Understanding Third-Party Risk Management: Types and Importance
Every organization today relies on an ecosystem of third-party vendors, but each partnership introduces potential operational, financial, and security risks. Understanding and actively managing these risks is critical to protecting business continuity and sensitive data.
Third-party risk management provides a structured approach to assess, monitor, and mitigate threats from external vendors, turning potential vulnerabilities into manageable, transparent processes.
This blog breaks down the lifecycle of third-party risk management, from vendor identification to offboarding, showing how organizations can build a repeatable, measurable system.
Key Takeaways
Lifecycle Approach Matters: Vendor risk must be managed across all stages: identification, evaluation, monitoring, and offboarding.
Continuous Monitoring is Key: Static assessments leave blind spots; continuous updates catch new risks in real time.
Automation Drives Efficiency: Reduces manual workload and accelerates vendor review cycles.
Framework Flexibility: Evaluate vendors against relevant industry standards or custom controls.
Collaboration Across Teams: Integrated workflows ensure risk insights are actionable for procurement, security, and operations.
Understanding Third-Party Risk Management
Engaging third parties, whether for IT services, software development, or supply chain operations, offers efficiency, cost savings, and specialized expertise. Yet it also introduces operational, security, and financial vulnerabilities that can ripple across your organization.
Third-party risk management is the structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating these risks, ensuring that outsourcing doesn’t compromise business continuity or sensitive data protection.
At its core, third-party risk management transforms vendor engagements from potential weak points into controlled, resilient partnerships. It combines due diligence, risk assessment, remediation, and continuous monitoring, enabling organizations to maintain operational resilience, protect intellectual property, and uphold environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards.
Learn more about: Understanding ESG Requirements: Key Insights and Regulations
Why Third-Party Risk Management Matters
Third-party relationships are no longer just transactional; they directly influence business security, operational continuity, and reputation. With vendors and service providers accessing sensitive systems and customer data, unchecked third-party exposure can create entry points for cyberattacks and operational disruptions. Extending risk management to subcontractors and other fourth parties is critical to closing these gaps.
Effective third-party risk management provides measurable safeguards and strategic oversight across all external relationships:
Ensures regulatory alignment: Regulations like GDPR and CCPA hold organizations accountable for third-party breaches, making oversight essential to avoid fines and reputational harm.
Drives operational resilience: By identifying vulnerabilities in supplier and service provider networks, businesses can prevent delays, defects, and disruptions, especially in complex supply chains.
Strengthens cybersecurity posture: Extending security protocols to third parties mitigates potential data breaches and leaks from external access points.
Protects reputation and brand trust: Monitoring third-party practices prevents unethical or negligent actions that could damage credibility with clients and stakeholders.
Reduces business impact and complexity: Effective TPRM limits financial and operational exposure while streamlining oversight across multiple external partners.
Ultimately, integrating third-party risk management into your operational strategy transforms vendor oversight from a reactive checklist into a proactive, measurable, and continuous control mechanism.
Mastering Third-Party Risk Management: Key Best Practices
Building a resilient third-party risk management program requires more than policies; it demands practical, data-driven actions.
Effective third-party risk management hinges on focusing resources where they matter most, leveraging automation, and expanding the scope beyond cybersecurity alone. Here’s how organizations can achieve a robust program:
Prioritize Your Vendor Inventory:
Segment vendors into tiers based on risk and criticality: Tier 1 for high-risk, high-impact vendors; Tier 2 for moderate; and Tier 3 for low. Factor in sensitive data handling, critical business functions, and contract value to determine prioritization. High-tier vendors require deeper due diligence, often including on-site assessments.
Use Automation:
Streamline repetitive TPRM tasks like onboarding, risk scoring, assigning mitigation responsibilities, triggering reassessments, and reporting. Automated workflows reduce manual effort, maintain consistency, and ensure continuous monitoring of high-risk vendors.
Think Beyond Cybersecurity:
A complete third-party risk management program considers reputational, operational, financial, geopolitical, compliance, and environmental risks. Limiting focus to cybersecurity leaves organizations exposed to broader vulnerabilities.
Adopting these practices transforms vendor oversight from reactive checks into a proactive, continuous process, reducing operational disruptions and supporting informed business decisions.
Auditive takes third-party risk management a step further by providing a dynamic, always-updated view of your vendor ecosystem. Instead of static assessments, it continuously monitors risk signals across critical vendors, helping teams act swiftly and maintain confidence in third-party relationships.
