Complete Guide to SOC 2 Compliance and Audits
Securing sensitive customer and organizational data is not just a regulatory requirement; it is a critical driver of trust and long-term business growth. Clients, partners, and regulators increasingly expect organizations to demonstrate strong controls over their information systems. Any gaps or lapses can result in financial penalties, legal liabilities, and reputational damage.
SOC 2, or Service Organization Control 2, is a widely recognized auditing standard that validates an organization’s commitment to managing data securely and maintaining operational reliability. Unlike SOC 1, which focuses on financial reporting, SOC 2 addresses operational and technical controls relevant to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. Collectively, these are known as the Trust Service Criteria.
Achieving SOC 2 compliance is not a one-time task, it requires meticulous planning, implementation of controls, documentation, and regular audits to ensure ongoing adherence.
Before we dive in:
SOC 2 is a compliance framework focused on security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
Compliance requires implementing controls, documenting processes, and undergoing Type I or Type II audits.
Vendor oversight is essential; third-party risk can affect SOC 2 compliance.
Best practices include pre-audit assessments, automated monitoring, comprehensive documentation, accountability, internal audits, and training.
Platforms like Auditive provide continuous monitoring, AI-powered Trust Profiles, and centralized vendor risk management through the Trust Center.
What is SOC 2?
SOC 2 is an auditing framework established by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) for service organizations handling sensitive data. It provides assurance that systems and processes are designed to protect customer information and mitigate operational risks. SOC 2 is especially relevant for technology and cloud-based service providers, such as SaaS companies, where data handling and uptime are critical.
Unlike SOC 1, which is focused on financial reporting controls, SOC 2 addresses non-financial controls across the Trust Service Criteria: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. Achieving SOC 2 compliance demonstrates that an organization has implemented adequate technical, administrative, and operational controls to safeguard client data.
SOC 2 Trust Service Criteria
SOC 2 compliance is structured around five Trust Service Criteria:
Security: Ensures systems are protected against unauthorized access, misuse, or breach. This includes network security, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and user access controls.
Availability: Measures whether systems are operational and accessible according to service level agreements. Regular system monitoring, redundancy, and disaster recovery planning are key components.
Processing Integrity: Validates that system processing is accurate, complete, and timely. Controls include validation rules, error-handling mechanisms, and monitoring transaction workflows.
Confidentiality: Safeguards sensitive information such as client data, business secrets, or proprietary information from unauthorized disclosure. Encryption, access restrictions, and secure storage are critical.
Privacy: Ensures compliance with privacy policies and regulations governing the collection, usage, retention, and disclosure of personal information.
By adhering to these criteria, organizations not only protect sensitive data but also provide clients and stakeholders with measurable assurances of operational reliability and risk management effectiveness.
Why SOC 2 Compliance Matters
SOC 2 compliance is more than a regulatory or contractual requirement; it provides a framework for organizations to proactively manage risks and strengthen trust with stakeholders.
Builds Client Trust: Demonstrates that an organization follows industry-leading practices to safeguard customer data. Clients and partners are more likely to engage with service providers that maintain SOC 2 compliance.
Supports Regulatory Compliance: SOC 2 controls often align with broader regulatory standards, such as HIPAA, GDPR, and CCPA, making it easier to comply with multiple frameworks.
Reduces Operational Risk: Implementing rigorous internal controls and monitoring systems reduces the likelihood of security breaches, downtime, and operational errors.
Enhances Market Competitiveness: SOC 2 certification can differentiate organizations in competitive industries, particularly in SaaS, cloud services, and technology sectors.
Organizations that fail to maintain SOC 2 compliance risk financial penalties, reputational damage, and lost business opportunities. Achieving compliance and maintaining it over time requires a proactive approach, continuous monitoring, and alignment with organizational risk management strategies.
Also read: How to Manage Risk in New Business Strategies
Types of SOC 2 Reports
SOC 2 reports come in two main types, each serving a distinct purpose:
Type I Report: Assesses the design and implementation of controls at a specific point in time. It evaluates whether the organization’s policies and procedures are adequately designed to meet SOC 2 criteria. Type I reports are typically used for readiness assessment and initial certification.
