Understanding Zero Trust Security Benefits
Traditional security models often operate on the assumption that everything inside an organization's network can be trusted. But as cyber threats grow more advanced and employees, data, and devices become increasingly distributed, that assumption no longer holds true. This is where Zero Trust Security steps in, a modern approach that challenges the old perimeter-based mindset.
By verifying every user, device, and request, regardless of location, Zero Trust helps organizations reduce risk, improve visibility, and stay resilient in the face of evolving threats. This blog explores what Zero Trust Security means, why it matters, how it works, and how businesses can unlock its full potential.
Overview
Zero Trust means no implicit trust; every user, device, and connection must be verified continuously, regardless of location.
It protects modern environments like remote workforces, multi-cloud setups, and SaaS-heavy ecosystems from evolving threats.
Benefits include stronger access control, reduced attack surface, and better compliance with frameworks like NIST and GDPR.
Common challenges include legacy system integration and cultural resistance, but they can be overcome with the right architecture.
Platforms like Auditive extend Zero Trust to vendors with automated risk assessments, real-time monitoring, and a Trust Center for continuous assurance.
Understanding Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust is more than just a concept; it represents a fundamental shift in how organizations approach security. Unlike traditional models that assume users and systems within the network perimeter can be trusted, Zero Trust operates on a simple but powerful principle: never trust, always verify.
In this model, every access request is treated with scrutiny, whether it originates inside or outside the organization’s environment. Users, devices, applications, and data are all considered potentially untrusted until they prove otherwise through continuous authentication, policy checks, and strict access controls.
This shift away from perimeter-based thinking reflects the reality of modern IT environments. With cloud services, remote teams, mobile endpoints, and IoT devices rapidly expanding the threat surface, relying on location or network boundaries for trust is no longer sufficient. Instead, Zero Trust focuses on protecting resources directly, no matter where they reside, by enforcing access based on identity, context, and compliance.
The result is a more robust and resilient security posture, capable of defending against both external breaches and internal misuse.
Why Zero Trust Security Matters for Businesses?
With cloud adoption and hybrid work on the rise, the traditional network perimeter is no longer enough. Data now moves across devices, locations, and platforms, creating new entry points for cyber threats.
Zero Trust helps reduce this risk by removing the assumption that anything inside your network can be trusted. It enforces strict identity checks, continuous monitoring, and limited access across all systems.
Key reasons businesses need Zero Trust:
No implicit trust; every user, device, and request must be verified.
Cloud and hybrid protection applies consistent security across environments.
Stops lateral movement, limits access to what’s strictly necessary.
Reduces attack surfaces and shrinks exposure through segmentation and policy enforcement.
Supports compliance and helps meet standards like GDPR and PCI DSS.
Zero Trust isn’t just about better defense; it’s about smarter, more adaptive security.