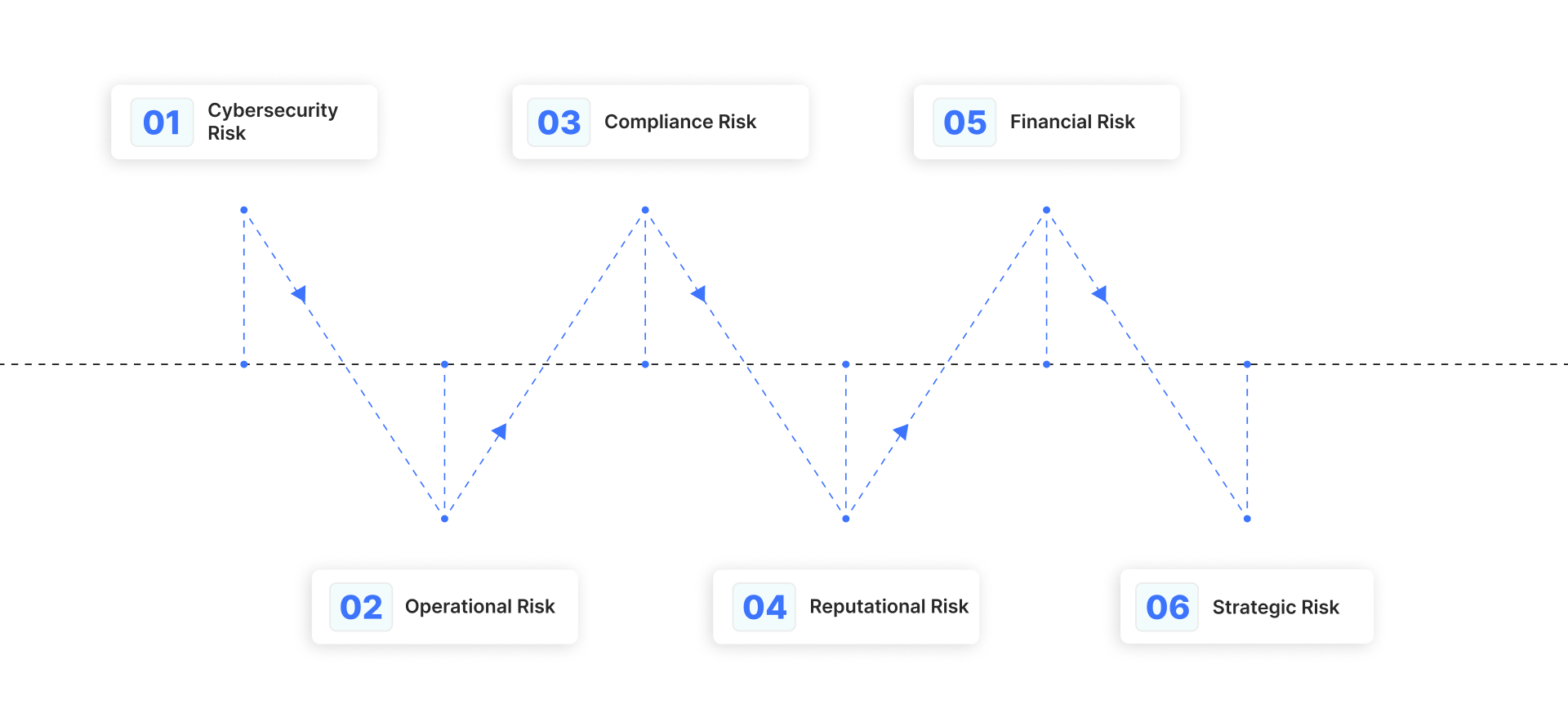
Identifying Key Risks in Third-Party Risk Management
Third-party vendors are critical to modern business operations, but they also introduce exposures that can disrupt your organization. Understanding these risks is essential for effective third-party risk management.
Cybersecurity Risk
Vendors may expose your organization to data breaches, cyberattacks, or other security vulnerabilities. Mitigation involves thorough pre-onboarding due diligence and ongoing monitoring throughout the vendor lifecycle to catch risks before they escalate.
Operational Risk
Vendor failures, delays, or service interruptions can disrupt day-to-day operations. This risk is managed through clearly defined service-level agreements (SLAs) and, for critical vendors, backup arrangements to maintain business continuity.
Legal, Regulatory, and Compliance Risk
Third-party actions can affect your adherence to laws, regulations, and contractual obligations, such as GDPR or HIPAA. This risk is especially relevant for industries like finance, healthcare, and government, where violations can lead to severe penalties.
