A Complete Third-Party Compliance Checklist To Perform Vendor Due Diligence
When dealing with high-stakes decisions, especially in industries like financial services, healthcare, or education, having a due diligence checklist is necessary. This checklist serves as a comprehensive guide to ensure that all risks are accounted for and that the necessary steps are followed during essential processes like mergers, acquisitions, or vendor onboarding.
This article will break down the key components of a due diligence checklist, the resources available, and how you can use this tool to maintain a secure and compliant environment.
Key Takeaways
A due diligence checklist ensures you assess all areas, like legal, financial, operational, and HR, during business evaluations, reducing risk and improving decision-making.
The checklist helps identify potential risks, including financial discrepancies, legal disputes, and cybersecurity vulnerabilities, ensuring that no essential element is overlooked.
Due diligence ensures compliance with industry-specific regulations (e.g., GDPR, healthcare compliance) and protects your organization from potential legal liabilities.
Vendor due diligence helps assess third-party security and compliance, safeguarding your business from future cybersecurity threats and ensuring strong partnerships.
By following a structured checklist, you ensure that all key aspects are covered, providing the necessary insights for making well-informed, strategic decisions.
What is a Due Diligence Checklist?
A due diligence checklist is a structured document or tool that helps organizations methodically evaluate and assess the risks, legal obligations, and other pertinent details when entering into contracts, acquisitions, or partnerships.
The goal of a due diligence checklist is to provide a systematic approach to gathering necessary information, analyzing risks, and ultimately making well-informed decisions. By breaking down complex processes into manageable sections, organizations can make more confident, strategic choices while reducing the risk of legal, financial, or operational pitfalls.
When working through your due diligence checklist for vendor risk management, ensuring vendor contract compliance is key. Auditive’s Contract Monitor helps you track critical contract terms, flag any discrepancies, and ensure adherence to compliance standards. By automating the review of contracts, you can easily spot hidden risks and stay on top of vendor obligations.
Now, let’s explore the resources available to help you get started.
What Due Diligence Resources are Available to Build Your Checklist?
To ensure a thorough due diligence process, organizations need access to a variety of resources. Below are some of the most useful resources available for due diligence:
1. Checklists
Due diligence checklists are the most straightforward and practical tools for managing the evaluation process. They are customizable, allowing you to tailor them to specific situations, such as mergers, acquisitions, or vendor onboarding. A well-prepared checklist allows organizations to review all the relevant information and avoid missing important details.
2. Model Forms
Model forms are predefined templates that cover various aspects of the due diligence process. These forms are especially useful in legal and compliance contexts, offering structured guidance for documenting findings. By using these forms, organizations can ensure consistency across multiple evaluations and reduce the risk of non-compliance.
3. Practice Notes and Legal Updates
Legal updates and practice notes provide industry-specific insights that include recent case law, compliance standards, and industry best practices. These resources help ensure that your due diligence process stays up-to-date with current laws and regulations, minimizing risk.
These resources, combined with a due diligence checklist, ensure that the evaluation process is both thorough and compliant with the necessary legal and operational standards.
Also Read: Direct Procurement Risk Management Strategies Explained
With the right resources, you can see how a checklist actually improves compliance.
How Does a Vendor Due Diligence Compliance Checklist Help?
A due diligence checklist is a powerful tool for organizing and maintaining focus during high-stakes evaluations. Here’s how it can help:
1. View the Big Picture and Recognize the Risks
A well-designed due diligence checklist helps stakeholders clearly see the broader picture. It identifies the key areas where risks might arise, such as financial discrepancies, legal disputes, or security vulnerabilities. With this understanding, your team can make more informed decisions that align with your company’s risk management strategy and compliance goals.
2. Identify, Organize, and Complete Any Interviews or Documents
Due diligence often involves gathering input from various departments, including legal, finance, compliance, and IT. A checklist helps ensure that each team member completes their tasks and submits the necessary documentation or conducts interviews. By organizing these tasks systematically, you avoid bottlenecks and ensure that no key detail is overlooked.
3. Maintain Thorough Documentation Throughout the Process
One of the key aspects of due diligence is ensuring that every step is thoroughly documented. From interviews with stakeholders to reviews of vendor contracts, maintaining clear, organized records is important. A due diligence checklist ensures that all documentation is tracked, stored, and reviewed appropriately, providing a clear audit trail for future reference.
