How to Prevent Data Breaches in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations hold some of the most sensitive and sought-after data, including medical records, insurance details, payment information, and personally identifiable information. This makes the industry a prime target for cyberattacks. From ransomware to insider threats, breaches in healthcare don’t just lead to financial loss, they compromise patient safety, erode trust, and risk regulatory penalties.
Despite increased investment in cybersecurity, attackers continue to exploit gaps in outdated infrastructure, poor access controls, and fragmented vendor ecosystems. For healthcare providers, prevention isn’t optional; it is a critical responsibility.
This blog explores the leading causes of data breaches in healthcare and outlines practical strategies to protect patient data, maintain compliance, and strengthen trust across the system.
Overview
Healthcare data is a prime target due to its sensitivity and value.
Common breach causes include insider threats, outdated systems, and third-party exposure.
Prevention strategies include data classification, DLP policies, encryption, and user behavior monitoring.
Third-party risk management (TPRM) platforms like Auditive offer trust-based visibility, real-time alerts, and centralized access insights.
A proactive, trust-driven approach is key to sustainable data protection.
The Current State of Healthcare Data Breaches
Healthcare remains one of the most frequently targeted sectors for cybercrime. The sheer volume of protected health information (PHI), combined with the urgency of medical operations, makes hospitals and healthcare systems especially vulnerable. Unlike other industries, healthcare environments require immediate data accessibility, which often leads to trade-offs in security design.
Over the past few years, the frequency and scale of breaches have grown significantly. Attackers are increasingly focused on extracting value from PHI, information that commands a high price on black markets due to its depth and permanence. Unlike credit card numbers, which can be replaced, medical histories are immutable and highly exploitable.
According to industry research, healthcare leads all sectors in breach volume and cost, with average incident losses surpassing $7 million. These events disrupt care, compromise regulatory compliance, and erode patient confidence, all while placing immense strain on internal IT and legal teams.
The message is clear: the healthcare industry is operating in a high-risk environment where every unsecured endpoint, third-party vendor, or human error presents an open door. Understanding this threat landscape is the first step toward designing systems that can withstand it.
Key Factors Behind Healthcare Data Breaches
Breaches in healthcare don’t occur randomly; they stem from a set of persistent vulnerabilities that expose sensitive patient data to risk. Understanding these weak points is essential for strengthening defense strategies.
1. Human error and insider missteps
Even the most secure environments are vulnerable to internal mistakes. Misdelivered emails, weak passwords, and mishandled access permissions continue to result in unauthorized data exposure. Phishing schemes remain especially effective when security training is lacking, giving attackers an easy foothold into critical systems.
2. Legacy infrastructure and unpatched systems
Many healthcare providers still rely on aging platforms that lack compatibility with modern security protocols. These legacy systems often can’t be taken offline for regular patching due to operational demands, creating long-standing vulnerabilities that attackers are quick to exploit.
3. Third-party and supply chain risk
The ecosystem around healthcare, billing providers, cloud vendors, diagnostic labs, often has direct access to internal systems. If even one vendor fails to uphold strict security practices, the consequences can cascade. Risk isn’t limited to internal operations; it extends to every entity connected to the network.
4. Targeted cyber threats
Healthcare data is highly valuable on the black market, which makes the industry a top priority for cybercriminals. Sophisticated threats like ransomware and persistent intrusion tactics are designed to move laterally through networks, silently collecting credentials or locking down operations. These attacks don’t just extract data; they disrupt care.
This is where organizations need more than just tools; they need a unified risk management strategy.
Auditive helps healthcare entities close these gaps with proactive breach prevention, vendor risk assessment, and trust-centered security models that go beyond surface-level defense.