Reputational Risk
Negative public perception stemming from a vendor’s failures, poor service, mishandled data, or security breaches can damage your organization’s trustworthiness. Incidents like the 2013 Target data breach show how reputational damage often spreads beyond the immediate event.
Financial Risk
Vendor mismanagement or failures can impact revenue, profits, or project viability. Supply chain breakdowns, cost overruns, or delayed product launches are common examples that can directly affect financial outcomes.
Strategic Risk
Decisions or performance issues from vendors may prevent your organization from achieving long-term objectives. Misalignment with business goals or reliance on underperforming partners can stall growth or innovation.
These risk areas often overlap. For example, a cybersecurity breach may simultaneously trigger operational disruptions, regulatory violations, reputational harm, and financial loss. Effective third-party risk management addresses these interconnected risks systematically.
Auditive transforms vendor risk from a static assessment into a continuous monitoring system. By tracking performance and exposures in real time, it helps teams make informed decisions, respond proactively to threats, and maintain a strong risk posture across all vendor categories.
Mapping Critical Third-Party Risks: A Strategic View
Third-party risk management is essential for safeguarding operational continuity, financial stability, and reputation. Identifying the types of risks vendors and partners can introduce helps organizations build a proactive and resilient risk management strategy.
Cybersecurity Risk
Vendors with access to your systems, networks, or data can become a vector for cyberattacks, including ransomware, phishing, or data breaches. These incidents not only compromise sensitive information but can also cascade into operational disruptions, regulatory violations, and financial losses. Continuous vendor due diligence, security questionnaires, penetration testing, and automated monitoring are key strategies to mitigate cybersecurity exposure.
Operational Risk
Operational risk arises when a third party fails to deliver critical services or products, causing business disruptions. This could include delayed shipments, system outages, or inadequate service support. Organizations often manage these risks through clear Service Level Agreements (SLAs), contingency planning, and identifying backup vendors for critical functions to ensure uninterrupted operations.
Legal and Regulatory Risk
Third parties can expose organizations to legal and regulatory consequences if they fail to adhere to applicable laws, contractual obligations, or data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific rules. Assessing a vendor’s regulatory posture, monitoring compliance obligations, and maintaining documented oversight are essential steps to mitigate these risks.
Must Read: HITRUST vs HIPAA: Key Differences Explained
Reputational Risk
A vendor’s actions or failures can directly affect public perception of your organization. Poor service delivery, negative media coverage, or data breaches caused by vendor negligence can erode customer trust and stakeholder confidence. Reputational risk management includes monitoring vendor behavior, incident response planning, and engaging in proactive communication strategies.
Financial Risk
Vendors can impact your organization’s financial health through cost overruns, failed deliveries, or mismanaged contracts. Examples include disrupted supply chains, pricing disputes, or underperforming service contracts. Financial risk mitigation involves contract clarity, continuous performance evaluation, and scenario planning for high-impact vendors.
Strategic Risk
Strategic risk occurs when a vendor’s decisions or performance hinder your organization’s long-term objectives. Examples include dependency on a single supplier, misalignment with business goals, or inability to scale with your growth. Addressing strategic risk involves vendor diversification, alignment of vendor capabilities with corporate objectives, and regular strategic reviews.
With Auditive, these risks are continuously monitored and scored, enabling organizations to transform third-party risk management from a static review into a dynamic, real-time oversight system. This ensures informed decision-making and mitigates potential threats before they impact business performance.
Managing the Third-Party Vendor Lifecycle
Managing third-party vendors isn’t a one-time task; it’s a continuous process that spans the entire relationship lifecycle. A strong third-party risk management program ensures risks are identified, assessed, mitigated, and monitored at every stage, from onboarding to offboarding.