Also Read: Direct Procurement Risk Management Strategies Explained
Now, let's see when you should actually use these templates in your vendor workflow.
When Can I Use a Due Diligence Checklist Template?
A due diligence checklist template is a versatile tool that can be used across a variety of situations. Below are some of the most common scenarios where using a template makes the due diligence process more efficient and effective:
1. Mergers and Acquisitions
In mergers and acquisitions (M&A), due diligence is a critical process that ensures both parties understand the financial, operational, and legal health of the company being acquired.
2. Vendor Onboarding
When onboarding new vendors, especially in sectors with stringent regulations (like healthcare or financial services), a due diligence checklist helps ensure that your vendors meet the required security, compliance, and performance standards.
3. Customer Due Diligence
In industries like banking or fintech, customer due diligence (CDD) is a significant component of compliance. A due diligence checklist for customer onboarding ensures that businesses meet anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements.
Also Read: Operational Risk Management: Overview and Guide
Let’s break down the key areas your checklist should cover for maximum impact.
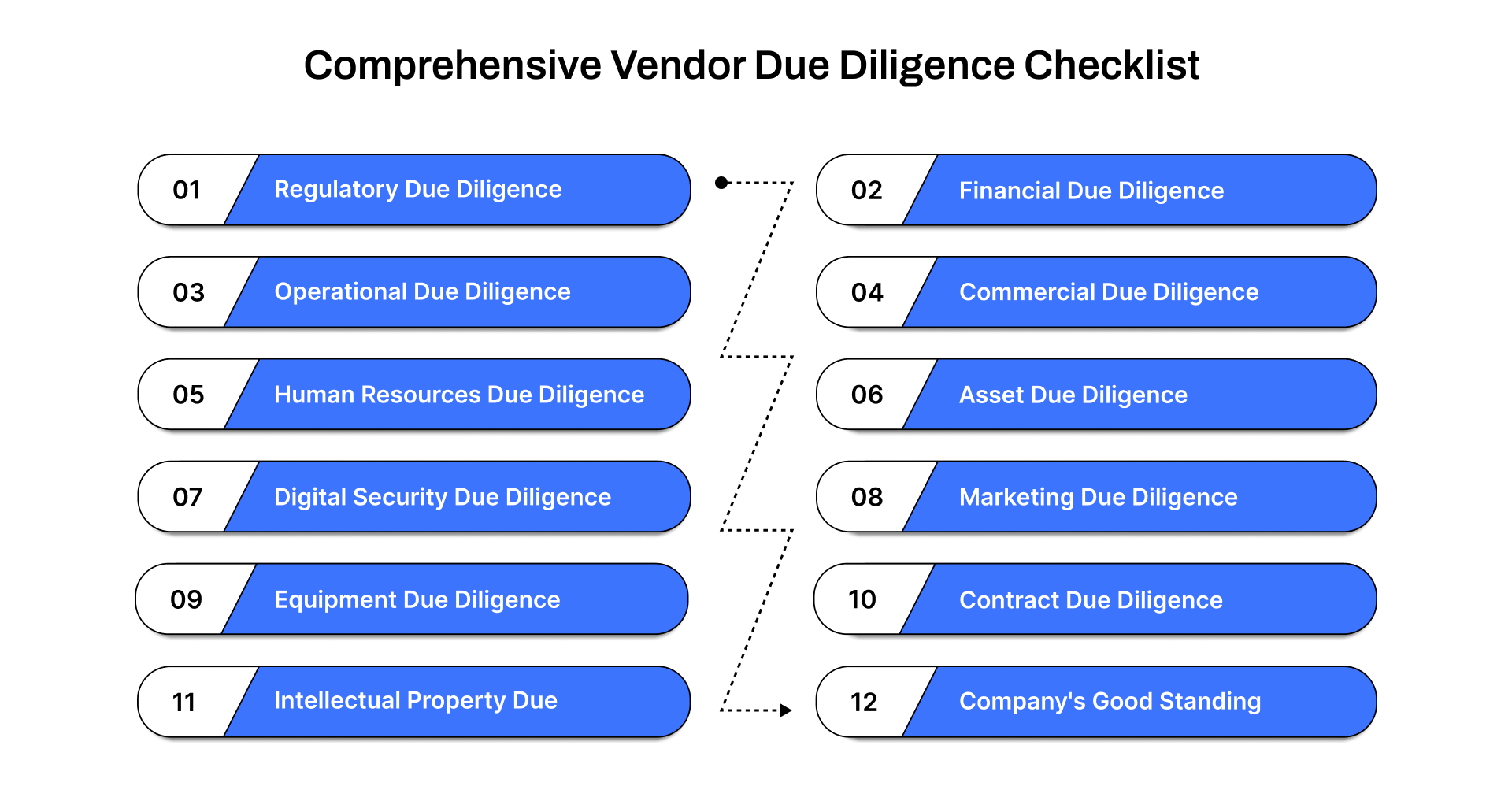
Comprehensive Vendor Due Diligence Checklist
In any high-stakes business decision, if you're entering a partnership, acquiring a company, or onboarding a vendor, conducting thorough due diligence is essential. Below is a detailed breakdown of critical areas to focus on in your due diligence checklist, ensuring you cover all bases when evaluating a target organization.