Type II Report: Evaluates the operational effectiveness of controls over a defined period, usually six to twelve months. Type II reports provide greater assurance to clients because they demonstrate that controls are not only implemented but consistently effective.
Organizations often pursue a Type I audit first to identify gaps and prepare for a Type II audit, which offers a more comprehensive validation for stakeholders.
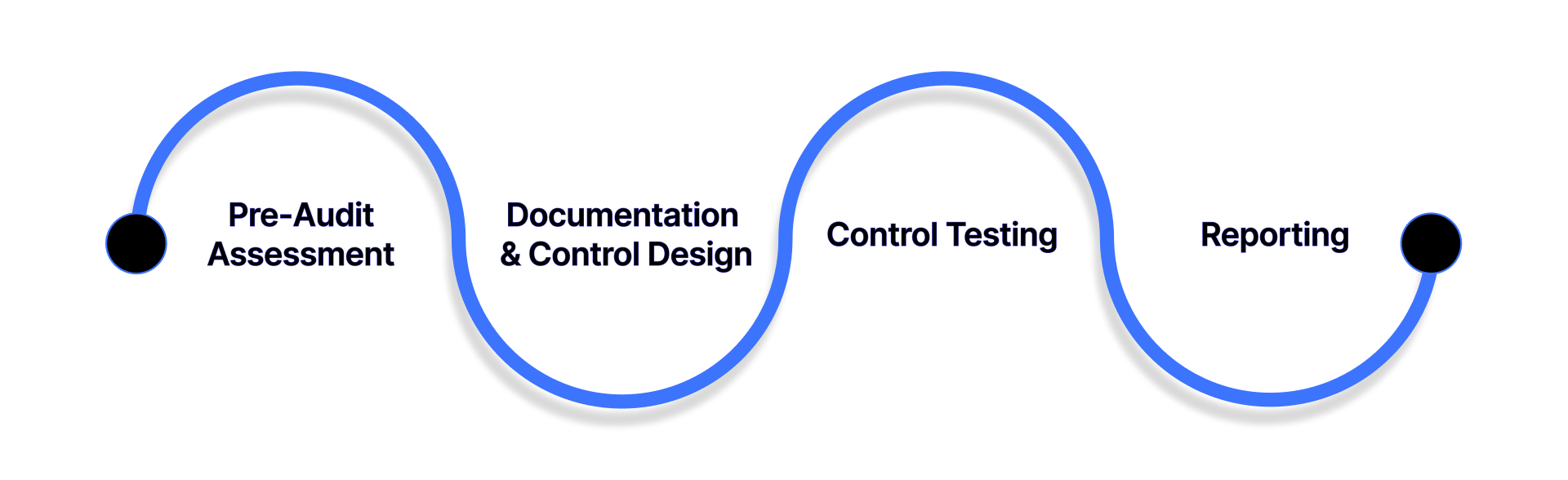
The SOC 2 Audit Process
Achieving SOC 2 compliance involves a structured audit process that includes preparation, evaluation, and reporting.
1. Pre-Audit Assessment
A readiness assessment is the first step, helping organizations identify gaps in policies, procedures, and technical controls. This involves reviewing security configurations, access management, incident response plans, and compliance documentation.
2. Documentation and Control Design
Auditors examine how controls are designed and documented. Evidence may include security policies, system architecture diagrams, access logs, and employee training records. Proper documentation ensures that auditors can validate compliance against the Trust Service Criteria.
3. Control Testing
Auditors test controls for effectiveness. In a Type I audit, they validate that controls exist and are appropriately designed. In a Type II audit, they verify that controls operate effectively over the audit period by reviewing operational logs, incident reports, and transaction histories.
4. Reporting
The final SOC 2 report includes:
Scope of the audit
Controls tested
Results and observations
Auditor’s opinion on compliance
Organizations can share these reports with clients to demonstrate adherence to security and operational standards.
