Ultimate Guide to ISO Supply Chain Risk Management
As global supply chains become more complex and vulnerable to both internal and external risks, companies must adopt structured risk management practices to stay resilient. ISO standards provide a proven framework for identifying, assessing, and mitigating these risks, helping businesses achieve compliance, enhance security, and prevent costly operational failures.
This guide explores the key elements of ISO supply chain risk management, offering actionable insights, tools, and best practices to help organizations manage risks effectively, strengthen their supply chain security, and maintain regulatory compliance.
Key Takeaways
ISO standards, like ISO 28000, provide a structured approach to assess and manage risks, ensuring a secure and compliant supply chain.
ISO helps ensure vendors meet security and regulatory requirements, reducing supply chain vulnerabilities and building trust between partners.
Ongoing risk monitoring ensures that security and compliance standards are maintained, enabling quick identification of potential threats and minimizing disruptions.
By using ISO standards, businesses can proactively manage risks, including cybersecurity, geopolitical, and operational disruptions, improving supply chain resilience.
ISO standards support businesses in adhering to global regulations, ensuring consistent risk management practices across international supply chains while maintaining compliance.
What Is Supply Chain Risk Management?
Supply chain risk management (SCRM) is all about identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could disrupt your operations. These risks can range from financial instability to geopolitical issues, and managing them effectively is imperative for long-term business success.
ISO standards, particularly ISO 28000, provide a framework for tackling these risks, making it easier to assess and manage them in real-time. By adopting these best practices, your business can stay ahead of potential disruptions and maintain smooth operations.
When it comes to ISO supply chain risk management, ensuring that your vendor contracts remain compliant is essential. Auditive’s Contract Monitor helps you track contract adherence, flag discrepancies, and ensure that key clauses meet regulatory standards. With real-time monitoring and automatic renewal reminders, you’ll always stay ahead of potential compliance issues.
Also Read: The Third-Party Risk Blueprint: Start Early to Safeguard Success
Next, let’s look into how supply chain predictive analytics helps improve risk management decisions.
What is Supply Chain Predictive Analytics?
Predictive analytics takes the guesswork out of managing supply chain risks. By using historical data, machine learning, and statistical models, it predicts potential disruptions, allowing businesses to act before problems arise.
For instance, predictive analytics can forecast supply chain delays due to weather or geopolitical events, enabling you to plan alternative strategies. This approach helps mitigate risks and ensures your business remains agile, even when faced with unexpected changes.
Now, let's explore why having a solid supply chain risk management plan is essential for your business.
Why is the Supply Chain Risk Management Plan Important?
A solid risk management plan is essential to safeguard your business from both expected and unexpected challenges. Having a plan in place helps streamline your approach to risk, making it easier to manage compliance, protect your reputation, and minimize operational disruptions.
Here’s why it’s crucial:
Prevents Disruptions: Minimizes unexpected supply chain interruptions by anticipating potential issues.
Ensures Compliance: Helps businesses stay compliant with industry regulations, including GDPR and ISO standards.
Protects Reputation: Reduces the risk of a security breach or operational failure that could damage your brand.
Optimizes Resources: Efficiently allocates resources to manage identified risks and avoid inefficiencies.
Builds Supplier Relationships: Clarifies expectations and standards, creating stronger and more reliable partnerships.
Also Read: Understanding Principles of Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM)
Let’s now look at the different types of supply chain risks you should be aware of.
2 Types of Supply Chain Risks
Understanding the types of risks is important in managing them effectively. There are two main categories: internal risks and external risks, both of which require different approaches.
1. Internal Risks
These risks originate within your organization or from within the supply chain partners you control.
Business/Operational Risks: Risks arising from inefficiencies, internal failures, or a lack of coordination within your organization.
Financial Risks: Instability due to issues like cash flow problems, bad debt, or poor financial planning.
Manufacturing Risks: Risks from production delays, quality issues, or equipment failures that affect the delivery schedule.
Contract and Compliance Risks: Failure to meet legal or contractual obligations, including regulations like GDPR or ISO requirements.
2. External Risks
These risks come from outside your organization, often beyond your direct control, but still impact the business.
Reputational Risks: Damage to your brand’s reputation due to a security breach, unethical business practices, or failure to meet quality standards.
Cybersecurity Risks: Potential threats from hacking, data breaches, and other digital vulnerabilities in your supply chain.
Geopolitical Risks: Risks arising from international political instability, trade tariffs, and border regulations that could disrupt global supply chains.
Environmental Risks: Risks from natural disasters, climate change, and other environmental factors that can affect production or transportation.