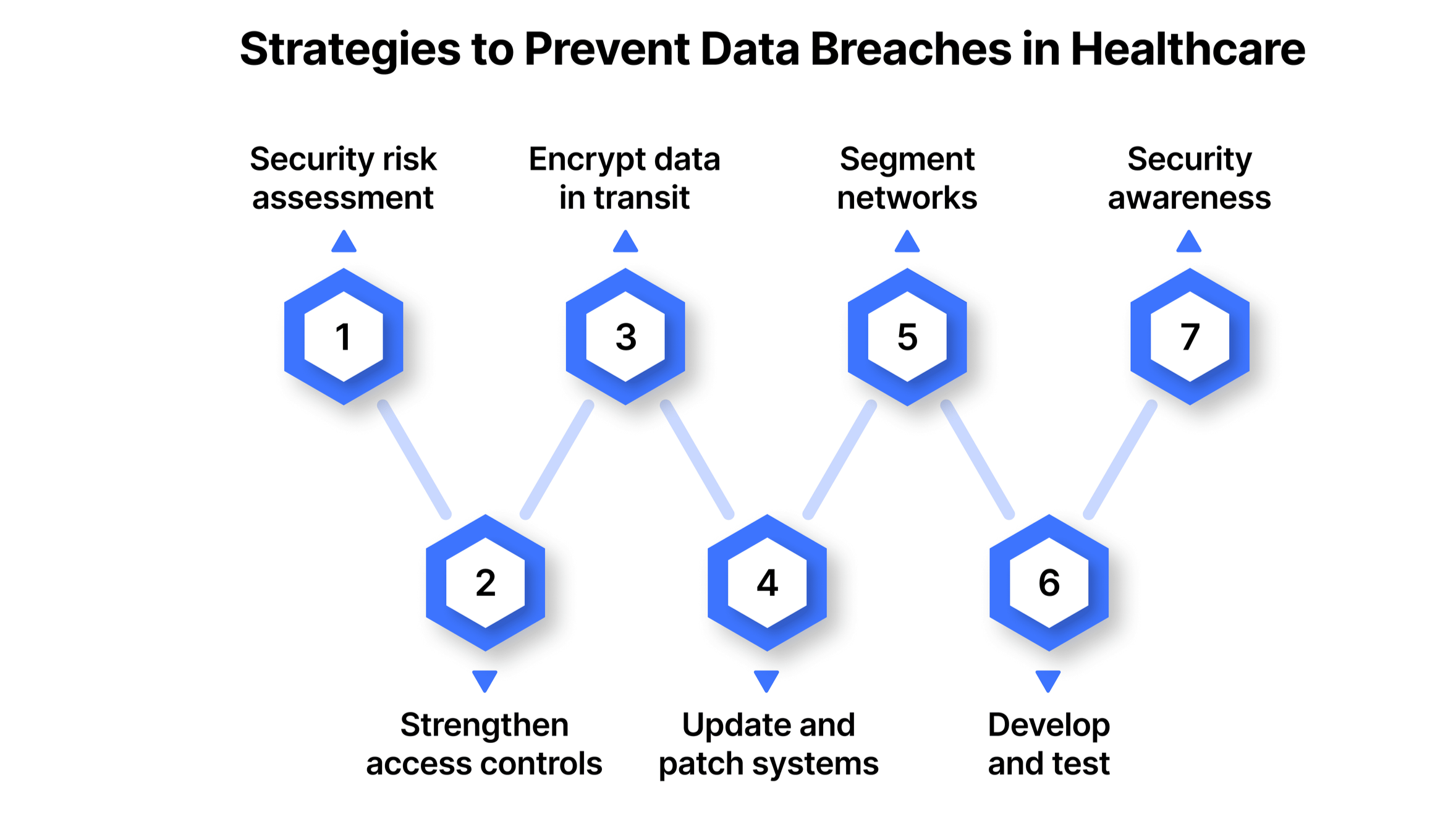
Proven Strategies to Prevent Data Breaches in Healthcare
A strong data protection strategy in healthcare isn’t built on a single solution; it’s the result of layered, deliberate actions. From access control to employee training, each step plays a key role in closing security gaps and safeguarding patient trust.
1. Conduct a thorough security risk assessment
Start by identifying all systems that store, process, or transmit protected health information (PHI). A structured risk analysis helps uncover weak points before attackers do.
Key actions:
Map all data flows and storage locations
Identify unpatched systems and misconfigured applications
Prioritize vulnerabilities based on impact and likelihood
2. Strengthen access controls
Limit access to sensitive data based strictly on role and responsibility. Misuse or over-permissioning often opens the door to internal risks.