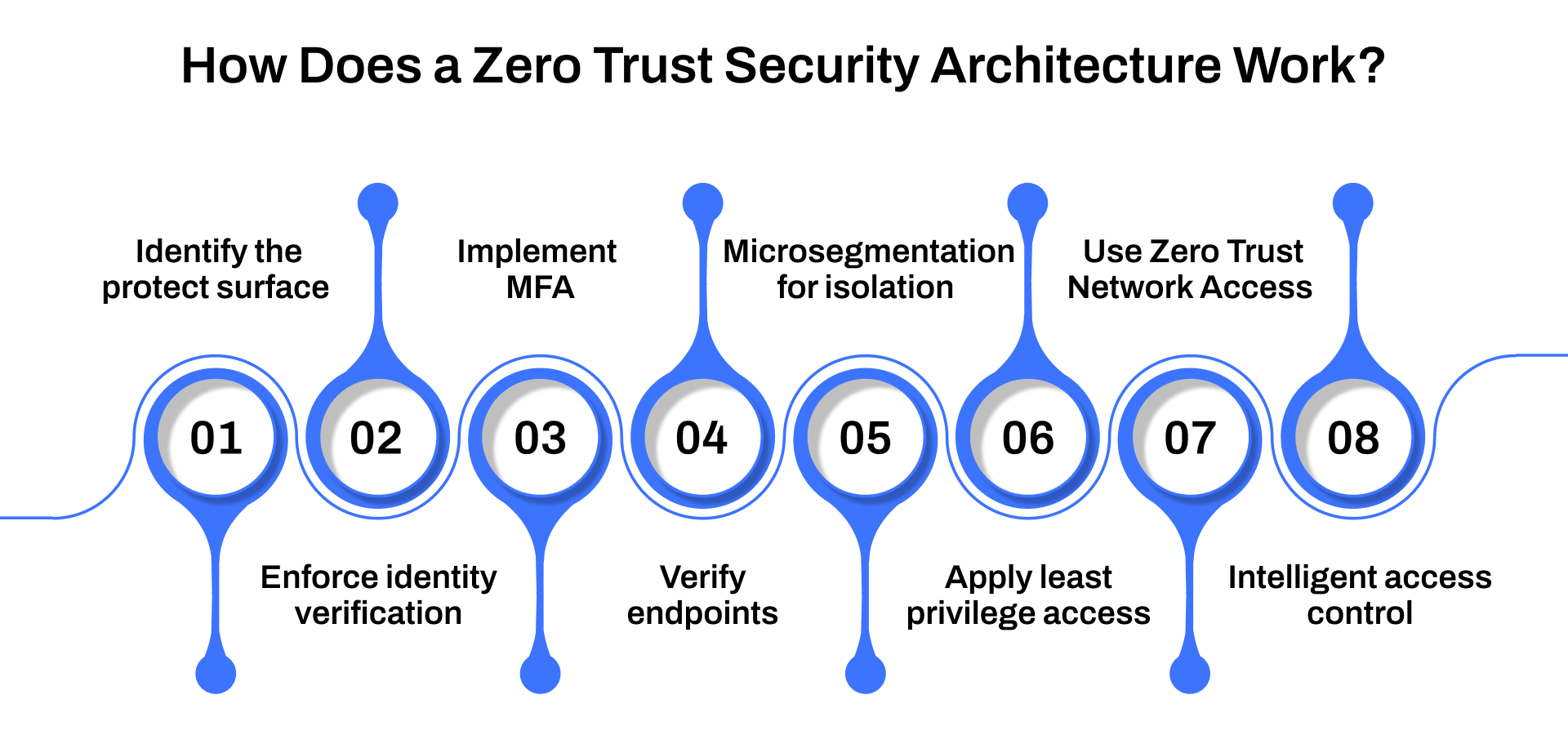
How Does a Zero Trust Security Architecture Work
As we discussed above, the Zero Trust Security architecture is built on a simple principle: never trust, always verify. Instead of assuming that everything inside the network is safe, it treats every user, device, and application as potentially untrusted until proven otherwise. Here’s how this model functions in practice:
1. Identify the protect surface
The foundation of Zero Trust begins with defining what needs the highest level of protection, your protected surface. This includes:
Data that is sensitive or regulated
Applications handling confidential processes
Assets such as servers, endpoints, or cloud platforms
Services critical to business operations
Unlike the ever-expanding attack surface, the protected surface is precise and manageable. By narrowing the focus, organizations can apply stronger controls exactly where they’re needed most.
2. Enforce strong identity verification
Access requests, regardless of origin, must pass strict identity verification. Users or devices are validated continuously, especially when behaviors change, such as logging in from a new location or using an unfamiliar device.
This isn’t limited to a one-time check. Continuous verification ensures that trust is evaluated based on real-time context, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
3. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwords alone are no longer enough. MFA adds additional layers of security by requiring users to confirm their identity through more than one method, like a code sent to a device or a biometric check. Even if one layer is compromised, others remain intact, dramatically reducing the likelihood of unauthorized entry.