1. Legal and Regulatory Due Diligence
Legal and regulatory checks are vital to ensure compliance and safeguard your company from future legal disputes. These checks cover various aspects of a company's legal standing and adherence to applicable laws.
Company Structure and Legal Standing: Verify the target company’s incorporation status and legal structure.
Contracts and Agreements: Review all key contracts, including vendor, customer, and partnership agreements.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Trademarks: Confirm ownership and protection of IP, patents, and trademarks.
Regulatory Compliance and Permits: Ensure compliance with relevant industry regulations and confirm that all necessary permits are in place.
Litigation and Legal Disputes: Investigate any ongoing or potential legal disputes that could affect the business.
Environmental and Sustainability Concerns: Assess the company’s environmental impact and compliance with sustainability regulations.
Data Privacy and Security: Ensure adherence to data protection laws (e.g., GDPR) and verify cybersecurity practices.
2. Financial Due Diligence
Financial due diligence is needed to assess the target company's financial health, ensuring you understand its true value and risks.
Historical Financial Statements: Review audited financial statements for the past three to five years to assess past performance.
Revenue and Expense Analysis: Evaluate the revenue streams, expenses, and profitability.
Assets and Liabilities Review: Assess the company’s balance sheet for assets, liabilities, and capital structure.
Taxation and Tax Compliance: Confirm that the company is up-to-date with tax filings and obligations.
Debt and Financing Agreements: Review debt obligations, credit agreements, and financing terms.
Financial Projections and Assumptions: Examine the financial projections and the assumptions behind them.
Cash Flow Analysis: Assess the company’s liquidity and cash flow health.
3. Operational Due Diligence
Operational due diligence focuses on evaluating the target company’s operations, ensuring everything runs smoothly and aligns with your strategic goals.
Understanding Business Operations: Examine the company’s business model and operational efficiency.
Assessing Internal Processes: Review internal processes, including workflow, management systems, and operational bottlenecks.
Supply Chain Evaluation: Analyze the strength and reliability of the company’s supply chain and its dependencies on key vendors.
Technology Infrastructure: Assess the company's IT systems, software, and cybersecurity measures.
Health and Safety Compliance: Ensure the company adheres to all relevant health and safety regulations, particularly in industries with physical operations.
Cultural Fit and Integration: Evaluate the company’s culture to ensure it aligns with your organization’s values and operational style post-acquisition.
4. Commercial Due Diligence
This stage focuses on assessing the business’s commercial viability and its potential for future growth.
Market Analysis and Industry Trends: Understand the company’s market position and how industry trends impact its business.
Competitor Analysis: Identify competitors and evaluate the target company’s competitive strengths and weaknesses.
Customer and Client Contracts: Review major customer and client contracts to understand relationships and terms.
Sales and Marketing Strategies: Evaluate the company’s sales strategies, marketing plans, and overall go-to-market approach.
Product and Service Portfolio: Analyze the company’s product offerings and the market demand for them.
Revenue Model Assessment: Understand how the company generates income and assess the stability of its revenue streams.
Market Entry and Expansion Strategies: Examine plans for expanding into new markets or launching new products and services.