Best practices:
Enforce the principle of least privilege
Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all critical systems
Monitor privileged access usage regularly
3. Encrypt data in transit and at rest
Encryption is non-negotiable when handling patient information. Whether it's stored on a local server or transmitted to an external partner, PHI must be shielded.
Implementation tips:
Use TLS 1.3 or higher for all communications
Apply full-disk encryption on laptops and mobile devices
Secure backup data with separate encryption keys
4. Update and patch systems promptly
Outdated software is a known attack vector. Healthcare systems must follow a disciplined patching schedule to stay ahead of exploits.
To-do list:
Automate patch deployment wherever possible
Monitor for vulnerabilities using threat intelligence feeds
Prioritize updates for internet-facing systems
5. Segment networks for risk containment
Separating critical systems reduces the blast radius of a breach. Not every device needs access to your EHR system.
Effective segmentation involves:
Isolating PHI databases from general-use systems
Restricting lateral movement within internal networks
Using firewalls and access control lists between zones
6. Develop and test an incident response plan
A data breach isn’t the time to scramble. Healthcare organizations need a predefined process to contain and recover quickly.
Core components:
Roles and responsibilities for each response team
Procedures for detection, containment, and recovery
Playbooks for handling ransomware and insider threats
7. Build a culture of security awareness
Human error is still one of the top causes of data breaches. Staff need to understand the impact of their everyday actions.
Key program elements:
Regular training on phishing, password safety, and device use
Simulated phishing tests to build resilience
Clear policies on data handling and reporting incidents
Seamless detection with Auditive
Detecting threats early requires visibility into behavior, not just alerts. Auditive enables healthcare providers to detect anomalies with context, combining real-time monitoring with user behavior analytics.
Identify unauthorized access attempts or unusual activity
Score user and entity behavior against risk thresholds
Surface actionable insights without overwhelming security teams
Auditive’s healthcare-ready platform helps organizations reduce breach exposure and meet compliance obligations without adding operational friction.
Using User Behavior Analytics to Detect and Prevent Threats
Healthcare data environments are complex, with countless users accessing critical systems daily, doctors retrieving patient files, administrators handling insurance data, or vendors interacting with shared platforms. This volume of legitimate activity can make it difficult to spot the signs of malicious behavior. That’s where user behavior analytics (UBA) becomes essential.
UBA helps organizations move beyond static rules and surface-level alerts. Instead, it analyzes patterns over time, what users typically access, when, how frequently, and from where, to flag deviations that may indicate internal misuse or compromised credentials. A sudden surge in medical record access, for example, or a login from an unrecognized location outside standard hours, can trigger a deeper investigation before real damage occurs.
Steps to effectively use UBA in healthcare settings
Implementing UBA requires more than just turning on a tool. It begins with setting a clear behavioral baseline. Each department functions differently, and what's normal for one role could be highly suspicious for another. Establishing accurate norms makes anomaly detection far more precise.
Key areas of focus should include:
High-risk indicators: Actions like exporting large datasets or repeated access to restricted files.
Tool integration: Ensuring your UBA solution works in sync with existing systems, identity management, electronic health records (EHR), and SIEM tools, to provide unified visibility.
Clear alert thresholds: Define what triggers an alert and outline how teams should respond to minimize dwell time and exposure.
Investigation workflows: Threat detection must be tied to structured response playbooks, whether through automated actions or human-led review.
Balancing visibility with operational flow
Monitoring systems must be intelligent enough to enhance security without disrupting care delivery. This balance is possible by prioritizing context, considering the user's role, department, time of access, and historical behavior. A flagged action in isolation doesn’t always imply intent, but patterns often do.
Equally important is transparency. Keeping employees informed about security protocols and the rationale behind monitoring promotes a culture of accountability without creating fear or friction.
Why Auditive matters in this equation?
Auditive takes a proactive approach to trust security, going beyond basic UBA. By embedding trust intelligence into healthcare systems, it detects risky behavior across users, devices, and vendors before it becomes a breach.
With real-time trust scoring and seamless integration into complex EHR and third-party environments, Auditive helps healthcare providers secure data without disrupting care delivery.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Best Practices for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare organizations are responsible for protecting large volumes of highly sensitive patient data. A focused Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategy is essential to reduce exposure and maintain compliance without slowing down care delivery.
