How to Manage a Vendor Data Breach Effectively
A vendor data breach can strike at the very heart of your organization’s security posture. Even if your internal systems are airtight, one weak link in your third-party ecosystem can expose sensitive data, disrupt operations, and damage hard-earned trust. As businesses increasingly depend on vendors for critical services, managing these risks has become a top priority.
The complexity of today’s supply chains means that a single compromise can cascade across multiple partners, making containment and communication all the more challenging. Beyond immediate financial loss, a vendor data breach can lead to regulatory penalties and long-term reputational harm that’s difficult to recover from.
That’s why proactive vendor data breach management is essential, not just for crisis response, but for building resilience. The following sections explore how to effectively prepare for, respond to, and recover from a vendor data breach while strengthening your overall cybersecurity and compliance posture.
Key takeaways:
Vendor data breaches can compromise sensitive information and affect business operations.
Early detection and immediate response in the first 24 hours are critical.
Steps include identifying the breach, engaging vendors, notifying regulators, and conducting a forensic investigation.
Preventive measures: implement vendor risk management, conduct audits, train teams, and use automated compliance tools.
Auditive’s Trust Center centralizes monitoring, automates compliance, and strengthens vendor relationships.
Scheduling a demo with Auditive helps organizations proactively manage vendor risk and build resilience.
Understanding Vendor Data Breaches
A vendor data breach happens when a third-party supplier or service provider with access to your company’s sensitive information suffers a security incident. This could lead to the exposure, theft, or unauthorised access of confidential data such as
Customer or employee information
Financial and transactional records
Intellectual property and trade secrets
Login credentials and authentication details
Unlike internal breaches, vendor-related incidents are more complex because they involve multiple stakeholders, shared systems, and varying security standards. Even a minor vulnerability in a vendor’s infrastructure can have a ripple effect across your organization’s ecosystem.
Common causes of vendor data breaches include:
Misconfigured cloud environments are exposing data publicly
Weak access management or shared credentials across systems
Outdated or unpatched software vulnerabilities
Phishing or social engineering attacks targeting vendor staff
Compromised software updates or supply chain manipulation
Such breaches can compromise hundreds of organizations simultaneously, as seen in large-scale supply chain attacks. What makes them particularly dangerous is the limited visibility and control companies have over third-party security measures.
Understanding how vendor breaches occur and identifying where your vendors may expose potential entry points is the first step toward building stronger defense and response strategies.
Also read: Third-Party Contract Management: Steps and Best Practices
Early Detection and Response: The First 24 Hours Matter
When a vendor data breach occurs, the first 24 hours are absolutely critical. This window often determines how well your organization can contain the damage, protect sensitive data, and preserve customer trust. A rapid, structured response ensures you stay compliant with regulations and maintain control of the narrative before it spirals into a full-blown crisis.
The first step is early detection. Many breaches go unnoticed for weeks or even months, giving attackers time to exploit stolen credentials or exfiltrate more data. By implementing continuous monitoring tools and threat intelligence systems, organizations can spot anomalies in vendor activity, such as unusual data transfers or suspicious login attempts, almost in real time.