Also Read: Understanding the Importance and Process of Risk Management
Next, let’s find out why supply chains break down and what causes these disruptions.
Why Supply Chains Break Down
Supply chains can break down for a number of reasons, many of which can be mitigated through effective risk management strategies. Understanding the root causes of these disruptions is key to building a resilient supply chain.
Global Events: Pandemics, natural disasters, and political instability can halt production and disrupt transportation networks.
Supplier Risks: A supplier's financial issues, compliance failures, or inability to meet deadlines can quickly ripple through the supply chain.
Cyber Threats: Cyberattacks on key systems or vendors can compromise sensitive data, halt operations, and cause widespread damage.
Demand Volatility: Unexpected changes in demand can lead to stockouts or overproduction, resulting in inventory management issues.
Compliance Risks: Failing to comply with regulatory requirements can lead to legal penalties, operational shutdowns, and reputational damage.
Next, let’s move on to the 5 key steps that can help you mitigate these risks effectively.
5 Steps to Strengthen Your Supply Chain Risk Management
Managing risks effectively requires a systematic approach. Below are five key steps to help you build a robust ISO supply chain risk management strategy:
1) Identify Risk
Identifying risks is the first step in any risk management process. This involves evaluating potential internal and external threats.
SWOT Analysis: Assess strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats within your supply chain to better understand potential risks.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): Evaluate the potential failure points and assess their impact to prioritize risk management efforts.
ISO 31000: Use this risk management standard to guide your risk identification and assessment processes.
2) Assess Risk
Once risks are identified, it’s important to assess their potential impact and likelihood to prioritize them effectively.
Likelihood and Impact: Determine the probability of each risk occurring and the potential consequences it may have.
Supplier Risk: Assess the financial stability, compliance levels, and performance history of your suppliers.
Third-Party Assurance: Ensure vendors are providing necessary assurances regarding their risk management practices and compliance.
3) Integrate Risk Management into Your Overall Supply Chain Strategy
Risk management should be embedded in your overall supply chain strategy. It’s not a one-time process but an ongoing effort to ensure that risks are proactively identified and managed.
4) Mitigate Risk
Mitigation involves taking steps to reduce the likelihood or impact of identified risks.
Diversification: Spread your risks across multiple suppliers or geographies to reduce reliance on any single entity.
Redundancy: Establish backup systems and contingency plans to ensure continuity if one part of the supply chain fails.
Strategic Partnerships: Build resilient partnerships with key suppliers to improve reliability and share risk management responsibilities.
5) Monitoring and Review
Constantly monitor your supply chain and review your risk management strategies to adapt to changing conditions. This will help you stay ahead of emerging risks and improve your overall risk resilience.
Now, let’s discuss some of the challenges companies face in managing supply chain risks.
5 Challenges of Risk Management in the Supply Chain
Effective risk management in the supply chain comes with its own set of challenges. These challenges must be addressed to maintain a resilient, compliant, and efficient operation.
Complexity and Lack of Visibility: Global supply chains are often complex, and a lack of visibility into certain areas can lead to overlooked risks.
Inadequate Risk Assessment Frameworks: Many businesses lack a comprehensive framework to assess all aspects of supply chain risk.
Supplier Non-Compliance and Performance Issues: Ensuring all suppliers comply with legal and regulatory standards can be difficult, especially when they operate across different jurisdictions.
Environmental and Regulatory Changes: Regulatory changes and environmental factors can have a significant impact on your supply chain.
Cybersecurity Threats: Increased reliance on digital tools exposes companies to cyber threats, which can disrupt operations and damage the supply chain.
Also Read: Practical Steps for Third-Party Risk Assessment
Next, let’s explore the best strategies for managing supply chain risk.
7 Strategies for Mitigating Supply Chain Risk and Enhancing Resilience
Managing supply chain risk requires proactive strategies. Below are some of the most effective ways to mitigate risks:
Establish Nearshore Sources (Friendshoring): Reduce geopolitical and transportation risks by sourcing suppliers closer to home.
Inventory Buffer and Safety Stock Management: Keep sufficient stock on hand to handle demand spikes or supply shortages.
Improve Supplier Visibility: Use technology to gain better insights into your suppliers' operations, ensuring you're aware of any potential risks.
Model Worst-Case Scenarios: Plan for worst-case scenarios, including disasters, geopolitical events, or market shifts, and develop strategies to minimize their impact.
Technological Tools for Real-Time Monitoring: Use software tools to monitor your supply chain in real time, enabling faster responses to emerging threats.
