PCI Audit Requirements and Preparation Steps
Ensuring the security of payment card data is a critical responsibility for any organization handling cardholder information. A PCI audit helps businesses verify that their systems, processes, and policies align with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). By undergoing a PCI audit, organizations can identify vulnerabilities, strengthen data protection measures, and maintain compliance with industry requirements.
Beyond regulatory adherence, PCI audits provide a structured approach to safeguarding sensitive payment information, reducing the risk of data breaches, and building trust with customers and partners. Proper preparation and understanding of the audit process are essential to achieve a successful assessment and maintain a strong security posture.
Let’s explore the details of a PCI audit and what it entails.
Before we dive in:
PCI DSS audits are critical for protecting cardholder data and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Preparation involves gap analysis, documenting activities, monitoring security controls, and performing risk assessments.
Maintaining accurate network diagrams, tracking access, and examining internal infrastructure is essential.
Risk management is key to ensuring all third-party partners meet compliance standards.
Auditive provides continuous monitoring, risk visibility, and streamlined audit preparation.
What is a PCI Audit?
A PCI audit is an evaluation process designed to ensure that an organization handling payment card data complies with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Developed by the PCI Security Standards Council, this standard is supported by major financial institutions, software developers, vendors, and merchants, with the goal of protecting cardholder information from unauthorized access or misuse.
During a PCI audit, a company’s security measures, policies, and processes are assessed to determine how effectively cardholder data is safeguarded throughout its lifecycle, from collection to storage and processing. This assessment is conducted by either an Internal Security Assessor (ISA) or an external Qualified Security Assessor (QSA).
To achieve compliance, organizations must meet the 281 specific requirements outlined in PCI DSS. These requirements cover a broad range of security controls, ensuring that all merchants and service providers who store, process, or transmit cardholder data maintain a consistently secure environment.
How Does a PCI DSS Audit Work?
A PCI DSS audit is designed to identify areas of non-compliance, provide guidance on remediation, and ensure that your organization meets the required standards for protecting cardholder data. The process typically involves several key steps:
Engage a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA): Only QSAs approved by the PCI Council can perform official audits. You can find a verified QSA from the PCI Council’s official list. It’s advisable to speak with multiple QSAs to assess their experience and approach before making a selection. Avoid companies claiming to be QSAs if they are not on the official list, as they may provide unrelated services or outsource your audit.
Review of Cardholder Data Environment (CDE): The auditor examines all components, devices, networks, and applications that store, process, or transmit cardholder data. This includes hardware, software, and the policies and procedures governing the use of these systems.
On-Site Assessment: The QSA visits your organization to observe operations, verify processes, and assess adherence to PCI DSS controls. The goal is not to penalize but to help identify vulnerabilities and recommend improvements.
Collaboration with a Compliance Leader: Assign a dedicated compliance leader from your organization to coordinate the audit, ensure corrective actions are implemented, and communicate effectively across teams. This person acts as the central point for compliance responsibilities and ensures accountability throughout the organization.
Throughout the audit, maintaining cooperation and engagement with the QSA is critical. Their role is to guide your organization toward full compliance, helping to secure cardholder data and strengthen your overall security posture.
Who Must Perform a PCI DSS Audit?
Compliance with PCI DSS is essential for any organization that processes, accepts, transmits, or stores payment card information. The audit requirements depend on the size of the organization and the volume of transactions handled.
Key points include:
High-Volume Merchants: Merchants processing over 1 million to 6 million payment card transactions annually (thresholds may vary by card brand) are required to undergo a full PCI DSS audit.
Large Service Providers: Service providers that store, transmit, or process more than 300,000 card transactions per year must also complete a PCI DSS audit.
Smaller Merchants: Organizations with lower transaction volumes typically complete a Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) and an Attestation of Compliance (AOC) instead of a full audit.
Data Breach Victims: Any merchant or service provider that has experienced a data breach exposing cardholder information must undergo an annual on-site PCI DSS audit, regardless of transaction volume.
By clearly defining who must be audited, organizations can ensure they meet compliance obligations and maintain strong security measures for cardholder data.
Also Read: How to Prevent Data Breaches in Healthcare
PCI Audit Requirements
Organizations subject to PCI DSS audits must meet specific requirements to ensure the security of cardholder data. The exact obligations depend on the organization’s PCI compliance level, which is determined by transaction volume and risk exposure. Core requirements typically include:
Engaging a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA): For on-site audits, a PCI DSS–certified QSA evaluates the organization’s policies, controls, and practices within its Cardholder Data Environment (CDE).
Internal Security Assessment: Organizations may appoint Internal Security Assessors (ISA) who are trained and certified by the PCI Security Standards Council to conduct annual internal audits.