4. Verify endpoints
Zero Trust goes beyond user validation. Every endpoint, laptops, smartphones, servers, must prove it’s secure and under the right user’s control. Tools like Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) help maintain visibility and control, scanning for vulnerabilities and enforcing security compliance before any device is allowed to connect.
5. Microsegmentation for targeted isolation
Rather than securing the entire network as one unit, microsegmentation divides it into small, secure zones. Each segment has its own access policies, which means even if an attacker breaches one area, the rest remains protected.
This method reduces lateral movement inside the network, a common tactic used by attackers once they gain initial access.
6. Apply least-privilege access
Users and devices should only have access to the data and systems they truly need. With least-privilege access, you limit unnecessary exposure, reduce the attack surface, and contain any potential damage from compromised accounts.
This approach also minimizes the burden on security systems, as fewer verification layers are triggered when access is restricted to only the essentials.
7. Use Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
ZTNA controls application-level access and removes the need for traditional VPNs. Every access session is verified based on the user's identity, device posture, and adherence to policy, regardless of whether the user is on the company network or working remotely.
ZTNA creates a secure, encrypted tunnel between the device and a proxy, hiding critical applications from public exposure. Only verified users can connect, keeping both internal and remote environments secure without compromising usability.
8. Intelligent access control with layer 7 and the Kipling method
At the perimeter of each microsegment, traffic is inspected at the application layer (Layer 7). It checks whether requests meet predefined security rules and blocks anything suspicious.
Using the Kipling method, the system asks fundamental questions, Who? What? When? Where? Why? and How?, before granting access. If the context doesn’t align with expected behavior, the request is denied.
A Zero Trust approach needs real-time decisions based on user behavior, device trust, and access context. Auditive supports this by continuously analyzing signals and enforcing dynamic access controls, helping organizations scale Zero Trust with confidence.
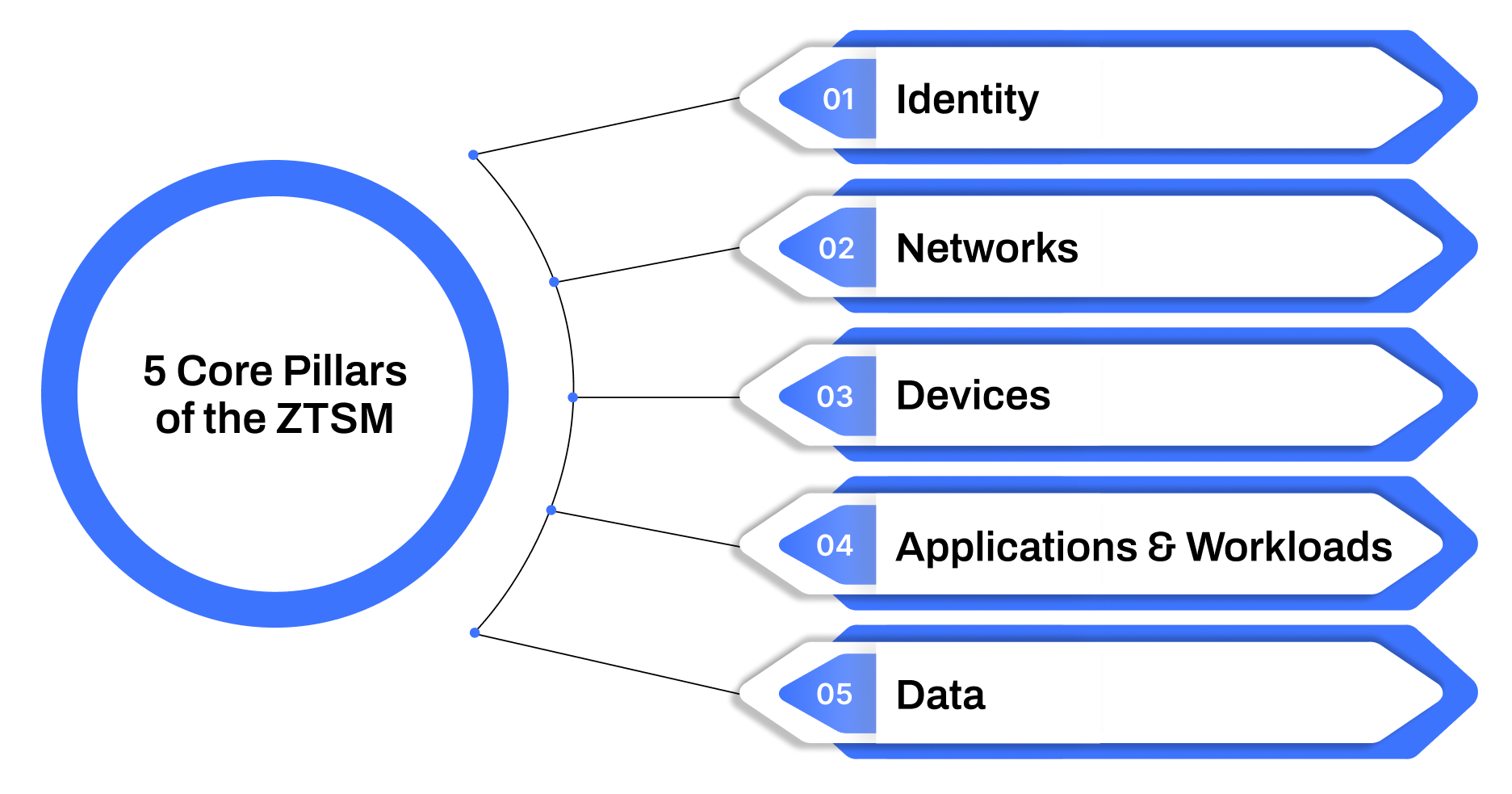
5 Core Pillars of the Zero Trust Security Model
