Creating a Third-Party Security Policy Guide
Every external partnership your organization builds opens new doors, not just for growth, but also for risk. As businesses increasingly depend on third-party vendors for critical operations, a single weak link in the chain can expose sensitive data or disrupt workflows. That’s why defining a third-party security policy is no longer optional, it’s an operational necessity.
A well-crafted third-party security policy helps you establish clear expectations, evaluate vendor security posture, and maintain control over shared data environments. It sets the foundation for structured oversight, continuous monitoring, and better decision-making, giving security leaders the confidence to manage complex vendor ecosystems without compromise.
Moving further, this guide breaks down how to build an effective third-party security policy that not only safeguards your organization’s data but also strengthens vendor accountability and long-term business resilience.
Before we dive in:
Third-party vendors can expose your organization to unseen risks.
A structured third-party security policy is key to managing those risks effectively.
Strong risk management ensures continuous monitoring and oversight.
A centralized strategy simplifies vendor data tracking and decision-making.
Tools like Auditive empower CISOs to take proactive control of their vendor ecosystem.
Understanding Third-Party Security: The Foundation of a Safe Vendor Ecosystem
A third-party vendor is any external entity, such as a cloud provider, payment processor, software supplier, or IT consultant, that supports your organization’s operations and often has access to sensitive data or systems. While these partnerships drive efficiency and innovation, they also expand your attack surface.
Third-party security refers to the strategies, policies, and technologies used to identify, monitor, and mitigate risks introduced by these external vendors. It ensures that every partner with system or data access maintains the same level of protection your organization enforces internally.
Even a single vendor vulnerability can compromise critical systems, disrupt operations, and erode stakeholder trust. That’s why building a strong third-party security framework has become a strategic necessity, one that underpins resilience, compliance, and confidence across industries like finance, healthcare, and education.
Why Strengthening Third-Party Security Can’t Be an Afterthought
In industries where data privacy and compliance are non-negotiable, third-party relationships have become both a necessity and a risk multiplier. According to the 2024 Prevalent Third-Party Risk Management Study, 61 % of companies reported a third-party data breach or security incident in the last 12 months.
Third-party security isn’t just a checkbox in the auditing process, it’s a direct reflection of how well an organization can safeguard customer data, meet regulatory expectations, and maintain business continuity. A single misstep can cascade into legal exposure, financial penalties, and loss of stakeholder trust.
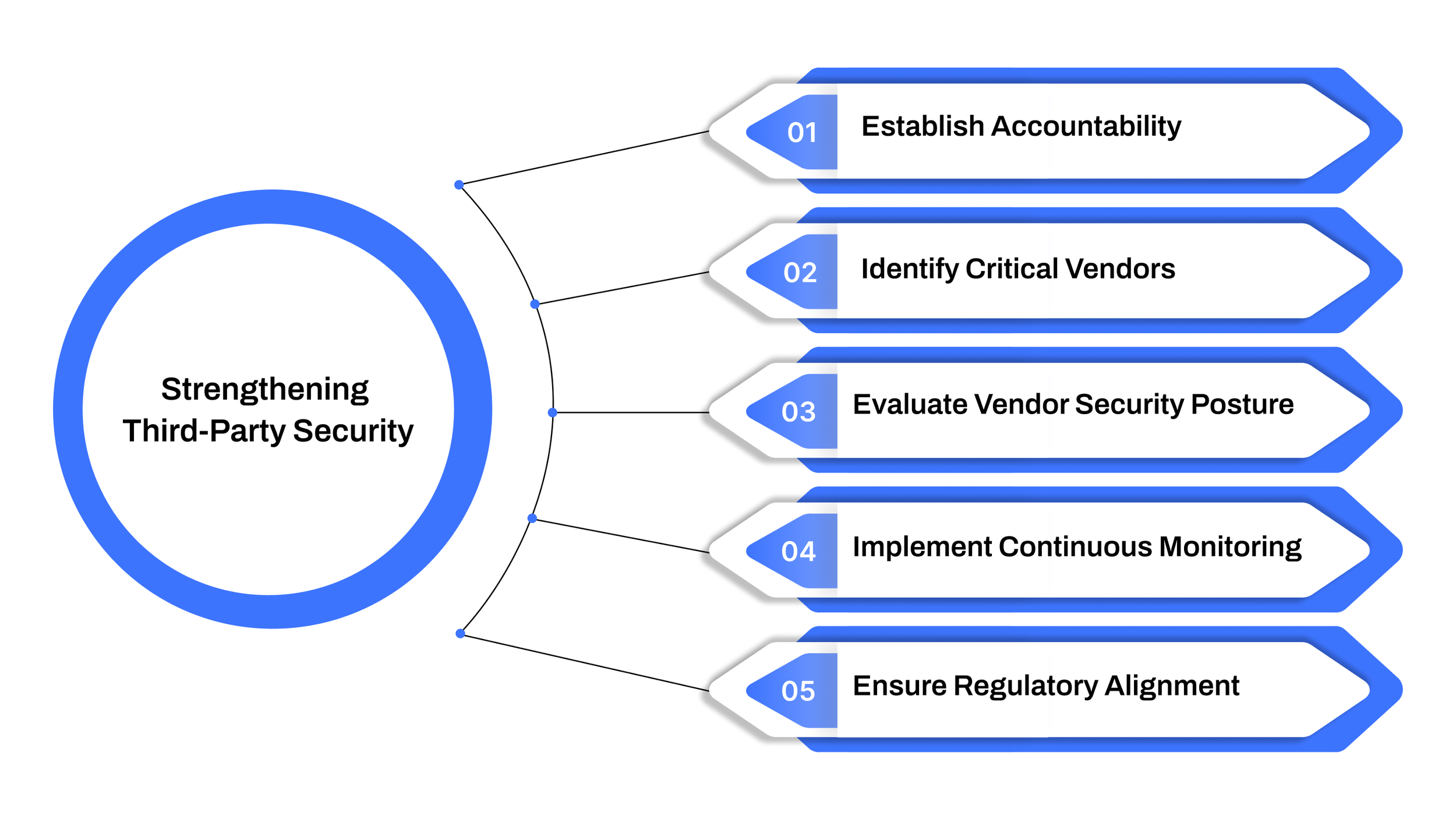
A strong third-party security policy helps organizations:
Establish accountability: Define clear ownership across procurement, IT, and compliance teams for vendor oversight.