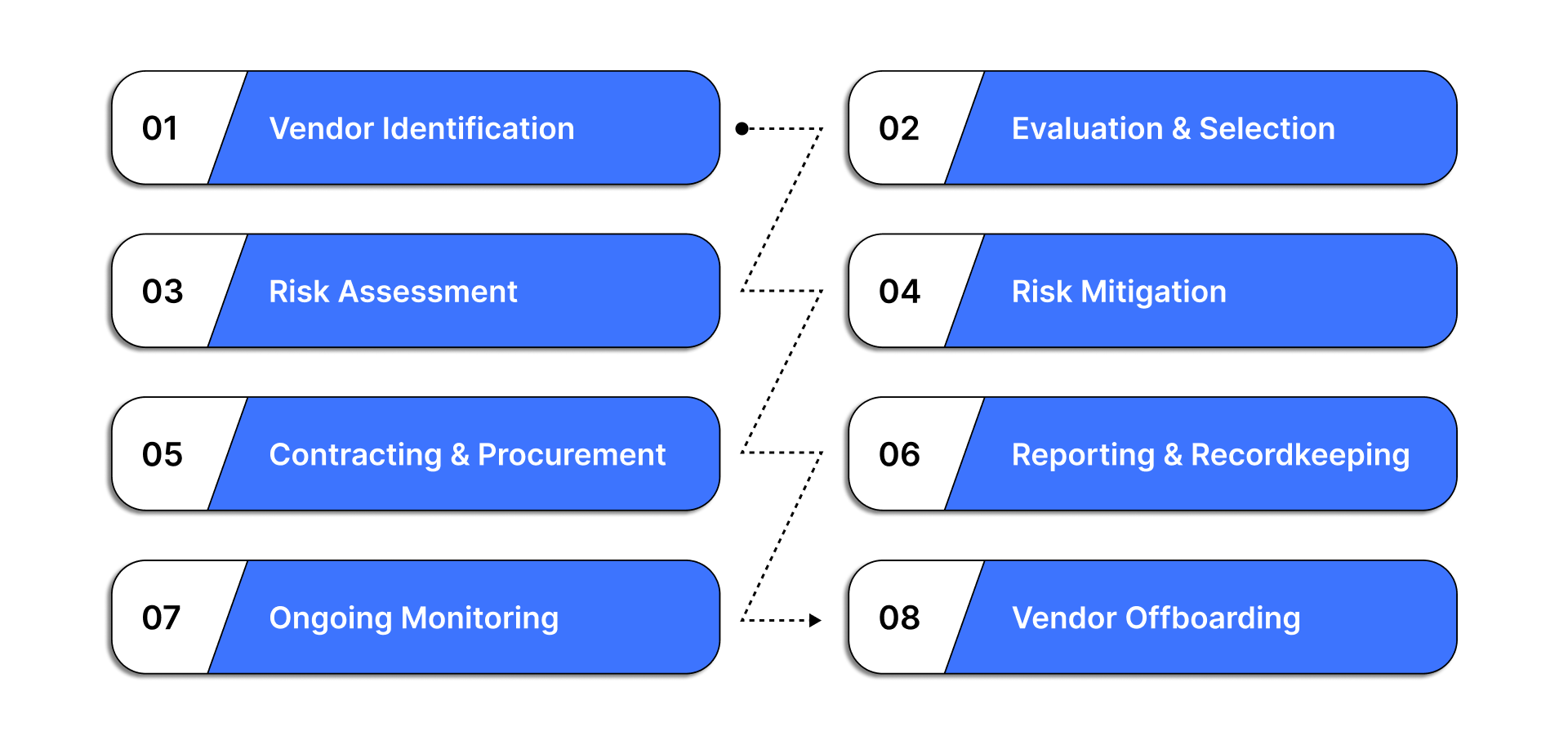
Key Phases of an Effective Third-Party Risk Management Lifecycle:
1. Vendor Identification
Establish a comprehensive inventory of all current and potential third parties. Consolidate existing vendor information from spreadsheets, procurement systems, CMDBs, and department interviews. Self-service portals can help business units add new vendors while capturing details such as:
Data types processed
Hosting information and certifications
Business context and scope of engagement
Vendor contact and expected procurement timelines
This information helps classify vendors by inherent risk, forming the foundation for your risk management strategy.
2. Evaluation & Selection
Assess RFPs and proposals against your organisation’s needs and risk appetite. Consider operational fit, security practices, financial stability, and regulatory alignment to select vendors that complement your risk management objectives.
3. Risk Assessment
Conduct detailed evaluations of vendors using standards like:
ISO 27001 & ISO 27701
NIST SP 800-53
SIG Core & SIG Lite
CSA CAIQ
Industry-specific frameworks such as HITRUST or HECVAT may also apply. Tools like third-party risk exchanges or assessment automation platforms reduce effort while providing structured, comparable insights.
4. Risk Mitigation
Once risks are identified, they are scored and assigned a risk owner. Mitigation involves validating that controls are in place to reduce risk to an acceptable residual level. Continuous monitoring is critical to detect events like breaches, regulatory updates, or negative publicity that could elevate risk.
