Understanding Data Leak Prevention: Key Benefits and Practices
Data is the backbone of every modern business, covering customer details, financial records, intellectual property, and internal communications. But with cyberattacks on the rise and the risk of human error always present, protecting this data has become a serious challenge.
A single data leak can result in heavy financial losses, compliance fines, and long-term damage to reputation. That’s why businesses are increasingly turning to Data Leak Prevention (DLP) as a proactive measure to secure sensitive information.
This blog breaks down what data leak prevention is, why it matters, the common types of leaks, and the best practices to strengthen your defenses.
Quick Glance:
Data leak prevention (DLP) safeguards sensitive information from accidental or intentional exposure.
Leaks can stem from human error, insider threats, or weak vendor security.
Benefits include protecting reputation, ensuring compliance, and reducing financial risks.
Best practices involve encryption, employee training, vendor risk management, and continuous monitoring.
Auditive strengthens DLP with integrated Vendor Risk Management and a Trust Center for transparency and trust.
What is Data Leak Prevention?
Data Leak Prevention (DLP) refers to a set of tools, policies, and practices designed to stop sensitive information from leaving an organization’s secure environment without authorization. In simple terms, it’s about ensuring the right data stays in the right hands.
DLP solutions operate across multiple layers, such as endpoints, networks, cloud platforms, and email systems, to detect unusual activity, enforce data-handling rules, and block suspicious transfers before damage occurs.
The purpose goes beyond just avoiding accidental data loss. A robust DLP strategy helps organizations:
Protect critical assets like financial records, trade secrets, intellectual property, and personally identifiable information (PII).
Comply with industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS, where strict safeguards for customer and business data are legally required.
Mitigate risks from both inside and outside threats, whether it’s an employee mishandling data or a cybercriminal attempting to exfiltrate it.
By combining real-time visibility with policy enforcement, DLP strengthens the overall security posture of a business. It becomes a proactive defense layer in the larger cybersecurity framework, ensuring data flows only through approved users, devices, and channels.
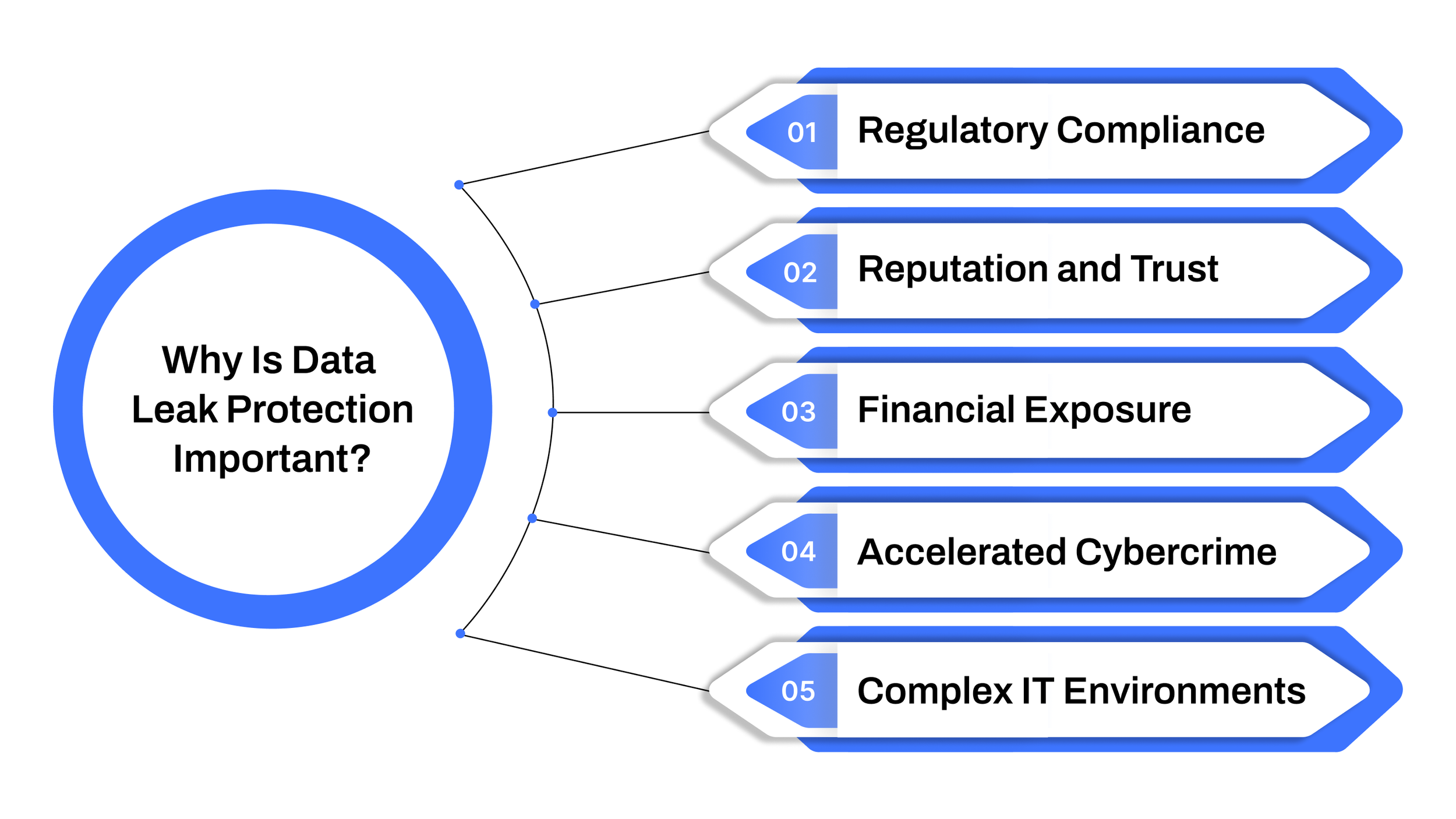
Why Is Data Leak Protection Important?