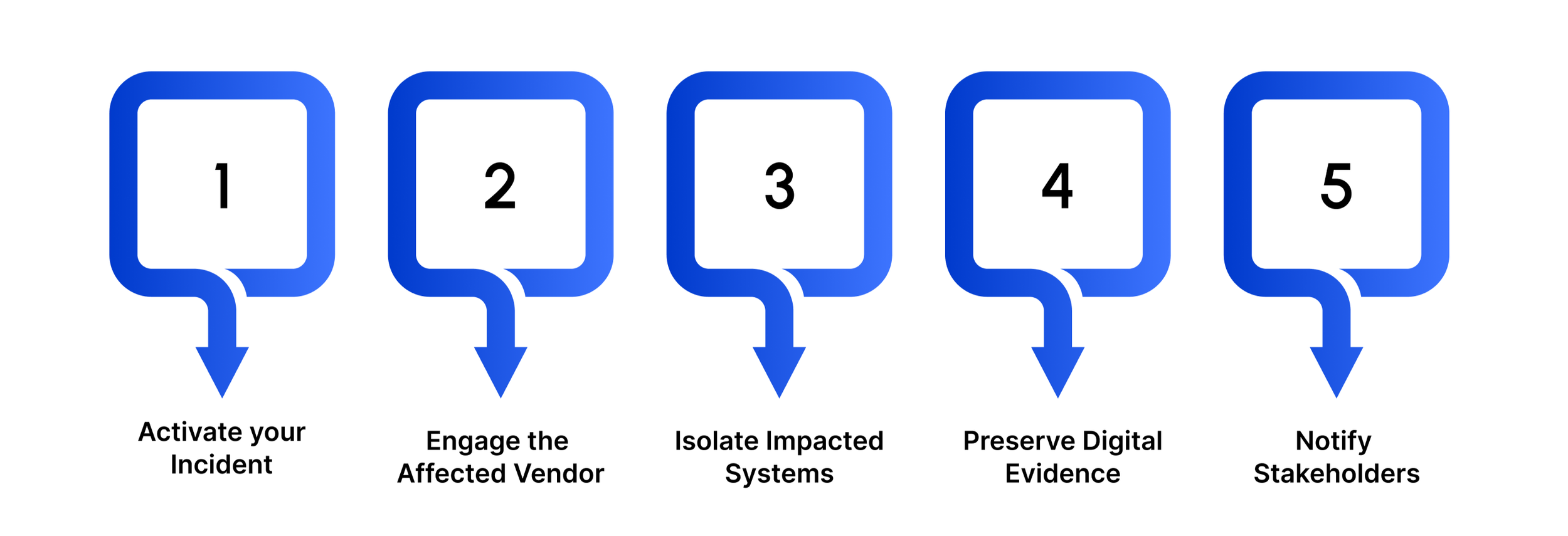
Once a breach is detected, a swift response plan should follow. Key actions within the first 24 hours include:
Activate your incident response team: Immediately involve your security, legal, and compliance teams to coordinate containment measures.
Engage the affected vendor: Request a full incident report, determine the breach scope, and ensure they initiate their own containment protocols.
Isolate impacted systems: Restrict access to compromised networks and revoke shared credentials to prevent further data leakage.
Preserve digital evidence: Secure logs, access records, and communications for forensic analysis and regulatory reporting.
Notify stakeholders: Communicate transparently with customers, partners, and regulators based on the severity and data sensitivity involved.
Speed and clarity are vital here; hesitation can lead to regulatory penalties, reputational harm, and greater data loss. By combining early threat detection with a rehearsed incident response plan, organizations can minimize disruption and demonstrate accountability.
At Auditive, we believe that a response is only as strong as the visibility behind it. Our solutions help organizations detect third-party vulnerabilities faster, streamline response workflows, and build the resilience needed to protect digital trust in complex vendor ecosystems.
Steps to Manage a Vendor Data Breach Effectively
Effectively managing a vendor data breach requires a thorough, step-by-step approach that combines immediate action with long-term risk reduction. Addressing each stage carefully ensures that the organization mitigates damage, maintains regulatory compliance, and strengthens its vendor risk management framework for the future.