5. Human Resources Due Diligence
Human resources due diligence is essential for assessing the company’s workforce structure, labor relations, and compliance with employment laws.
Organizational Structure and Leadership: Review the leadership team and organizational structure to ensure stability and operational effectiveness.
Employee Contracts and Agreements: Assess employment contracts and terms for key employees and contractors.
Employee Benefits and Compensation: Review employee benefits, compensation packages, and any outstanding liabilities related to them.
Labor Agreements and Union Relationships: Evaluate the company’s relationships with unions (if applicable) and any collective bargaining agreements.
HR Policies and Procedures: Ensure compliance with employment laws and internal HR policies.
Workforce Composition and Talent: Review the company’s workforce composition to assess talent gaps and alignment with organizational goals.
Cultural Assessment: Assess the company’s workplace culture, ensuring compatibility with your organization’s values.
6. Real Estate and Asset Due Diligence
When conducting due diligence on real estate and assets, the following areas must be evaluated:
Asset Valuation: Conduct an assessment of the tangible assets to determine their current market value and any potential depreciation or appreciation.
Lease Agreements and Rental Income: Review all lease agreements to understand rental income streams, payment terms, and potential risks related to lease renewals.
Environmental Site Assessments: Perform environmental assessments to check for any hazardous materials, contamination, or compliance issues with environmental regulations.
Facility and Infrastructure Condition: Evaluate the condition of the facilities, infrastructure, and any maintenance requirements, assessing potential capital expenditures needed for repairs or upgrades.
Liabilities and Obligations: Identify any financial obligations, outstanding debts, or liabilities related to real estate or physical assets.
7. IT Systems and Digital Security Due Diligence
In evaluating the target company’s IT systems and digital security, focus on the following key components:
IT Systems and Software Inventory: Conduct an inventory check to identify all the IT systems and software currently in use, ensuring compatibility and compliance with industry standards.
Data Security and Privacy Measures: Assess the company's data protection practices, ensuring compliance with relevant privacy laws and regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
Cybersecurity Vulnerability Assessment: Perform a thorough evaluation of the company’s cybersecurity defenses to identify any vulnerabilities that cyber threats could exploit.
Disaster Recovery and Continuity Plans: Review the company’s disaster recovery protocols and business continuity plans to ensure minimal disruption in case of an IT system failure.
Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Verify that the company’s IT practices align with relevant compliance standards and regulatory requirements.
Technology Infrastructure Integration: Assess how well the company’s technology infrastructure can integrate with your own systems or processes if a merger or acquisition takes place.
Software Licensing and Contracts: Ensure that the company holds valid software licenses and is in compliance with contractual obligations related to software usage.
Employee IT Training and Awareness: Evaluate the company’s employee training programs to ensure staff are aware of cybersecurity best practices and data protection protocols.
8. Sales and Marketing Due Diligence
The sales and marketing due diligence process should involve:
Sales and Marketing Strategy Overview: Review the company’s sales and marketing plans to understand their approach, target audience, and effectiveness.
Sales and Marketing Coordination: Analyze how well sales and marketing teams work together, including communication and strategy execution.
Revenue by Customer: Look at revenue generation by customer to assess profitability and identify key revenue drivers.
Marketing Expense vs. Revenue Growth: Examine the relationship between marketing spend and its direct impact on revenue growth.
Sales Contract Details: Review existing sales contracts, focusing on terms, expiry dates, and renewal clauses.
Top Provider List: Identify the top 10 vendors and evaluate their contracts and reliability.
Sales Reports by Category: Analyze sales reports segmented by product category or service type for better market insights.
Credit Terms with Customers: Review the credit terms provided to customers to assess payment schedules and any potential collection risks.
Market Share and Channel Sales: Assess the company’s market share and the percentage of sales derived from each channel (e.g., online, direct, indirect).
9. Property, Plant, and Equipment Due Diligence
Due diligence for property, plant, and equipment should cover:
Equipment: Review the condition, ownership, and value of any machinery or operational equipment.
Real Estate: Assess the real estate holdings, including property ownership, leasing agreements, and any associated risks.
Technology: Evaluate the company’s technology assets, including proprietary systems, software, and hardware infrastructure.
Inventory: Examine the current inventory, its valuation, and its relation to the company’s operations.