Regular Supply Chain Risk Assessments: Regularly evaluate your supply chain risks to ensure your management strategies remain effective and up-to-date.
Internal Risk Awareness Training: Educate your team about supply chain risks to create a culture of vigilance and proactive risk management.
Also Read: Implementing Successful Vendor Risk Management and Assessments: 10 Best Practices
Now, let's examine the ISO 28000 standard, which is a game-changer for supply chain security.
What is ISO 28000?
ISO 28000 is an internationally recognized standard for supply chain security management. It helps organizations assess, manage, and mitigate supply chain risks, ensuring that proper security measures are in place to protect against disruptions. The ISO 28000 standard also facilitates compliance with global regulations and improves supply chain resilience.
Let’s take a closer look at why implementing ISO 28000 can significantly enhance your supply chain risk management.
Why Implementing ISO 28000 is the Ultimate Solution for Supply Chain Security?
Adopting ISO 28000 provides several key benefits, including:
Protection from Threats: It safeguards your supply chain against physical, cyber, and regulatory risks.
Increased Trust from Customers and Partners: Achieving certification demonstrates your commitment to security and builds credibility with stakeholders.
Compliance with Legal Requirements: Helps businesses comply with local and international regulations related to supply chain security.
Optimized Risk Management Processes: Streamlines your risk management efforts, making it easier to identify, assess, and mitigate risks.
Competitive Advantage: ISO certification positions your company as a leader in secure and compliant supply chain operations.
Also Read: Steps to Develop a Vendor Onboarding Process and Checklist
Next, we’ll break down the key elements of the ISO 28000 standard and why they matter.
5 Key Elements of ISO 28000
ISO 28000 includes several key elements that form the backbone of an effective supply chain security management system:
Risk Assessment: Identifying and evaluating risks across the supply chain.
Risk Management: Developing strategies to mitigate and manage identified risks.
Physical and Technical Security: Ensuring both physical and cybersecurity measures are in place.
Continuous Improvement: Regularly reviewing and improving security measures to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with relevant supply chain regulations.
In ISO supply chain risk management, assessing vendor risk swiftly and accurately is key to maintaining compliance. Auditive’s Supplier Risk Assessment Agent uses AI to evaluate third-party risks faster, analyzing data against your custom controls. This allows you to quickly identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure that your vendors are fully compliant with ISO standards.
Now, let’s explore the benefits of obtaining ISO 28000 certification for your business.
Benefits of ISO 28000 Certification
The certification brings a range of benefits, such as:
Enhanced Supply Chain Security: ISO 28000 strengthens your defenses against security risks and disruptions.