Here’s how providers can implement effective DLP safeguards:
1. Classify and control sensitive data
Begin with visibility. Locate all critical data, whether in EHRs, imaging systems, or cloud apps, and classify it based on regulatory and business sensitivity.
Map where protected data lives
Classify by sensitivity (e.g., PHI, payment data)
Align protections with classification levels
2. Define and enforce smart DLP policies
Set clear policies around who can access, move, or share sensitive data, then back those policies with controls that work at scale.
Create rules for handling and sharing PHI
Extend policies to mobile and remote users
Use automated enforcement wherever possible
3. Implement purpose-built DLP tool
Tools should monitor real-time behavior across devices, cloud services, and external channels, catching violations before data leaves your control.
Monitor for risky activity across all channels
Block unauthorized transfers or uploads
Audit and investigate incidents proactively
Auditive enhances this visibility with intelligent trust signals, giving healthcare teams early alerts when data handling deviates from normal behavior.
4. Secure data in transit
Prevent data interception during transfer between systems or vendors.
Use modern encryption (e.g., TLS 1.3, IPsec)
Use modern encryption (e.g., TLS 1.3, IPsec)
Replace email/file shares with secure transfer tools
Monitor transfer logs for irregular access
5. Reduce third-party risk exposure
Vendors and partners should follow the same rigorous standards as your internal teams.
Perform risk assessments before granting access
Limit third-party access to only essential data
Set clear breach notification and compliance terms
Auditive’s trust architecture helps monitor third-party interactions, providing full audit trails and vendor compliance insights.
6. Make security awareness part of the culture
Even with strong tools, employees can accidentally create risk. Ongoing education is key.
Train all staff on DLP responsibilities
Focus on high-risk roles (admin, billing, IT)
Update training as threats evolve
How Auditive Supports Healthcare Organizations in Strengthening Data Security
Auditive helps healthcare providers move beyond reactive controls by building a trust-first foundation for data security. Its platform continuously monitors who has access, how it’s being used, and where implicit trust creates risk.
Key ways Auditive makes a difference:
Real-Time Trust Monitoring
Tracks unusual access patterns and permission drift to surface hidden threats early.
Third-Party Risk Oversight
Maps external access, enforces least-privilege, and provides full audit visibility for vendors and partners.
Automated Trust Decisions
Continuously evaluates access risks and automates remediation to reduce manual effort.
Centralized Trust Intelligence
Delivers one source of truth for access data, risk scoring, and compliance reporting.
With Auditive, healthcare teams can prevent breaches before they happen, backed by real-time insights, automated enforcement, and audit-ready trust architecture.
Conclusion: Proactive Protection Starts with Trust
Data breaches in healthcare are no longer just an IT concern, they’re a patient safety issue, a financial risk, and a reputational threat. Prevention requires more than patching vulnerabilities; it demands complete visibility into how data is accessed, used, and shared, across internal teams and external vendors.
Auditive enables healthcare organizations to strengthen their defenses by eliminating blind spots, automating trust decisions, and enforcing least-privilege access across systems. With a dedicated Trust Center, real-time risk scoring, and robust Vendor Risk Management capabilities, Auditive helps security teams stay ahead of threats without slowing down operations.
Schedule a personalized demo today and explore how our Trust Center and Vendor Risk Management capabilities can strengthen your data security posture.
FAQs
Q1. What is the most common cause of data breaches in healthcare?
A1. Insider threats, both malicious and accidental, are among the leading causes, often due to misconfigured access, phishing, or untrained staff.
Q2. How can healthcare providers protect data in transit?
A2. Encrypt all data in motion using secure protocols (e.g., TLS 1.3), use VPNs, and monitor transfer logs for unusual activity.
Q3. What is Vendor Risk Management in healthcare security?
A3. It refers to assessing, managing, and continuously monitoring the security posture of third-party vendors who handle sensitive data or systems.
Q4. Why is a Trust Center important for compliance?
A4. A Trust Center centralizes data access insights, risk scoring, and audit readiness, supporting compliance with HIPAA, HITECH, and more.
Q5. How does Auditive help prevent healthcare data breaches?
A5. Auditive automates trust decisions, detects access anomalies in real time, and offers end-to-end visibility across users, systems, and third-party vendors.