Also Read: How to Change Vendors and Successfully Onboard New Suppliers
10. Contract Due Diligence
Contract due diligence includes reviewing all relevant contractual agreements, such as:
Customer Contracts: Review the terms, conditions, and expiration dates of all major customer contracts to ensure compliance and assess renewal risks.
Vendor Contracts: Examine vendor agreements for risks related to terms, pricing, and performance expectations.
Joint Venture/Partnership Agreements: Assess any joint ventures or partnerships for profitability, obligations, and exit strategies.
Settlement Agreements: Review any settlement agreements to identify liabilities or ongoing obligations.
Franchising Agreements: Examine any franchising agreements, focusing on terms and brand protection.
Receivables and Payables Schedules: Analyze accounts receivable and payable to identify potential issues in cash flow or liabilities.
Leases: Review all equipment and property leases to assess renewal clauses, terms, and costs.
Non-Compete Agreements: Assess non-compete clauses for potential conflicts or restrictions.
Employee Contracts: Review employee contracts for terms related to termination, benefits, and compensation.
Loan Agreements: Review any loans or credit agreements, understanding the terms, interest rates, and repayment schedules.
11. Intellectual Property Due Diligence
Evaluating intellectual property (IP) is crucial for understanding the value and protection of proprietary assets:
Trade Secrets: Confirm ownership and protection of trade secrets and confidential business information.
IP Claims and Litigation: Review any existing or past IP-related legal claims or disputes.
Domain Names: Verify ownership of important domain names and associated rights.
Issued Patents: Review issued patents, including their status and any potential infringement risks.
Patent Applications: Assess pending patent applications and their potential impact on business operations.
Design Patents and Applications: Review any design patents or applications related to the company’s products or services.
Industrial Designs: Evaluate any registered industrial designs for protection and exclusivity.
Copyrights and Licenses: Review copyrights, licensing agreements, and usage rights for the company’s creative works and materials.
Trademarks: Examine trademarks for ownership, protection status, and potential infringements.
Advertising and Branding Rights: Assess agreements regarding the ownership and rights to advertising materials, logos, and slogans.
12. Company's Good Standing and Organization Due Diligence
For a comprehensive view of the company’s legal status and organization:
Organizational Chart: Review the company’s organizational structure and management hierarchy.
Shareholders and Ownership: Understand shareholder ownership percentages and voting rights, including any options or convertible securities.
State of Incorporation: Confirm the company’s legal incorporation status in relevant jurisdictions.
Company Minutes and Bylaws: Examine the company’s minutes book and bylaws for governance and operational compliance.
State and Country Presence: Identify the states or countries where the company operates, owns assets, or conducts business.
Articles of Incorporation: Review the company’s Articles of Incorporation and any amendments.
Annual Reports: Evaluate the last three years of annual reports for business performance insights.
Certificate of Good Standing: Obtain certificates of good standing from relevant jurisdictions to confirm the company’s legal standing.
As you work through your third-party compliance checklist to perform vendor due diligence, Auditive’s Partner Trust Exchange gives you real-time risk data across your entire supplier network. You get up-to-date security and compliance information for each vendor, so you can validate controls, document risk ratings, and make approval decisions based on current evidence, not outdated questionnaires.
Knowing the areas to cover is one thing; applying best practices is what makes it effective.
