigation plans.
Periodic reassessments to identify emerging or shifting risks.
Incident reporting systems to capture new risks as they arise.
Stakeholder engagement to validate the effectiveness of responses.
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure whether strategies are working and review the overall risk plan at least annually, or more frequently in fast-changing industries. This culture of continuous improvement ensures resilience and adaptability.
An effective risk management process involves identification, assessment, mitigation, resource allocation, and monitoring. A strong plan doesn’t just define these steps but embeds them into the organization through ownership, accountability, and continuous refinement. By merging structured frameworks with modern data-driven tools, businesses can anticipate, prepare for, and minimize risks in a way that supports long-term stability and growth.
Common Risk Blind Spots for New Businesses
While most entrepreneurs are aware of broad categories like financial or operational risks, it’s often the overlooked details that become the biggest threats. These blind spots tend to appear in the early stages of business growth, when enthusiasm and speed overshadow caution:
1. Over-dependence on a single supplier or client
Many startups rely on one dominant customer for revenue or one vendor for supply. While this may seem efficient at first, it creates a structural vulnerability. A sudden contract termination, a supplier going out of business, or even a shift in pricing can disrupt the entire operation overnight. Diversifying both suppliers and customer bases helps reduce this exposure.
2. Inadequate cash flow forecasting
Profitability doesn’t always equal liquidity. New businesses often fall into the trap of strong projected sales but insufficient working capital to cover payroll, rent, or supplier invoices. Without realistic forecasting models and contingency buffers, companies may find themselves unable to operate even when sales look promising.
3. Compliance gaps in emerging markets
Global expansion is attractive, but regulatory landscapes differ dramatically across regions. For example, data privacy rules in the EU are far stricter than in many other jurisdictions. Missing these nuances can result in legal penalties, reputational damage, and barriers to market entry.
4. Cyber risks from adopting fast but insecure tech solutions
In the race to scale, startups sometimes choose cost-friendly, quick-to-deploy technologies without considering long-term security. Cloud misconfigurations, weak authentication practices, or unvetted SaaS platforms can become gateways for cyberattacks that threaten both customer trust and business continuity.
By shining a light on these often-ignored areas, businesses can take early, proactive steps that significantly increase their chances of long-term resilience.
Building a Risk-Aware Culture in New Businesses
Even the most comprehensive risk management frameworks can fail if they aren’t supported by the right culture. A risk-aware culture ensures that employees at all levels understand risks, talk about them openly, and take ownership of mitigation efforts. For new businesses, embedding this culture from day one creates a lasting advantage:
1. Encouraging transparency about failures and risks
Teams should feel safe raising red flags without fear of blame. Early reporting of potential issues, whether it’s a supply chain bottleneck, a technical bug, or a compliance concern, gives leadership the time to act before the risk escalates.
2. Embedding risk awareness in day-to-day operations
Risk management should not be an annual review exercise. It must be integrated into project planning, vendor onboarding, financial forecasting, and product development. This way, employees see it as a natural part of business, not an afterthought.
3. Training teams early on risk ownership
Assigning risk responsibilities to specific roles ensures accountability. For instance, the product team should monitor technology risks, while procurement tracks vendor risks. When everyone knows their part, risk management becomes a collective responsibility rather than a siloed function.
Here’s where Auditive makes a measurable impact: by providing real-time insights into vendor performance, compliance gaps, and emerging risks, it reinforces this culture with data-backed decision-making. Leaders no longer have to rely only on intuition or delayed reports. Instead, they get a unified Trust Center that helps them communicate risk clearly across teams, turning awareness into action.
How Auditive Elevates Risk Management
New businesses can’t afford blind spots, every vendor dependency, compliance gap, or financial exposure matters. Traditional risk tools often leave leaders reacting too late.
Eliminate 80% of manual risk review work: Auditive’s network-driven automation slashes time spent on vendor risk evaluation.
Achieve 4× faster vendor onboarding: Leverage pre-vetted supplier networks to bring vendors on board in minutes, not days.
Drive 35% higher seller response rates: Auditive’s streamlined interface encourages faster and more consistent engagement from vendors.
With a centralized Trust Center, real-time vendor risk monitoring, and continuous compliance tracking, Auditive gives leaders a single source of truth. Instead of chasing risks across spreadsheets, they get clear, actionable intelligence to guide decisions and build resilience.
The result? Risk management shifts from a defensive exercise to a strategic advantage, empowering businesses to grow with confidence.
Conclusion
Effectively managing risk from a new business is not about eliminating uncertainty; it’s about preparing for it, minimizing vulnerabilities, and turning risk into opportunity. By adopting structured risk management processes, addressing common blind spots, and building a risk-aware culture, businesses can achieve both resilience and agility.
Platforms like Auditive make this journey even more seamless. With real-time vendor risk management and a centralized Trust Center, leaders can gain actionable visibility, automate compliance, and confidently scale operations without being weighed down by hidden risks.
Take the next step: If you’re ready to transform your risk strategy from reactive to proactive, Auditive equips you with the tools to stay ahead of third-party risks and protect your business growth.
FAQs
Q1. What is the biggest risk for new businesses?
A1. The most common risks include financial mismanagement, over-reliance on a single client, and gaps in compliance. Cybersecurity and vendor-related risks are also critical.
Q2. How does ERM differ from traditional risk management?
A2. ERM takes a holistic approach by integrating risks across finance, operations, compliance, and strategy, unlike traditional methods that often focus on one area.
Q3. Why should startups focus on vendor risk management early?
A3. Vendors can introduce compliance, financial, and reputational risks. Effective vendor risk management ensures business continuity and regulatory alignment from the start.
Q4. How can technology help in managing business risks?
A4. Technology platforms like Auditive automate manual processes, centralize risk insights in a Trust Center, and provide real-time monitoring to reduce oversight gaps.
Q5. What’s the role of culture in risk management?
A5. Even the best frameworks fail without a risk-aware culture. Encouraging transparency, accountability, and risk ownership ensures strategies are effectively implemented.