Protection of Company Reputation: A certified security management system demonstrates your commitment to protecting customer and partner data.
Increased Transparency: Provides stakeholders with confidence in your operations.
Better Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that you comply with industry regulations, avoiding penalties.
Improved Relationships with Business Partners: Strengthens your relationships by demonstrating security and compliance standards.
Also Read: Managing Vendor Relationship: Definition, Tips, and Strategies
Now, let’s examine the key clauses of ISO 28000:2007 and their relevance to your business.
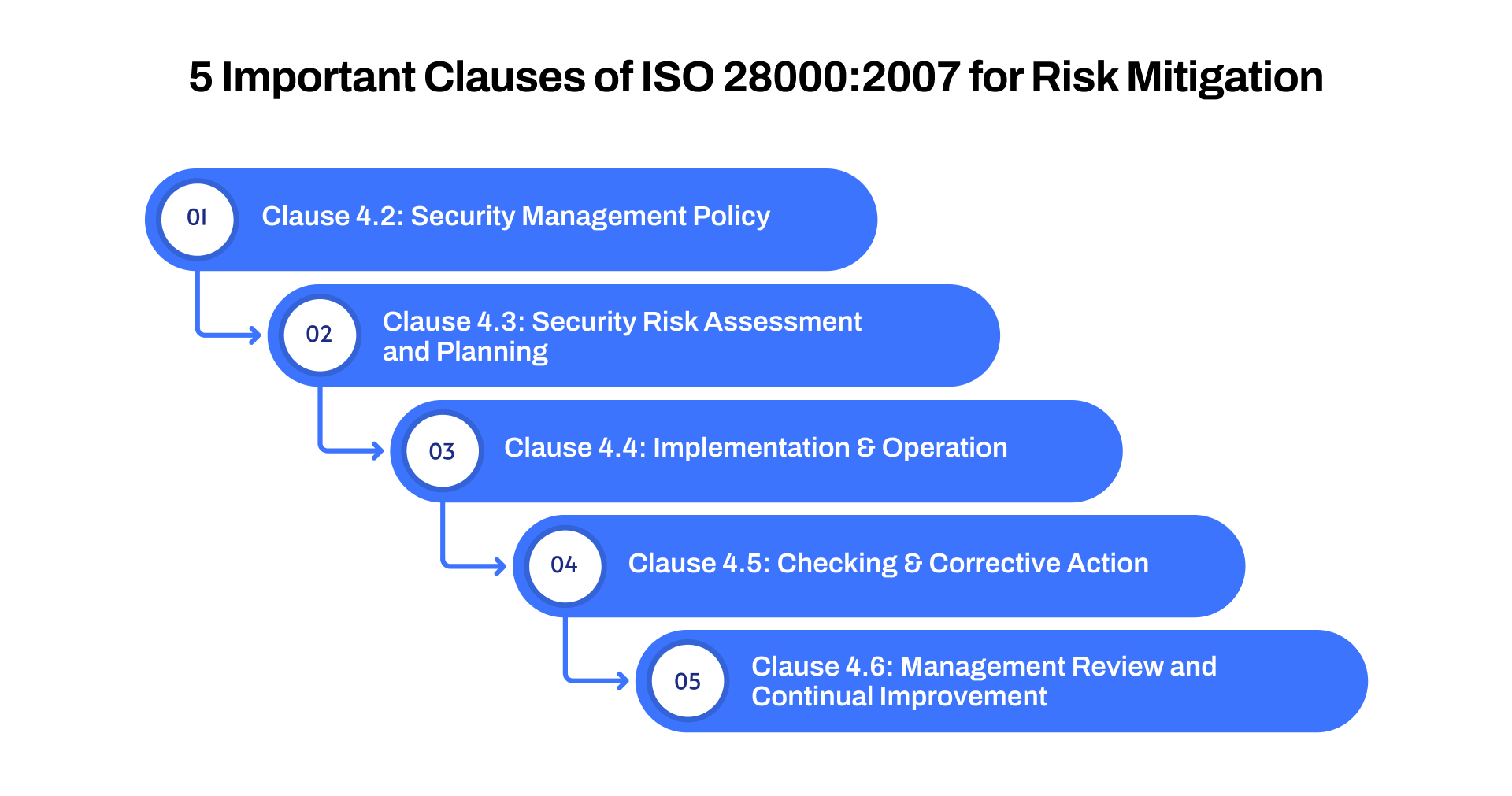
5 Important Clauses of ISO 28000:2007 for Risk Mitigation
ISO 28000:2007 outlines a robust framework for managing supply chain security through several key clauses:
1. Clause 4.2: Security Management Policy
This clause requires organizations to develop and maintain a comprehensive security management policy, establishing the foundation for supply chain security and risk management practices.
2. Clause 4.3: Security Risk Assessment and Planning
It emphasizes the need for identifying potential risks within the supply chain and creating effective strategies to address these risks, ensuring a proactive security approach.
3. Clause 4.4: Implementation and Operation
This clause outlines the implementation of the security measures, ensuring that the planned actions are operationalized across all levels of the supply chain to mitigate identified risks.
4. Clause 4.5: Checking and Corrective Action
It focuses on monitoring and evaluating security performance regularly, with the requirement to take corrective actions when security measures do not meet set objectives or standards.
5. Clause 4.6: Management Review and Continual Improvement
This clause calls for continuous monitoring, reviewing, and improving the supply chain security system, ensuring ongoing compliance and addressing emerging risks as the supply chain grows.
Next, let's walk through the ISO 28000 certification process and how to get started.
A 9-Step Process to Achieve ISO 28000 Certification
Achieving ISO 28000 certification is a step-by-step process that ensures supply chain security and compliance:
Preparation: Begin by thoroughly understanding ISO 28000’s requirements and aligning your current practices with the standard to prepare for the certification process.
Gap Analysis: Identify any discrepancies between your existing processes and the ISO 28000 requirements, focusing on areas where security measures may be lacking or insufficient.
Implementation Plan Development: Create a structured plan to close the gaps identified in the analysis, outlining specific steps and timelines for integrating ISO-compliant security practices throughout the supply chain.
System Implementation: Deploy the necessary security measures across your supply chain, ensuring that all operations are aligned with ISO 28000 standards and that all stakeholders follow the updated processes.
Team Training: Train employees at all levels on ISO 28000 practices, ensuring they are knowledgeable about the new security policies and equipped to follow them effectively.