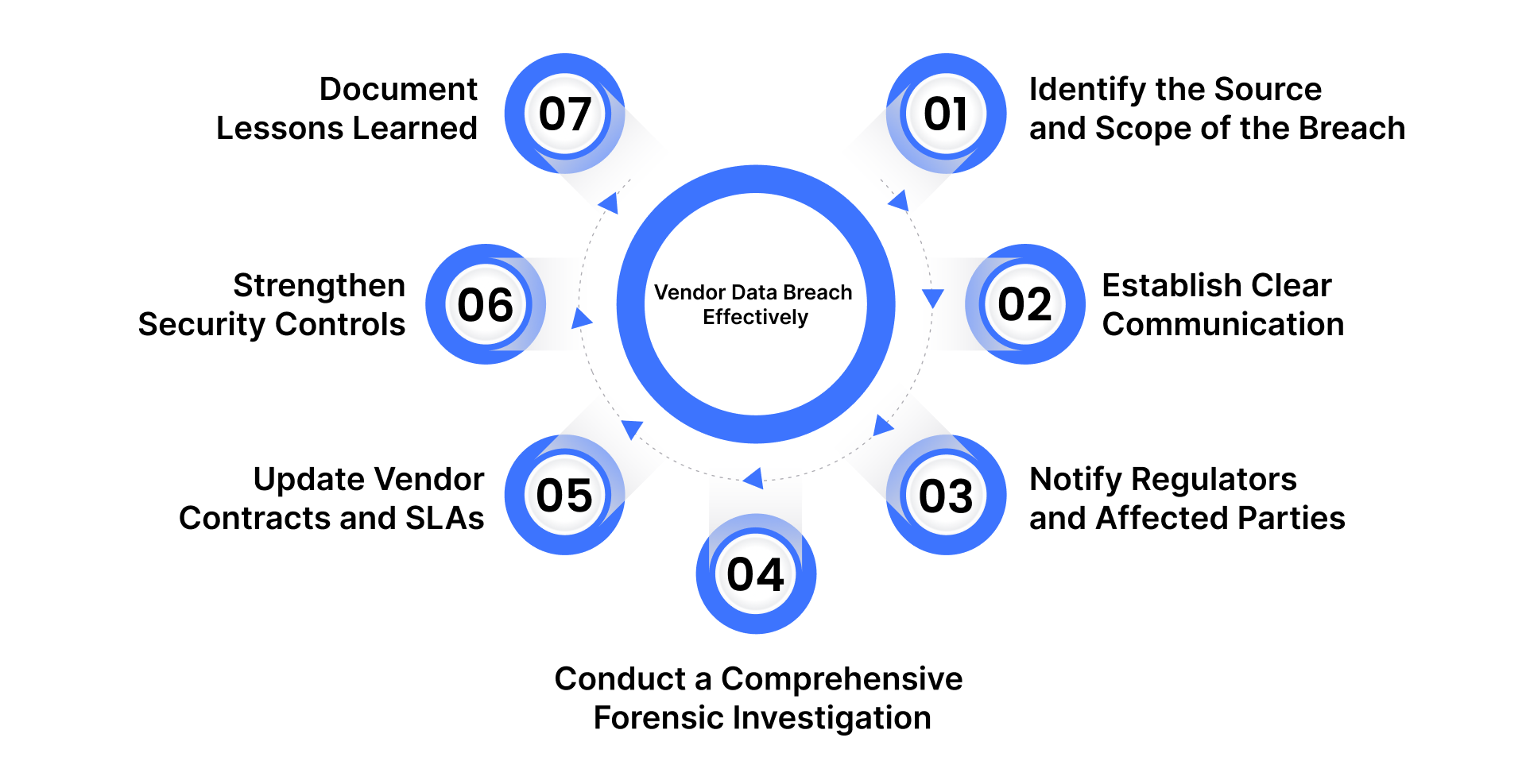
Step 1: Identify the Source and Scope of the Breach
The first priority in managing a vendor breach is to understand where and how it occurred. Quickly mapping out affected systems, services, and data types helps in prioritizing response efforts and containing the incident.
Actions to consider:
Pinpoint all affected systems, applications, and databases connected to the vendor.
Identify compromised accounts, credentials, or access points that may have been exploited.
Categorize the sensitivity of the exposed data, including personal, financial, or proprietary information.
Determine the potential impact on business operations, clients, and partners.
Identifying the source and scope accurately ensures that subsequent steps are targeted, efficient, and effective, reducing the risk of further data exposure.