Implementing SOC 2 Controls
SOC 2 compliance requires organizations to implement controls across multiple domains:
Technical Controls
Firewalls, intrusion detection, and antivirus systems
Encryption of data at rest and in transit
Access control mechanisms and multi-factor authentication
Administrative Controls
Security policies and procedures
Employee training and awareness programs
Background checks and role-based responsibility assignments
Physical Controls
Secure data center facilities
Access logs and monitoring
Environmental safeguards (fire suppression, temperature monitoring)
Consistent application and monitoring of these controls are essential to achieve and maintain SOC 2 compliance.
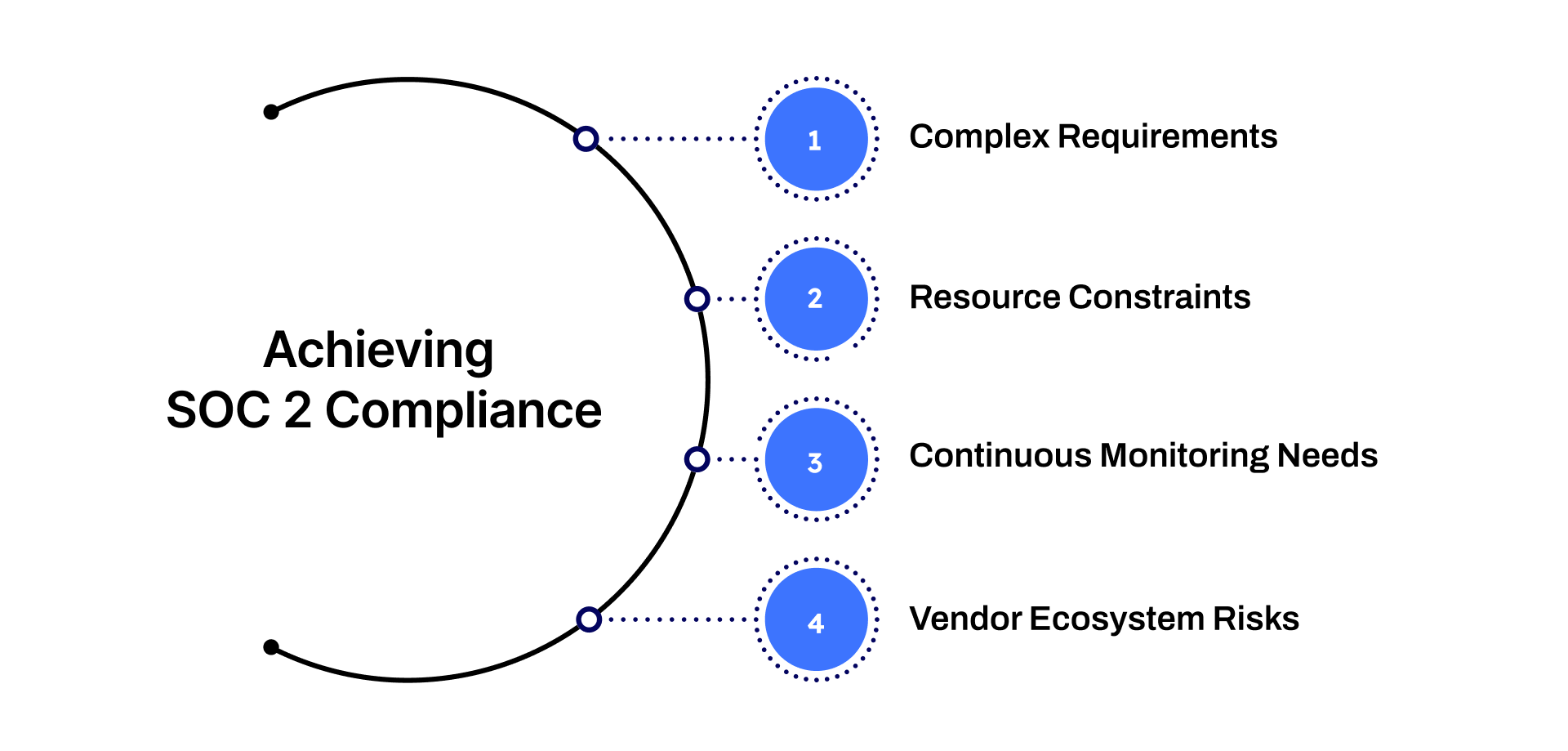
Challenges in Achieving SOC 2 Compliance
Organizations face several challenges while implementing SOC 2 compliance:
Complex Requirements: Mapping organizational processes to the Trust Service Criteria can be intricate and time-consuming.