Identify critical vendors: Prioritize those with access to sensitive data or core systems.
Evaluate vendor security posture: Conduct thorough assessments before and during partnerships.
Implement continuous monitoring: Track performance over time, not just during onboarding.
Ensure regulatory alignment: Map vendor practices to frameworks like HIPAA, PCI DSS, or SOC 2 depending on the industry.
With rising supply-chain attacks and expanding digital dependencies, third-party security policies have become a cornerstone of modern enterprise resilience, not a formality to meet.
Also read: Third-Party Debit Card Security Breach Insights
Why Every Enterprise Needs a Defined Third-Party Security Policy
The reality for modern enterprises is clear: your security is only as strong as your weakest vendor. Either it’s a payroll provider, data processor, or cloud service, every external partner introduces potential entry points for risk. A clearly defined third-party security policy provides the structure needed to identify, assess, and manage those risks before they impact operations or regulation.
A mature third-party risk management program doesn’t just focus on operational metrics, it evaluates the full spectrum of risk, including:
Information handling and data access controls
Vendor financial and operational stability
Following frameworks and regional regulations
Ethical practices and labor standards
Business continuity and incident response capabilities
A decentralized business model can easily blur accountability, making it essential to have a governance structure that aligns with your organization’s risk tolerance and ethical obligations.
Manual assessments, spreadsheets, and periodic reviews can’t keep pace with vendor ecosystem, risks evolve too fast.
Go beyond check-the-box vendor reviews with Auditive. Its network-based platform connects real-time vendor trust profiles, AI-driven document processing, and live incident feeds, reducing up to 80% of review workload for risk teams.
Practical Steps to Build a Strong Third-Party Security Policy
Implementing a third-party security policy is more than a standard exercise, it’s about embedding security at every stage of the vendor lifecycle. From onboarding to offboarding, each step plays a critical role in minimizing risk, maintaining visibility, and ensuring accountability. Here’s how to build and sustain an effective third-party security framework.
1. Perform Due Diligence Before Signing
Before formalizing any vendor partnership, conduct a thorough security assessment. Ensure that your third parties maintain security standards equal to or higher than your own. A vendor’s vulnerability can quickly become your organization’s exposure point.
Key questions to ask:
Does the vendor have a formal incident response and notification plan?
How do they document and resolve detected vulnerabilities?
Do they conduct regular penetration testing or external audits?
Taking time to evaluate these factors upfront can prevent costly breaches later.
Must read: Supplier Due Diligence for Managing Procurement Risk
2. Build Security Requirements into Contracts
Once you’re confident in a vendor’s internal security posture, integrate specific security obligations into your contracts. These should clearly outline data handling expectations, legal mandates, and testing frequency.