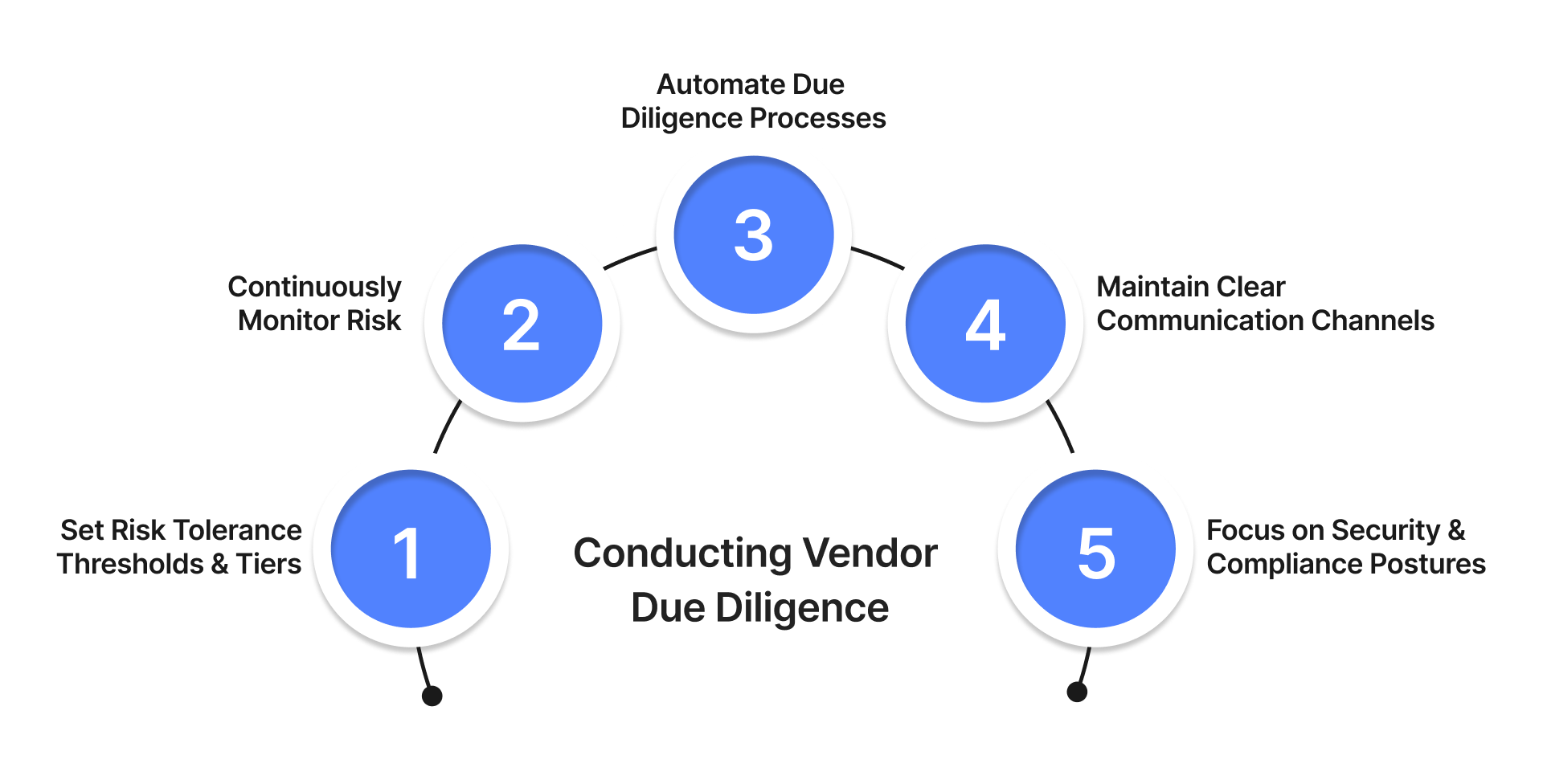
5 Best Practices for Conducting Vendor Due Diligence
Due diligence is an ongoing process, especially when dealing with vendors who play a vital role in your supply chain. Below are some best practices to follow:
1. Set Risk Tolerance Thresholds and Tiers
Establish clear thresholds for acceptable levels of risk when evaluating vendors. Categorize vendors based on their risk profile (e.g., high, medium, low) and tailor the due diligence process accordingly. This ensures you invest more resources into higher-risk vendors while maintaining efficiency with lower-risk ones.
2. Continuously Monitor Risk
Due diligence doesn’t stop after the initial assessment. Continually monitor your vendors’ security posture, financial health, and compliance with your terms. By regularly checking up on your vendors, you can stay ahead of any potential issues, ensuring that your organization remains secure and compliant.
3. Automate Due Diligence Processes
Where possible, automate parts of the due diligence process using digital tools. Automation can help track compliance, assess risks, and review vendor documents efficiently. This reduces the time spent on manual tasks, helping your team focus on more strategic decision-making.
4. Maintain Clear Communication Channels
Ensure that there is open communication between your organization and the vendors throughout the due diligence process. Clear communication helps build trust and ensures that vendors understand their obligations and expectations. This is particularly important in sectors with strict compliance requirements like financial services and healthcare.