Step 2: Engage the Vendor and Establish Clear Communication
Immediate collaboration with the vendor is crucial. Establishing a dedicated communication channel enables a coordinated response while ensuring accountability on both sides.
Actions to consider:
Request detailed breach information from the vendor, including the timeline and suspected vulnerabilities.
Set clear expectations for mitigation, including deadlines for patches, updates, and system checks.
Maintain open communication with internal stakeholders, such as IT, legal, and risk management teams, to align on actions.
Document all communications for compliance purposes and future audits.
Transparent and structured communication with the vendor allows for faster containment and clearer accountability and strengthens trust between the organization and its partners.
Step 3: Notify Regulators and Affected Parties (Compliance Aspect)
Timely notifications are a regulatory and ethical necessity. Complying with data protection laws and industry standards helps prevent legal penalties and reputational damage.
Actions to consider:
Inform relevant data protection authorities, regulators, or industry oversight bodies as required.
Notify affected clients, customers, or employees about the potential data exposure, including guidance on protective measures.
Prepare audit-ready documentation for regulatory review, detailing the breach, actions taken, and mitigation strategies.
Review regional and industry-specific compliance obligations, such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, or financial reporting requirements.
Prompt and transparent reporting demonstrates responsibility and reduces long-term risks associated with non-compliance while maintaining stakeholder confidence.
Step 4: Conduct a Comprehensive Forensic Investigation
A forensic investigation uncovers how the breach occurred, the methods used, and the full extent of the impact. This information is critical for preventing recurrence and addressing vulnerabilities.
Actions to consider:
Analyze system logs, access records, and network activity to trace the breach’s origin.
Determine if malware, phishing, insider threats, or other attack vectors were involved.
Identify whether the breach affected other systems or vendors indirectly.
Produce a detailed forensic report outlining findings, lessons, and recommendations for corrective measures.
A thorough forensic investigation provides actionable insights, helping the organization strengthen controls, close security gaps, and guide future incident response strategies.
Step 5: Review and Update Vendor Contracts and SLAs
Vendor agreements and service level agreements (SLAs) must clearly define security obligations and breach responsibilities. Revising these ensures accountability and reduces the risk of future incidents.
Actions to consider:
Include explicit breach notification timelines and reporting obligations in contracts.
Specify minimum security standards, monitoring expectations, and audit rights.
Update remediation responsibilities and penalties for non-compliance.
Align contracts with regulatory and industry standards relevant to your business and data types.
Updating vendor contracts and SLAs strengthens your organization’s legal and operational posture, ensuring vendors are fully accountable for protecting sensitive data.
Step 6: Strengthen Security Controls and Vendor Monitoring Systems
After containing the breach, focus shifts to preventive measures and continuous monitoring. Enhancing security reduces the likelihood of recurrence and improves overall resilience.
Actions to consider:
Implement stricter access controls, multi-factor authentication, and network segmentation.
Use automated vendor monitoring tools to track compliance and detect anomalies in real time.
Conduct regular vulnerability assessments, penetration tests, and security audits of vendor systems.
Review and refine incident response procedures, incorporating lessons learned from the breach.
Strengthening security controls and monitoring systems ensures that your vendor ecosystem remains resilient and proactively protected against evolving threats.
Step 7: Document Lessons Learned and Build Resilience
A post-incident review is essential for continuous improvement and organizational learning. Documenting lessons learned helps prepare for future incidents and strengthens long-term risk management.
Actions to consider:
Conduct a detailed post-mortem analysis of the breach and response effectiveness.
Update incident response plans and internal policies based on identified gaps.
Train internal teams and vendors on improved protocols and preventive measures.
Integrate insights into ongoing vendor risk management and trust center practices.
Documenting lessons learned turns a crisis into an opportunity for improvement, ensuring your organization emerges stronger, more resilient, and better prepared for future challenges.