5. Contracting & Procurement
Contracts should include clauses covering:
Scope of services/products
Data processing and protection
SLAs, deliverables, and response times
Confidentiality, IP ownership, indemnification, and liability
Termination clauses and relationship terms
Reviewing these clauses ensures vendors adhere to your risk and operational requirements.
6. Reporting & Recordkeeping
Centralized dashboards help maintain visibility and track key metrics such as:
Total supplier count and classification by risk
Status of risk assessments and contracts
Risks grouped by severity and stage in the mitigation process
Historical risk trends and incidents
Maintaining an auditable record ensures transparency and facilitates regulatory reporting.
7. Ongoing Monitoring
Risk is dynamic; vendor performance, financial health, regulatory landscape, and industry developments must be continuously observed. Monitor:
Mergers, acquisitions, or divestitures
Internal process or operational changes
Negative news or unethical behaviour
Contract modifications and SLA breaches
Financial viability and workforce changes
Continuous oversight helps proactively detect and address emerging risks.
8. Vendor Offboarding
Proper offboarding ensures security and regulatory integrity. Document all offboarding steps, revoke access, retrieve assets, and maintain a complete evidence trail to demonstrate effective risk management.
Auditive elevates this lifecycle from static checkpoints to a live, dynamic system. By automating risk detection, real-time monitoring, and reporting, your third-party risk management policy becomes actionable, scalable, and continuously up-to-date, ensuring your vendor oversight is not only documented but also operational.
How Auditive Supports the Third-Party Risk Management Lifecycle (Accurate & Up-to-Date)
Auditive aligns directly with each phase of a third-party risk management lifecycle, from onboarding to ongoing oversight, offering tools that automate workflows, update vendor posture in real time, and provide a shared basis for risk decisions.
Instant Vendor Intake & Baseline Risk Data: Through AuditiveX Free, you can add a new vendor immediately. Even if the vendor hasn’t submitted documents, Auditive generates a baseline risk profile using public metadata and known signals, giving you an initial view of exposure in seconds.
Dynamic Vendor Profiles with Continuous Updates: Auditive continuously monitors vendor posture, including incident reports, control or certification changes, and public threat signals, ensuring that your vendor data doesn’t stale the moment it’s collected.
AI‑Powered Risk Reviews & Questionnaire Automation: Security questionnaires, assessments against frameworks (e.g., ISO, SOC 2), and document reviews are automated, reducing manual burden and speeding up vendor evaluation cycles.
Framework‑Agnostic and Customizable Controls Mapping: Auditive supports multiple industry and custom frameworks, allowing you to evaluate vendors against standards relevant to your business, not forcing a one-size-fits-all checklist.
Integrated Workflows and Collaboration Across Teams: With pre‑built integrations and in‑platform communication, procurement, security, and operations can review vendor risk together, eliminating siloed tracking and duplicate efforts.
In effect, Auditive transforms vendor oversight from a periodic, manual process into a continuously monitored, automated lifecycle, making each stage of third-party risk management actionable with minimal overhead.
Final Thoughts
Effectively managing third-party risk is no longer optional; it’s central to safeguarding your operations, data, and reputation. A structured third-party risk management approach ensures each phase, from vendor identification to offboarding, is monitored, mitigated, and continuously improved.
Platforms like Auditive transform this process from manual, point-in-time assessments into a live, continuously updated system, giving organizations real-time visibility into vendor risk, automating assessments, and reducing operational friction.
Schedule a demo with Auditive to see how your organization can streamline vendor oversight, reduce risk exposure, and gain actionable insights across your entire third-party ecosystem.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a vendor risk management policy and a lifecycle?
A policy defines the rules and expectations; the lifecycle outlines the operational stages from vendor onboarding to offboarding, ensuring ongoing risk visibility.
2. How often should vendors be monitored for risks?
Monitoring should be continuous, with automated alerts for changes in certifications, incidents, financial stability, or compliance status.
3. Can Auditive integrate with existing procurement or risk systems?
Yes. Auditive is designed to work alongside existing enterprise systems, allowing seamless data sharing and workflow automation.
4. What types of risks are most commonly tracked in a 3rd-party program?
Operational, security, financial, and regulatory risks are prioritized, but programs can be customized for any vendor-related risk exposure.
5. Is Auditive suitable for both small and large organizations?
Absolutely. Auditive scales across enterprise-level portfolios as well as smaller vendor ecosystems, providing consistent risk insights regardless of size.