Report on Compliance (ROC): After evaluation, the QSA or ISA generates a ROC to confirm compliance for submission to the acquiring bank.
Ongoing Security Measures: Compliance is not a one-time activity. Organizations must continuously test and monitor their systems through vulnerability scans, penetration tests, and controls testing to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of credit and debit cardholder data.
Documentation and Evidence: Maintaining detailed records of all compliance activities, security measures, and audit findings is essential for demonstrating adherence during the annual audit cycle.
Meeting these requirements ensures that an organization not only achieves PCI DSS compliance but also strengthens its overall data security posture and reduces the risk of breaches.
For organizations seeking streamlined management of these requirements, platforms like Auditive can provide continuous monitoring, compliance tracking, and real-time reporting across all payment systems.
How to Prepare Yourself for the PCI DSS Audit
Preparing for a PCI DSS audit requires meticulous planning, comprehensive documentation, and ongoing monitoring to protect cardholder data and ensure compliance. Below is a detailed step-by-step guide to get your organization ready for the audit.
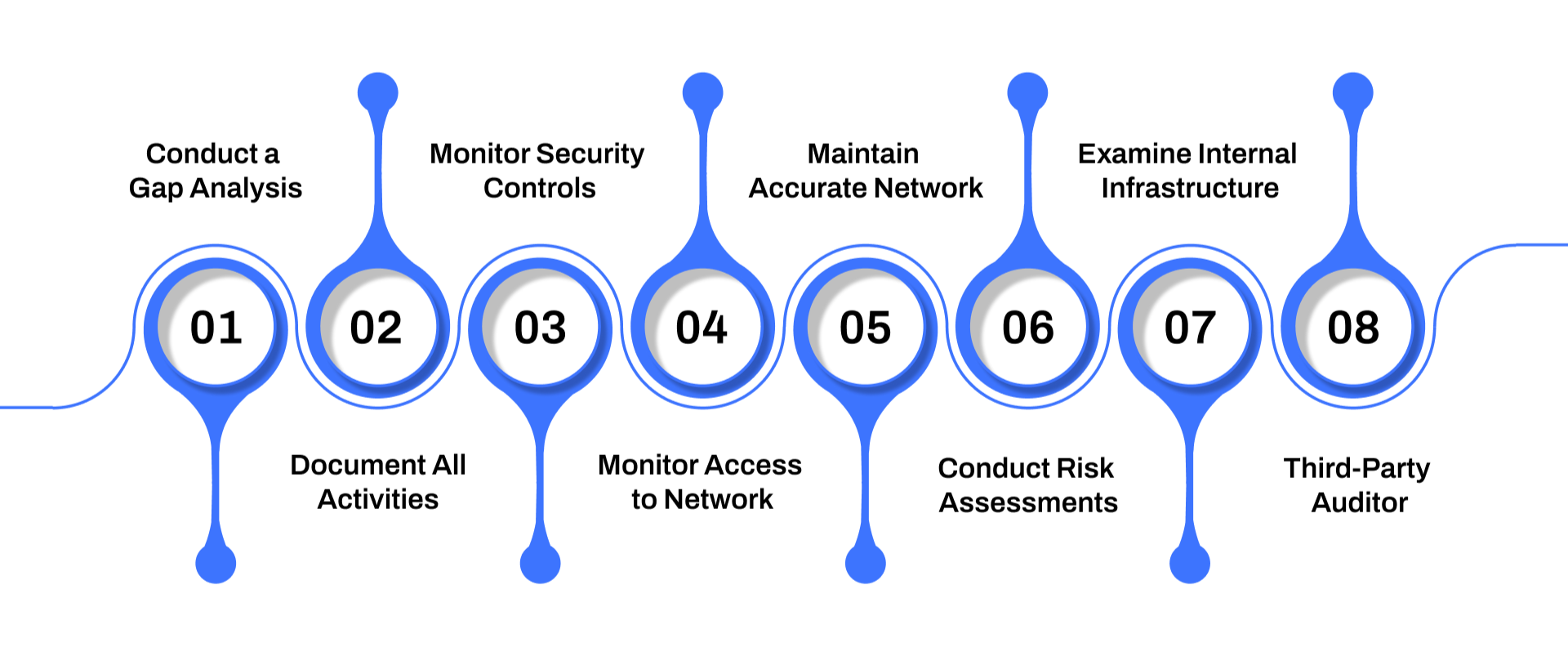
1. Conduct a Gap Analysis and Remediation
Begin by assessing your current information security program against the latest PCI DSS 4.0 requirements. Identify areas where your controls or processes are insufficient and create a remediation plan.