Resource Constraints: Small to mid-sized organizations may lack dedicated staff or expertise for compliance initiatives.
Continuous Monitoring Needs: Maintaining compliance requires regular audits, monitoring, and remediation.
Vendor Ecosystem Risks: Third-party vendors can introduce additional vulnerabilities that must be monitored consistently.
Using a platform like Auditive can simplify these challenges by providing continuous monitoring, automated compliance workflows, and integrated vendor risk management.
Learn more about: Understanding Vendors: Definition, Types, and Differences
Simplifying SOC 2 Compliance and Vendor Risk Management
SOC 2 compliance extends beyond internal controls to include third-party vendors that access or process sensitive data. Auditive offers a modern Trust Center and AI-powered Trust Profiles to streamline SOC 2 compliance and enhance vendor oversight.
Key Features:
Continuous Monitoring: Real-time insights into vendor compliance and security posture.
AI-Powered Trust Profiles: Automatically generate and maintain profiles to demonstrate compliance to clients and auditors.
Seamless Vendor Onboarding: Quickly onboard vendors and assess risk without manual effort.
Integrated Workflows: Auditive integrates with procurement, GRC, and ITSM systems for holistic compliance management.
Flexible Access Levels: Start with AuditiveX Free for core monitoring or upgrade to AuditiveX Plus for enterprise-level capabilities, advanced assessments, and 100+ integrations.
By making use of Auditive, organizations can reduce manual effort, maintain continuous SOC 2 compliance, and strengthen their vendor risk management strategy.
Final Thoughts
SOC 2 compliance is a vital framework for service organizations handling sensitive data. Achieving compliance demonstrates a commitment to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy, while also strengthening trust with clients, partners, and regulators.
However, SOC 2 compliance extends beyond internal systems, it must encompass third-party vendors. Effective vendor risk management is critical, as gaps in vendor controls can compromise your compliance posture and increase operational risks. Centralized solutions, such as Auditive’s Trust Center, provide continuous monitoring of vendors, automated assessments, and AI-powered Trust Profiles, streamlining compliance processes and ensuring transparency across the organization’s ecosystem.
By integrating internal controls, continuous monitoring, and proactive vendor oversight, organizations can:
Minimize operational and compliance risks
Enhance client and stakeholder trust
Simplify audits and maintain sustainable SOC 2 compliance
Strengthen your SOC 2 compliance program and gain real-time visibility into vendor risks.
Book a demo with Auditive today to see how the Trust Center can transform your compliance and vendor risk management processes.
FAQs
1. What is SOC 2 compliance?
SOC 2 compliance ensures that service organizations manage customer data according to the Trust Service Criteria: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
2. Why is SOC 2 compliance important?
SOC 2 demonstrates your commitment to safeguarding data, supports regulatory requirements, strengthens client trust, and reduces operational risks.
3. What is the difference between SOC 2 Type I and Type II audits?
Type I evaluates the design and implementation of controls at a point in time, while Type II assesses operational effectiveness over a period, typically 6–12 months. Type II provides stronger assurance to clients and stakeholders.
4. How does vendor risk management relate to SOC 2?
Third-party vendors often have access to sensitive systems and data. Integrating vendor risk management ensures that external partners meet compliance standards, reducing exposure to operational and security risks.
5. How can Auditive help with SOC 2 compliance?
Auditive provides a Trust Center for centralized compliance monitoring, AI-generated Trust Profiles, continuous vendor risk oversight, and seamless workflow integrations, making SOC 2 compliance easier to achieve and maintain.