Zero Trust isn't built on blind faith or static boundaries. Instead, it operates on the assumption that threats can exist both inside and outside the network. To enforce this mindset, organizations must architect their security strategies around five key pillars. Together, these elements ensure that access is precisely controlled, continuously evaluated, and always aligned with real-time risk.
1. Identity
Every access decision starts with identity. It's not enough to know a username and password, organizations need to be certain of who the user is and whether they’re authorized to do what they’re requesting. That’s where Identity and Access Management (IAM), Single Sign-On (SSO), and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) play a critical role. These controls verify identities dynamically and enforce role-based permissions, closing the door on impersonation and privilege creep.
2. Networks
Rather than treating the network as a single trusted zone, Zero Trust segments it into isolated environments. This microsegmentation ensures that if an attacker does gain access, their ability to move laterally is extremely limited. Every connection between systems, internal or external, is evaluated and secured individually.
3. Devices
Every connected device, whether it’s a laptop, smartphone, or printer, represents a potential point of compromise. Zero Trust demands that only compliant and recognized devices be granted access. This requires complete visibility into your device inventory, real-time health checks, and the ability to deny access if a device falls out of compliance.
4. Applications and workloads
Applications and workloads often communicate with one another behind the scenes, and these interactions can become blind spots. Zero Trust treats applications as untrusted by default, requiring continual verification. Runtime checks and behavioral monitoring help ensure applications operate within expected parameters.
5. Data
Zero Trust extends deeply into data protection. It’s not just about who accesses the data, but how it’s classified, stored, used, and moved. Encryption, dynamic access policies, and detailed audit trails ensure that sensitive information remains protected at every stage, whether it’s in motion, in use, or at rest.
What Are the Main Benefits of Zero Trust Security?
As digital infrastructure grows more distributed and complex, organizations need a framework that assumes nothing and verifies everything. That’s exactly what Zero Trust Security delivers, by shifting away from legacy perimeter defenses and moving toward identity-based, context-aware control at every level of access. The result is a stronger, more adaptable cybersecurity posture across your entire environment.