Include clauses that cover:
Regular phishing and penetration testing (at least annually)
Documented remediation and issue-tracking processes
Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) with explicit access control terms
This contractual alignment ensures both sides are accountable for maintaining a secure operational environment.
Learn more about: Third Party Contract Management: Steps and Best Practices
3. Define Roles, Responsibilities, and Decision Criteria
Ambiguity in accountability often leads to security gaps. Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of everyone involved in vendor oversight, from IT and legal to safety and procurement teams.
Best practices:
Assign ownership for risk evaluation and escalation procedures
Establish measurable decision criteria for accepting or mitigating vendor risks
Quantify risks using standardized scoring models to ensure consistency
These definitions make your program auditable and defensible, especially during regulatory reviews or post-incident investigations.
4. Conduct Continuous Vulnerability Assessments
Vendor security management isn’t a one-time task. Continuous assessment ensures your third-party ecosystem stays resilient against evolving threats. Schedule periodic security audits, review vendor performance reports, and monitor access activities across systems.
Automated tools can simplify this process by flagging anomalies and unauthorized access in real time. A proactive monitoring approach not only enhances visibility but also strengthens your ability to respond swiftly to incidents.
5. Establish a Secure Offboarding Process
When vendor relationships end, improper offboarding can leave your systems exposed. Ensure all data access is revoked, credentials are disabled, and organizational information is permanently erased.
Include the following in your offboarding checklist:
Verified destruction or deletion of all sensitive data (with documentation)
Revocation of all system and facility access privileges
Review of subcontractor data handling to ensure security
This step protects your organization even after the partnership concludes.
Maintaining this level of diligence across hundreds of vendors can overwhelm even well-resourced security teams. Auditive simplifies the process by providing a unified platform where CISOs and security teams can:
Automate continuous vendor monitoring and vulnerability tracking
Integrate security assessments directly with procurement workflows
Centralize vendor documentation and legal evidence
By integrating Auditive into your existing workflow, you gain 24/7 visibility into vendor risks, streamline
Find the Right Platform to Strengthen Your Third-Party Security Policy
Every external partnership, whether for cloud hosting, payroll systems, or data analytics, introduces potential security exposure. Even one vendor with weak controls can compromise your network and damage customer trust. That’s why selecting a purpose-built platform to manage your third-party security policy is critical.
The right solution should do more than store vendor data; it should help you identify, monitor, and mitigate risks continuously. When evaluating options, focus on tools that:
Provide continuous visibility into vendor security posture and data handling practices.
Automate risk assessments to detect potential threats faster.
Offer centralized dashboards for tracking vendor performance and documentation.
Integrate seamlessly with existing procurement and workflow systems.
Support real-time alerts for any changes in vendor security ratings or incidents.
Among available solutions, Auditive stands out for its precision and adaptability. Built for CISOs and security teams, it:
Consolidates all vendor insights, ensuring clarity and control.
Delivers continuous monitoring and automated assessments across your vendor ecosystem.
Connects easily with existing tools, reducing manual work while enhancing visibility.
With Auditive, third-party risk management becomes less about reacting to threats and more about staying ahead of them, giving your organization the confidence to operate securely and scale responsibly.
Final Thoughts
Building a resilient security posture starts with understanding and managing the risks that come with external vendors. A well-defined third-party security policy ensures your organization stays vigilant, proactive, and informed, especially as vendor ecosystems grow more complex. Integrating structured processes and providing visibility into every third-party relationship, helping you identify vulnerabilities before they escalate into real threats.
Platforms like Auditive bring this approach to life by unifying monitoring, automation, and reporting under one roof, giving security leaders the clarity and control they need to protect what matters most.
Schedule a demo with Auditive to experience how continuous monitoring and intelligent insights can redefine your third-party security strategy.
FAQs
1. What is a third-party security policy?
A third-party security policy outlines how an organization manages and secures relationships with external vendors, defining expectations, responsibilities, and security measures to prevent data breaches and operational risks.
2. Why is risk management important?
Risk management helps identify and mitigate potential threats from external vendors, ensuring your organization’s data and systems remain secure even when managed by third parties.
3. How does Auditive improve vendor management?
It centralizes all vendor data, including risk scores, documentation, and performance metrics, providing real-time visibility and simplifying oversight for security teams.
4. What features should I look for in a third-party security management tool?
Look for platforms that offer continuous monitoring, automated assessments, risk scoring, and seamless integration with your existing workflows.
5. How can Auditive help my organization?
Auditive enables CISOs and security teams to streamline vendor monitoring, automate assessments, and manage all third-party risks, helping you stay secure, efficient, and in control.