Key actions:
Identify gaps in access controls, encryption methods, and monitoring processes.
Develop remediation strategies such as implementing firewalls, anti-virus software, multi-factor authentication, and encryption.
Provide staff security awareness training to mitigate human error risks.
Closing note: A thorough gap analysis ensures that all weaknesses are addressed proactively, reducing the risk of non-compliance and enhancing your overall security posture.
2. Document All Activities
Maintaining detailed documentation is critical for demonstrating compliance during the audit. Every process affecting cardholder data should be recorded clearly.
Focus on documenting:
Encryption protocols, key management practices, and authentication mechanisms.
Cardholder data handling procedures across all systems, including storage, transmission, and processing.
Updates to business policies, IT systems, or software that could impact PCI DSS compliance.
Closing note: Comprehensive documentation not only provides proof of compliance but also establishes a clear reference framework for your internal teams and auditors.
3. Monitor Security Controls Continuously
Continuous monitoring ensures that security measures remain effective and consistently enforced across the organization.
Include:
Periodic reviews of all security controls in stores, data centers, and back-office environments.
Verification that staff consistently follow security protocols and access policies.
Assessment of changes to technologies, systems, or processes for potential impact on compliance.
Closing note: Ongoing monitoring strengthens your control environment and ensures that vulnerabilities are addressed promptly, keeping your organization audit-ready at all times.
4. Track and Monitor Access to Network Resources
Proper logging and access monitoring are essential to detect suspicious activity and support forensic investigations.
Key steps:
Maintain comprehensive audit trails for all systems and applications handling cardholder data.
Monitor network access to quickly identify unauthorized activity or anomalies.
Use logs for investigations, demonstrating accountability and control effectiveness.
Closing note: Accurate tracking of network activity not only helps prevent breaches but also provides evidence of compliance for auditors.
5. Maintain Accurate Network Diagrams
Clear network diagrams help auditors understand how cardholder data flows through your infrastructure.
Ensure diagrams:
Include all systems that store, process, or transmit cardholder data.
Show segmentation between networks and firewall placements.
Reflect updates due to new systems or changes in infrastructure.
Closing note: Well-documented network diagrams simplify audits, improve data security, and reduce the likelihood of compliance gaps.
6. Conduct Risk Assessments
Regular risk assessments identify vulnerabilities and help prioritize remediation efforts.
Include:
Evaluating potential threats and their likelihood of occurrence.
Assessing the impact of each risk on cardholder data.
Implementing mitigation strategies, addressing high-risk areas first.
Closing note: A structured risk assessment ensures that your organization is prepared for potential threats and demonstrates a proactive approach to security.
Learn more about: How to Conduct a Comprehensive Security Risk Assessment?
7. Examine Internal Infrastructure
Testing internal systems regularly ensures ongoing compliance and identifies emerging vulnerabilities.
Focus on:
Web Application Testing – Verify that all applications processing cardholder data are secure.
Vulnerability Scans – Conduct quarterly internal and external scans.
Penetration Testing – Simulate attacks annually to evaluate system defenses.
Closing note: Routine infrastructure evaluations maintain security and reduce the chance of audit findings related to system weaknesses.
8. Consult with a Third-Party Auditor (QSA)
Engaging a Qualified Security Assessor provides expertise, validates controls, and identifies gaps before the audit begins.
Benefits include:
Clarifying PCI DSS requirements specific to your environment.
Verifying remediation efforts and compensating controls.
Maintaining ongoing compliance support throughout the year.
Closing note: Working with a QSA ensures audit preparedness, reduces surprises, and provides expert guidance to maintain strong PCI DSS compliance.
By following these steps, organizations can approach PCI DSS audits confidently, mitigate risks to cardholder data, and maintain a secure, compliant environment year-round. A proactive approach not only satisfies auditors but also strengthens your overall security posture.
For continuous monitoring and simplified PCI compliance, Auditive offers automated workflows, centralized dashboards, and real-time vendor risk insights, helping you stay audit-ready without manual overhead.
Streamline PCI DSS Compliance with Auditive
Auditive simplifies PCI DSS compliance by providing a centralized platform to monitor, assess, and manage all your third-party relationships. By using automated workflows, organizations can reduce manual effort, track compliance in real time, and maintain all critical data.