Here’s how a Zero Trust approach creates tangible security and operational advantages:
1. Stronger protection of sensitive data
Zero Trust architecture significantly lowers the risk of data breaches by enforcing continuous verification and tightly controlled access. Instead of trusting a device or user once and allowing persistent access, it requires ongoing validation based on role, behavior, and context. This minimizes opportunities for lateral movement and unauthorized data exposure, especially in cloud-native and hybrid environments.
2. Granular access control across users and devices
Rather than granting broad access based on network location, Zero Trust enforces the principle of least privilege. Every user and device must authenticate individually every time they attempt to connect. This not only reduces insider risk but also limits damage in the event of credential theft or endpoint compromise.
With platforms like Auditive, teams can automatically assess and align SaaS vendor access with real-time policy requirements, ensuring critical resources are shielded from unnecessary exposure.
3. Smaller attack surface, lower breach potential
Cloud migration, edge computing, and remote work have stretched the traditional perimeter beyond recognition. Zero Trust responds by shrinking the attack surface, micro-segmenting networks, isolating workloads, and preventing lateral movement. Even if an attacker gains access, containment measures stop them in their tracks.
Auditive reinforces this by giving organizations full visibility into how vendors interact with internal systems, helping teams rapidly detect configuration drift or new exposure points.
4. Scalability and adaptability to complex environments
Zero Trust architectures are built to evolve with the business. Whether scaling across multiple cloud providers or onboarding new tools and users, this framework adapts without sacrificing control. Adaptive authentication methods allow organizations to maintain strong security postures even in fast-moving, high-change environments.
5. Robust authentication standards
At the core of Zero Trust is identity assurance. Multi-factor authentication, certificate-based access, and tokenized login protocols are all key components. These controls ensure that only legitimate users and devices ever gain access, even if perimeter defenses are bypassed.