Tools like Auditive provide continuous vendor monitoring, automated risk scoring, and a centralized trust center, allowing businesses to respond swiftly, maintain compliance, and enhance vendor risk management across their entire ecosystem.
Preventive Measures for the Future
After managing an immediate vendor data breach, organizations must shift focus toward preventive strategies that minimize the risk of recurrence. Implementing effective frameworks, continuous monitoring, and transparent communication ensures long-term resilience and strengthens trust with clients, partners, and vendors.
Learn more about: How to Prevent Data Breaches in Healthcare
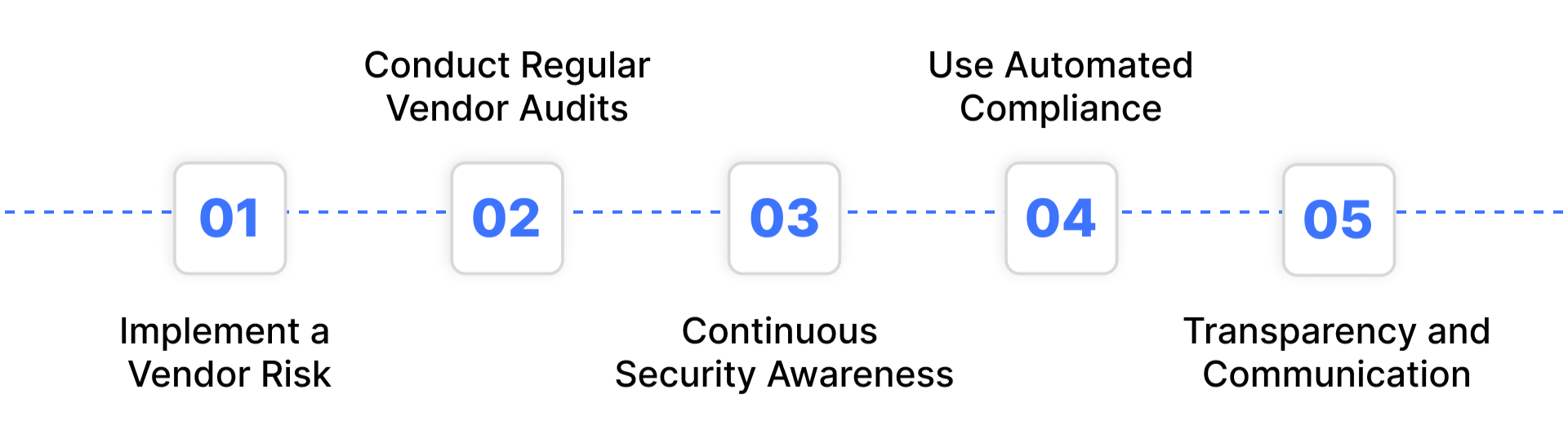
Implement a Vendor Risk Management Framework
Establishing a structured vendor risk management (VRM) framework is fundamental to proactively identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks across your vendor ecosystem. A strong VRM framework provides:
Clear policies and procedures for vendor onboarding, assessment, and monitoring.
Standardized risk scoring and prioritization of critical vendors based on potential impact.
Defined responsibilities and accountability for internal teams managing vendor relationships.
A comprehensive VRM framework creates a structured approach to risk, helping organizations stay ahead of potential threats before they escalate.
Conduct Regular Vendor Audits and Risk Assessments
Periodic audits and risk assessments of vendors ensure that security controls remain effective and aligned with organizational standards. Key practices include:
Scheduling routine security and compliance audits for all critical vendors.
Evaluating vendor adherence to contracts, SLAs, and regulatory obligations.
Analyzing audit results to identify vulnerabilities and corrective actions.
Prioritizing high-risk vendors for deeper assessments or additional controls.
Regular audits and risk assessments provide ongoing assurance that vendors maintain strong security practices, reducing exposure to future breaches.