Documentation Development: Prepare and organize all required documentation to support the audit process, including policies, procedures, and compliance records that demonstrate adherence to ISO 28000.
Internal Audit: Conduct an internal audit to review the security systems and processes, ensuring they align with ISO 28000 requirements and identify areas for further improvement before the official audit.
Certification Audit: An external auditor will evaluate your organization’s security measures and systems against ISO 28000 standards. Upon passing the audit, you will receive certification.
Monitoring and Improvement: After certification, continue to monitor your supply chain security, regularly reviewing processes and making necessary adjustments to ensure continuous compliance and improvement.
Also Read: Creating a Vendor Risk Assessment Questionnaire: A Simple Guide
Let’s see how Auditive's solutions can help you streamline and improve your supply chain risk management efforts.
Strengthen Your ISO Supply Chain Risk Management with Auditive’s Solutions
Effective ISO supply chain risk management requires ongoing monitoring, accurate risk assessments, and seamless vendor evaluations. Auditive offers powerful tools to streamline these processes, ensuring you remain compliant with ISO standards. Here’s how Auditive helps you manage vendor risks in line with ISO supply chain risk management best practices:
Contract Monitor: Auditive’s Contract Monitor ensures vendor compliance with ISO standards, tracking contract adherence and regulatory requirements. Extract key contract details in seconds, flag deviations, and automatically monitor missed SLAs.
Partner Trust Exchange: Partner Trust Exchange allows you to tap into a network of compliant suppliers, providing real-time updates on their security practices and regulatory compliance. This transparency enhances your ISO supply chain risk management, ensuring informed, trustworthy partnerships.
Accelerated Intake Form: With the Accelerated Intake Form, you can automate your third-party intake process, immediately assessing inherent risk in new suppliers based on ISO 28000 and ISO 31000 guidelines. Streamline your risk evaluation process and ensure quick compliance checks.
Questionnaire Copilot: Auditive’s Questionnaire Copilot uses AI to automate the completion of RFPs and risk questionnaires, ensuring that vendor data aligns with ISO supply chain risk management requirements. This boosts efficiency and accuracy while reducing manual workload.
Supplier Risk Assessment Agent: The Supplier Risk Assessment Agent performs fast, AI-powered assessments of vendor risk, measuring compliance against custom controls aligned with ISO 28000. It provides actionable insights, enabling quick responses to potential vulnerabilities in your supply chain.
Supply Chain Continuous Monitoring: Supply Chain Continuous Monitoring ensures ongoing risk tracking, allowing you to receive real-time notifications for any changes that affect ISO compliance across your supply chain. Monitor incidents, from cyber threats to financial instability, and mitigate risk in real time.
Read how PayNearMe gained trust with clients by centralizing and sharing security information through Auditive’s platform; check out the full case study.
By integrating these Auditive solutions, you can streamline your ISO supply chain risk management processes, ensuring your vendors remain compliant, your data is secure, and your supply chain is resilient.
Wrapping Up
Implementing ISO supply chain risk management through standards like ISO 28000 helps businesses build resilient, secure, and compliant supply chains. By following best practices, assessing risks, and staying ahead of disruptions, organizations can ensure operational continuity and enhance their reputation in the marketplace.
With Auditive, you can automate the process of contract monitoring, perform AI-powered assessments, and receive real-time updates on vendor security and compliance practices. This ensures you remain proactive in managing vendor relationships, addressing risks as soon as they arise, and maintaining ISO-compliant standards.
Get in touch with Auditive and enhance your vendor risk management strategy and stay ISO-compliant.
FAQs
1. How does ISO 28000 help businesses assess supply chain risks?
ISO 28000 provides a comprehensive framework for identifying, assessing, and managing risks, ensuring your supply chain remains secure and compliant with global standards.
2. Can ISO supply chain risk management reduce financial disruptions?
Yes, implementing ISO standards helps mitigate financial risks by ensuring robust vendor management, compliance, and contingency plans, preventing disruptions that could harm financial stability.
3. What role does ISO 28000 play in enhancing supply chain security?
ISO 28000 strengthens security by outlining risk management processes, improving supplier assessments, and ensuring continuous monitoring to protect against disruptions and cyber threats.
4. How can ISO standards help with vendor compliance in global supply chains?
ISO standards provide guidelines for monitoring and evaluating vendor compliance, ensuring alignment with security practices and regulatory requirements, especially in international supply chains.
5. What are the main challenges in implementing ISO supply chain risk management?
Challenges include aligning internal processes with ISO standards, ensuring vendor compliance across global networks, and maintaining continuous monitoring to address emerging risks.