Auditive complements these mechanisms by verifying not just who is accessing your environment but also how secure the vendor’s practices are, based on industry frameworks like ISO 27001 and SOC 2.
6. Built-In compliance alignment
Zero Trust helps organizations stay compliant with evolving data privacy and security regulations by offering better control and documentation of data access, usage, and storage. Whether it’s GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, this model supports compliance by design, encrypting data in transit and at rest, and restricting access to authorized users only.
With Auditive’s Trust Center, organizations can consolidate vendor compliance evidence, track risk assessments, and demonstrate continuous security monitoring, turning audit readiness into a streamlined, automated process.
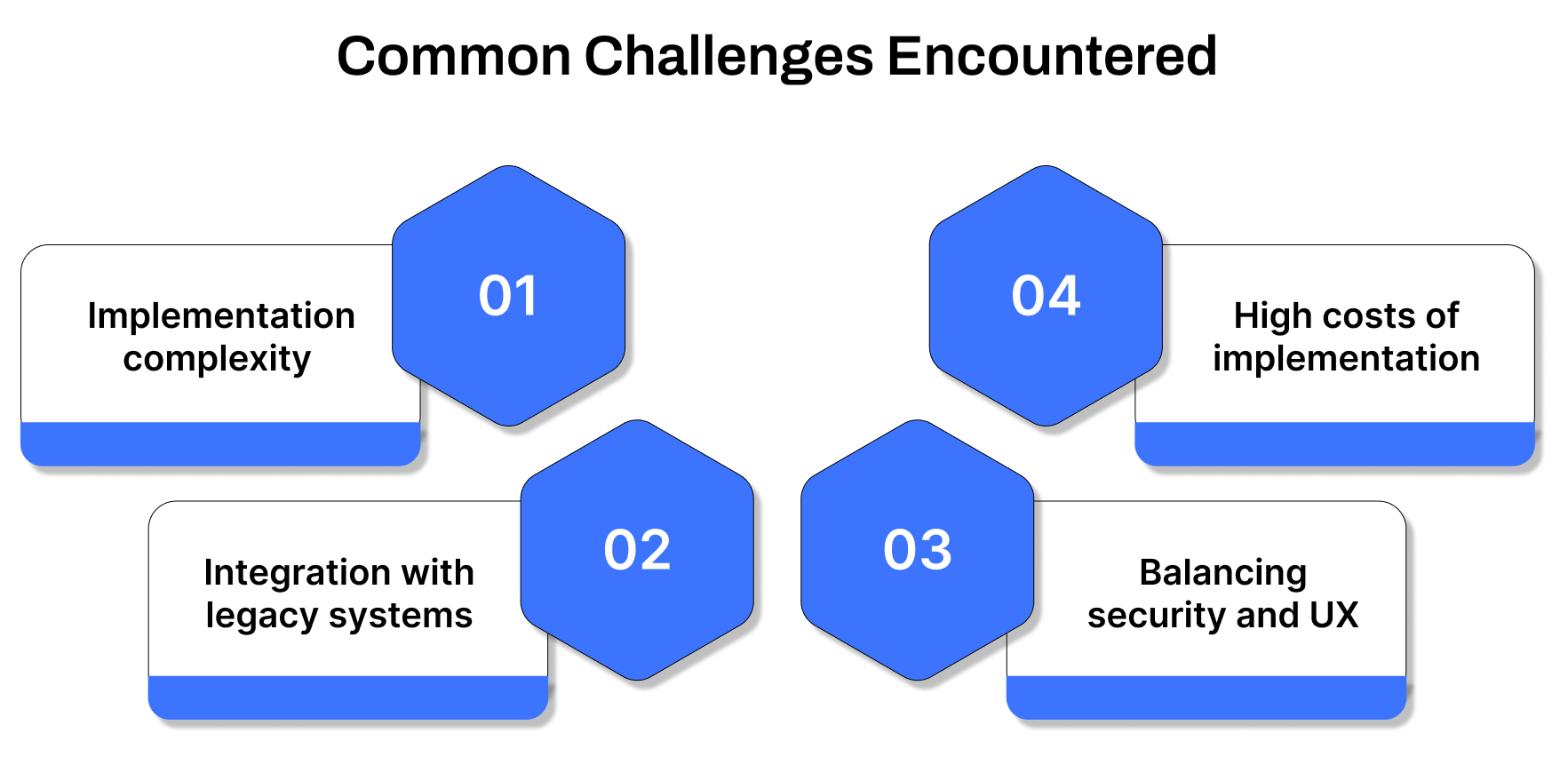
Common Challenges Encountered When Adopting Zero Trust Security
Implementing Zero Trust isn’t just about adopting a new framework, it’s about reshaping how your organization approaches identity, access, and data control. While the benefits are substantial, several challenges often emerge during the transition:
1. Implementation complexity
Laying the groundwork for Zero Trust requires deep understanding of your digital environment. Every endpoint, user, and data flow must be identified and secured. This becomes harder as businesses scale or rely on third-party platforms.
Mapping every asset and connection is time-consuming
Data is often spread across SaaS apps, cloud providers, and external networks
Endpoint visibility across BYOD (bring your own device) environments is limited
2. Integration with legacy systems
Traditional systems weren’t designed for dynamic security models. Zero Trust demands real-time access decisions, while legacy infrastructure often relies on static permissions.
Older systems may lack APIs or modern identity support
Conditional access rules don’t translate well from static configurations
Retrofitting old applications can be risky and expensive
3. Balancing security and user experience
Security should protect, not disrupt. Without careful planning, users may find Zero Trust controls intrusive.
Continuous verification can lead to authentication fatigue
Overly strict controls may slow down daily tasks
Users may bypass security when frustrated, creating new risks
4. High implementation and maintenance costs
Building Zero Trust involves more than just policy changes; it demands investment in tools, training, and ongoing optimization.