Continuous Security Awareness and Training
Human error remains one of the top causes of data breaches. Continuous security awareness programs for both internal teams and vendor personnel help foster a culture of vigilance:
Conduct targeted training on recognizing phishing attempts, social engineering, and other threats.
Update training regularly to reflect evolving cybersecurity risks and regulatory requirements.
Promote vendor engagement by encouraging participation in collaborative security exercises.
Educated and alert teams, combined with proactive vendor engagement, strengthen the organization’s overall cybersecurity posture.
Use Automated Compliance Monitoring Tools
Using technology for continuous monitoring ensures that vendors remain compliant and reduces the burden of manual oversight:
Deploy automated tools to track vendor performance, compliance, and risk in real time.
Receive alerts for non-compliance, security incidents, or deviations from contractual obligations.
Integrate monitoring systems with internal IT and risk management platforms for seamless oversight.
Automation not only enhances efficiency but also provides a reliable safety net that can detect and respond to threats faster than manual processes.
Know more about: Effective Continuous Risk Monitoring Practices and Techniques
Establish a Trust Center for Transparency and Communication
Creating a trust center allows organizations to centralize vendor risk information, improve visibility, and strengthen stakeholder confidence:
Share compliance statuses, risk assessments, and certifications with stakeholders in a single, accessible portal.
Promote transparent communication between vendors, clients, and internal teams.
Maintain an up-to-date record of vendor risk profiles and incident histories.
A trust center builds credibility and accountability, serving as a hub for all vendor risk management efforts and supporting long-term business resilience.
Auditive: Enhancing Vendor Data Breach Management
Managing vendor data breaches effectively requires continuous monitoring, transparency, and proactive risk management. Auditive centralizes these processes, helping organizations safeguard sensitive data and maintain compliance effortlessly.
Real-Time Vendor Risk Monitoring: Live incident alerts, dynamic vendor trust profiles, and prioritization of high-risk vendors enable fast detection and response.
Centralized Trust Center: Provides a single source of truth for vendor compliance, audit results, and regulatory reporting, fostering transparency and trust.
Automated Compliance & Risk Assessment: Continuous evaluation of vendor adherence to regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and SOC 2, with seamless integration into existing systems.
Proactive Vendor Engagement: Vendors can share compliance evidence proactively, and AI-powered insights highlight potential vulnerabilities and remediation steps.
By combining real-time monitoring, automation, and a centralized trust center, Auditive empowers organizations to manage vendor data breaches effectively while strengthening vendor relationships and organizational resilience.
Conclusion
Effectively managing a vendor data breach is no longer optional; it is a critical aspect of modern risk management. Organizations must adopt a structured approach that combines early detection, thorough investigation, and preventive measures. Implementing a strong vendor risk management framework ensures continuous oversight of third-party partners, reducing the likelihood and impact of breaches.
Using a centralized Trust Center, such as Auditive, provides transparency, streamlines compliance reporting, and strengthens stakeholder confidence. By integrating real-time monitoring, automated risk assessments, and proactive vendor engagement, businesses can not only respond efficiently to breaches but also build long-term resilience and trust in their vendor ecosystem.
Schedule a demo with Auditive to see how a Trust Center and automated vendor risk management can safeguard your organization from data breaches.
FAQs
1. What is a vendor data breach?
A vendor data breach occurs when a third-party provider’s systems are compromised, potentially exposing sensitive data of your organization or customers.
2. How can I detect a vendor data breach early?
Early detection relies on real-time monitoring tools, automated alerts, and continuous vendor risk assessments to spot anomalies promptly.
3. What steps should I take immediately after a breach?
Contain the breach, notify affected stakeholders, conduct a risk assessment, and secure access points to prevent further impact.
4. How does a Trust Center help in vendor risk management?
A Trust Center centralizes vendor compliance and audit information, improves transparency, and provides actionable insights for risk mitigation.
5. Can automation reduce the impact of vendor breaches?
Yes, automating monitoring, compliance checks, and reporting accelerates response times, reduces human error, and ensures ongoing oversight.