Key benefits of using Auditive for PCI compliance:
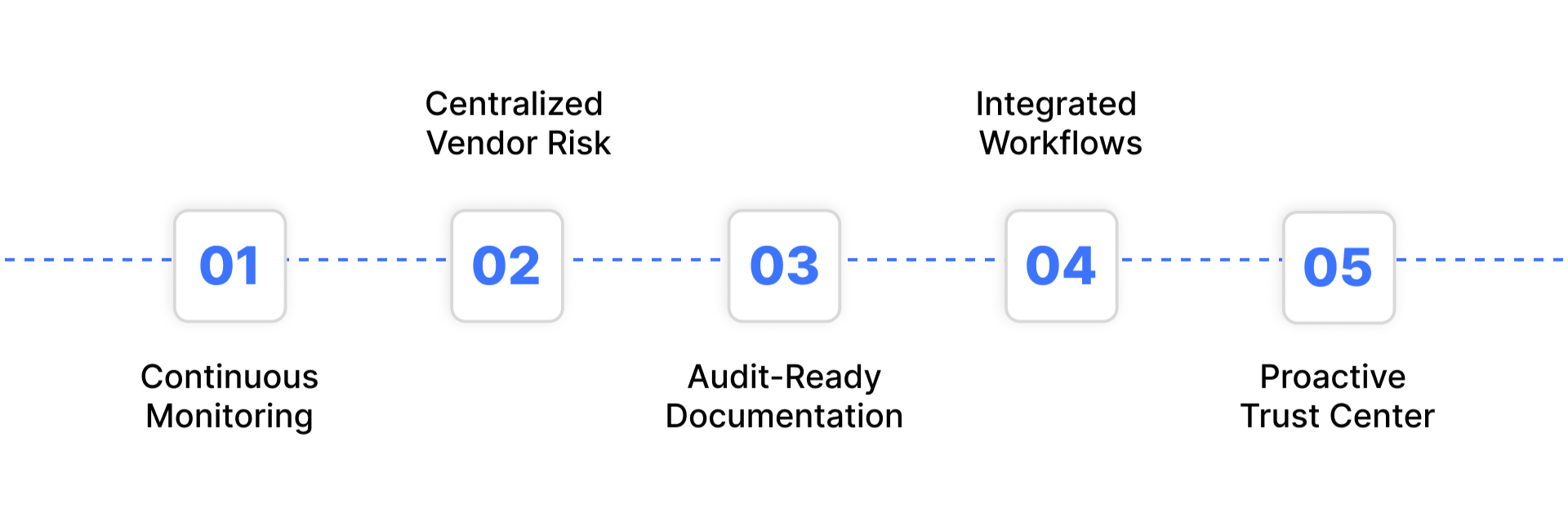
Continuous Monitoring: Automatically track security controls, access logs, and system changes across your cardholder data environment.
Centralized Risk Assessment: Maintain a complete inventory of all vendors, monitor risk levels, and proactively address vulnerabilities.
Audit-Ready Documentation: Collect and organize evidence, reports, and compliance records for easy review during PCI DSS audits.
Integrated Workflows: Seamlessly connect Auditive with your existing systems for procurement, IT, and operations, minimizing disruptions while ensuring compliance.
By maintaining thorough preparation, regular risk assessments, and clear oversight of your cardholder data environment, organizations can not only meet PCI DSS requirements but also strengthen overall cybersecurity posture and build trust with stakeholders.
Final Thoughts
Preparing for a PCI DSS audit can seem daunting, but with careful planning, comprehensive risk assessment, and continuous monitoring, your organization can ensure compliance while strengthening security across your cardholder data environment. Risk Assessment plays a critical role in this process, ensuring that all third-party vendors handling sensitive data meet stringent security standards. By utilizing a centralized approach, organizations can maintain transparency, track compliance across vendors, and safeguard valuable information.
Platforms like Auditive simplify this process by providing continuous monitoring, risk assessment workflows, and centralized documentation, making PCI DSS compliance manageable and efficient. Whether it’s monitoring vendors, maintaining audit-ready records, or proactively addressing security gaps, Auditive ensures your organization stays ahead of compliance challenges.
Book a demo with Auditive to see how it can make your PCI DSS audit preparation seamless.
FAQs
1. What is a PCI DSS audit?
A PCI DSS audit evaluates an organization’s adherence to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards to ensure cardholder data is protected.
2. Who must perform a PCI DSS audit?
Organizations that handle cardholder data, including merchants and service providers, must undergo audits by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) or internal security teams, depending on their merchant level.
3. How often should a PCI DSS audit be conducted?
Annual audits are typically required, but organizations should continuously monitor security controls throughout the year to maintain compliance.
4. What are key steps to prepare for a PCI DSS audit?
Conduct a gap analysis, document all processes, monitor security controls, track network access, maintain network diagrams, perform risk assessments, and review internal infrastructure.
5. How can risk management help with PCI DSS compliance?
It ensures that all third-party vendors handling cardholder data meet compliance standards, reducing security risks and supporting audit readiness.