Initial setup (e.g., IAM, segmentation, monitoring) is costly
Hiring and upskilling teams add to the budget strain
Post-deployment fine-tuning and upkeep are resource-intensive
Turning complexity into clarity
These hurdles are real, but they’re not insurmountable. What organizations need is a smarter way to manage trust, one that reduces manual overhead while increasing visibility and control. That’s where Auditive comes in.
With a unified platform built to support Zero Trust principles, Auditive helps teams:
Monitor and manage third-party access with ease
Automate policy enforcement based on real-time risk
Strengthen vendor risk management and simplify compliance tracking via the Trust Center
By streamlining SaaS security operations and integrating deeply with your existing stack, Auditive empowers security teams to make Zero Trust not only possible but practical.
Real-World Use Cases of Zero Trust Security Model
Zero Trust is more than a framework; it’s being actively used to solve real security challenges across industries. Here are a few impactful examples:
1. IoT Device Protection
Connected devices like sensors and cameras often become weak links. Zero Trust continuously verifies their behavior, applies strict access controls, and ensures all communication is secure, minimizing the risk of malware infiltration.
2. Multi-Cloud Security
With businesses operating across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, Zero Trust enforces identity-based access and denies any unverified attempts, regardless of platform or location.
3. Secure Remote Access
Zero Trust replaces traditional VPNs with identity and context-based verification. Users get access only to what they need, reducing lateral movement and improving control over distributed teams.
Solutions like Auditive take these Zero Trust principles a step further by embedding them into your vendor and SaaS ecosystems. Through centralized visibility, vendor risk management, and a built-in Trust Center, Auditive helps you adopt Zero Trust at scale without slowing down business.
How Auditive Enables Zero Trust Security at Scale
Adopting a Zero Trust approach isn’t just about internal controls; it also means extending that discipline to your external vendors and SaaS tools. Auditive makes this easier by giving you complete visibility and control over your third-party ecosystem.
With continuous monitoring, vendor-specific risk assessments, and a centralized Trust Center, Auditive helps ensure every access point, internal or external, meets your Zero Trust standards. From onboarding to ongoing compliance, it keeps your organization secure without slowing down innovation.
Conclusion
It is a necessary shift in how organizations secure access, data, and operations in a cloud-first, perimeter-less world. But achieving true Zero Trust means going beyond internal systems. You need full visibility and control over every third-party tool, vendor integration, and SaaS app connected to your network.
Auditive helps you extend Zero Trust principles across your external ecosystem with intelligent vendor risk management, continuous monitoring, and a robust Trust Center that aligns with modern compliance needs. Whether you're securing remote workforces, sensitive workloads, or hybrid environments, Auditive ensures you're not just checking boxes; you’re building a security-first culture rooted in visibility, accountability, and trust.
Ready to modernize your Zero Trust strategy?
Visit Auditive to see how smarter third-party security can help you move faster without compromising trust.
FAQs
Q1. What is the core principle of Zero Trust Security?
A1. The Zero Trust model is based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It requires all users and devices to be authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated before being granted access.
Q2. How does Zero Trust differ from traditional network security?
A2. Traditional models assume trust within the perimeter, while Zero Trust assumes that threats can exist both inside and outside the network. It focuses on granular access control and continuous verification.
Q3. Is Zero Trust only for large enterprises?
A3. Not at all. Businesses of all sizes benefit from Zero Trust. Scalable tools and services like Auditive make it easier for mid-size companies to adopt Zero Trust principles effectively, especially across SaaS and vendor environments.
Q4. What role does vendor risk management play in Zero Trust?
A4. Vendors and SaaS applications often have access to critical systems and data. Without proper oversight, they become a major attack surface. Vendor risk management ensures these third-party connections adhere to Zero Trust policies.
Q5. How does Auditive’s Trust Center support Zero Trust adoption?
A5. Auditive’s Trust Center offers a centralized, real-time view into vendor security postures, certifications, and risks. It helps organizations maintain compliance, reduce blind spots, and enforce Zero Trust controls across their external ecosystem.