5. Focus on Security and Compliance Postures
Always prioritize the security and compliance status of your vendors, especially in industries that handle sensitive information. Regularly assess their cybersecurity measures, compliance with data protection laws (like GDPR), and ability to meet your company’s risk management standards.
Also Read: How to Change Vendors and Successfully Onboard New Suppliers
Now, see how Auditive can make your due diligence process smarter and simpler.
Simplify Your Vendor Due Diligence with Auditive
Effective vendor risk management is crucial for industries like financial services, healthcare, and education. With Auditive, you can streamline the due diligence checklist for vendor risk management by automating the monitoring and evaluation process, ensuring compliance, and minimizing potential threats. Here’s how Auditive transforms your due diligence efforts:
Contract Monitor: Contract Monitor ensures that suppliers adhere to contractual obligations by extracting key contract information in seconds, tracking deviations, and sending automated renewal reminders. This ensures that contracts stay up-to-date and compliant with your vendor risk management strategy.
Partner Trust Exchange: Partner Trust Exchange connects enterprise buyers and their suppliers with continuous, real-time data. It gathers risk-relevant information across your entire supplier network, allowing you to evaluate vendors based on the most current, transparent data and streamline ongoing due diligence.
Accelerated Intake Form: The Accelerated Intake Form automates your third-party intake, providing immediate awareness of inherent risks. This tool categorizes vendors using AI, ensuring that you assess risk exposure early in the due diligence process and take prompt action.
Questionnaire Copilot: With Questionnaire Copilot, Auditive uses AI to complete over 80% of risk questionnaires in minutes. Automating the process saves time and ensures comprehensive vendor evaluations aligned with your due diligence checklist requirements.
Supplier Risk Assessment Agent: Supplier Risk Assessment Agent speeds up vendor risk assessments, using AI to analyze third-party data against your custom controls. This tool helps you assess risk quickly, making your due diligence process more efficient and accurate.
Supply Chain Continuous Monitoring: Supply Chain Continuous Monitoring enables real-time tracking of vendor risks throughout the contract lifecycle. Auditive alerts you to any incidents, such as security breaches or financial instability, ensuring your risk exposure remains manageable at all times.
See how Pelago streamlined their processes and gained significant ROI with Auditive, freeing up valuable resources; read the case study now.
By integrating Auditive into your vendor due diligence checklist, you can streamline the risk assessment process, improve vendor trust, and ensure that all partners meet your security and compliance standards.
Final Thoughts
A due diligence checklist is an essential tool for any organization looking to minimize risks and ensure compliance in various business processes. If you're working through mergers and acquisitions, vendor onboarding, or customer due diligence, this checklist helps you remain organized and focused on key risks.
For CISOs and decision-makers in sectors like financial services, healthcare, and education, using a comprehensive checklist ensures that nothing is overlooked and that risks are properly managed.
Auditive helps you automate and streamline risk assessments, track contract compliance, and ensure that all vendor practices align with your company’s security and regulatory standards. With real-time monitoring, automated risk evaluations, and transparent reporting, Auditive makes vendor management faster, smarter, and more compliant.
Contact Auditive and take control of your vendor risk management today and ensure comprehensive due diligence.
FAQs
1. How can I assess the potential cybersecurity risks during vendor due diligence for a cloud-based service provider?
Evaluate the vendor’s cloud security certifications, encryption protocols, disaster recovery plans, and data residency practices to ensure compliance with your security requirements.
2. What specific financial metrics should be prioritized during due diligence for a target company in the healthcare sector?
Focus on revenue stability, cost structure, reimbursement rates, profit margins, and regulatory compliance, which are essential in evaluating financial health in healthcare businesses.
3. How do I assess a vendor’s adherence to GDPR during due diligence, particularly in non-EU regions?
Verify the vendor’s use of Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs), GDPR-compliant data protection measures, and cross-border data transfer policies to ensure legal compliance.
4. What are the best practices for evaluating intellectual property (IP) risks in due diligence for an EdTech startup?
Examine IP ownership, patent and copyright status, licensing agreements, and any ongoing IP litigation that could impact the company’s market position and valuation.
5. How can I assess the cultural fit of a target company during due diligence, especially in M&A scenarios?
Conduct surveys and interviews with key personnel, review organizational values, and assess leadership styles to ensure alignment with your company's culture and operational goals.