A data leak is not just a technical mishap; it’s a full-scale business crisis. When sensitive information such as customer PII, financial statements, or strategic plans is exposed, the damage often extends far beyond the IT department. It can disrupt operations, weaken customer relationships, and put long-term business stability at risk.
Data Leak Prevention (DLP) helps organizations safeguard this critical information against risks like employee mistakes, insider threats, misconfigurations, or third-party negligence. As businesses expand their digital footprint, the possibility of accidental or malicious leaks grows, making DLP an essential layer of modern security.
Here’s why it holds so much weight:
Regulatory compliance – Laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA demand strict controls over sensitive data. Non-compliance isn’t just a technical gap; it can mean multi-million-dollar penalties.
Reputation and trust – Customer trust takes years to build but only one leak to destroy. Loss of credibility can damage brand value, disrupt partnerships, and reduce investor confidence.
Financial exposure – Data breaches are costly. IBM’s research shows the average breach cost is $4.48 million, covering legal battles, fines, response measures, and lost revenue.
Accelerated cybercrime – For attackers, leaked data is a shortcut. Instead of spending time probing systems, they can exploit stolen information immediately.
Complex IT environments – With remote work, BYOD, and SaaS adoption, traditional security perimeters no longer apply. Sensitive data now lives across multiple platforms, increasing the risk of accidental leaks.
In short, data leak protection isn’t optional; it’s mission-critical. One small lapse can trigger a domino effect of financial, legal, and reputational damage that no organization can afford.
3 Types of Data Leakage
Data leakage isn’t just a technical mishap; it’s a business risk that can undermine compliance, trust, and revenue. Sensitive data can escape in different ways, and understanding these patterns is essential for shaping strong prevention strategies.
Broadly, data leaks fall into three major categories:
1. Accidental Data Leaks
These are the most common, and often the most underestimated. They usually happen due to human error rather than malicious intent. Common examples include:
Sending confidential files to the wrong recipient because of email auto-complete.
Attaching outdated or incorrect documents containing sensitive information.
Uploading files to unsecured cloud storage or public folders by mistake.
Even though unintentional, the damage can be severe. A single misdirected file could expose customer PII, financial reports, or intellectual property, triggering regulatory fines and reputational damage.
Learn more about: Reputational risk management
2. Insider Threats
Sometimes, the danger comes from within. Insider threats involve employees, contractors, or business partners deliberately leaking information. Motivations vary, from personal grievances to monetary gain through competitors or cybercriminal groups. Methods often include:
Copying data to USB drives or personal devices.
Forwarding sensitive documents to personal email accounts.
Taking screenshots or photos of restricted information.
These incidents are particularly dangerous because insiders already have legitimate access to systems and know where sensitive data resides. That makes their actions harder to detect without specialized monitoring and controls.
3. External Attacks via Digital Channels
Cybercriminals don’t always need to break into servers; they exploit everyday communication and collaboration tools. External attacks often involve:
Phishing or spoofing emails that trick employees into sharing credentials.
Compromising cloud platforms, messaging apps, or file-sharing services.
Leveraging malware to siphon off sensitive records undetected.
For example, UpGuard researchers in 2021 uncovered misconfigured Microsoft PowerApps portals that exposed over 38 million sensitive records from 47 organizations. It wasn’t an intentional leak, but a single configuration oversight became a large-scale data exposure.
Addressing these risks requires more than just tools; it demands a strategy built on trust and visibility. This is where Auditive helps organizations strengthen their defenses and ensure sensitive data remains protected.
Data Leak Protection Benefits
Adopting data leak prevention (DLP) tools and strategies does more than just block threats. It strengthens the entire security posture of an organization while building confidence among stakeholders.
Here are the key benefits:
1. Stronger Data Security
DLP solutions continuously monitor how information moves inside and outside the network. By flagging suspicious activity, such as unauthorized file transfers, unencrypted emails, or unusual access attempts, security teams can intervene before an incident escalates. In some cases, this early detection prevents not just small leaks but also larger breaches planned by attackers during the reconnaissance phase.
2. Greater Visibility and Control
One of the most valuable outcomes of DLP implementation is complete visibility into sensitive data. Security teams gain real-time insights into where data lives, how it flows across systems, and who has access. This clarity helps identify weak points, enforce data-handling policies, and reduce the risk of insider threats or careless data sharing.
3. Protection of Intellectual Property (IP)
For organizations that thrive on innovation, such as software companies, research firms, and design studios, intellectual property is often the crown jewel. Losing proprietary code, product designs, or trade secrets can erase years of investment and hand competitors an unfair advantage. Studies show that nearly half of U.S. businesses have already experienced IP theft. DLP ensures that sensitive IP is protected from accidental leaks and deliberate exfiltration attempts.
4. Compliance with Regulations
Industries such as healthcare, finance, and retail must comply with strict data protection laws like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS. Failure to meet these obligations can lead to heavy penalties, legal consequences, and reputational harm. DLP solutions help enforce compliance by preventing unauthorized sharing, encrypting sensitive data, and ensuring policies align with regulatory standards.
5. Building Customer Trust
Every data breach makes headlines, and public confidence is hard to rebuild once lost. Demonstrating strong data protection practices reassures customers that their information is in safe hands. By showing a commitment to data leak prevention, organizations not only protect themselves but also strengthen long-term customer relationships and brand reputation.
Data Leak Prevention Best Practices
Protecting sensitive information isn’t about one tool or policy; it requires a layered, disciplined approach. The following best practices help organizations strengthen their data leak prevention (DLP) strategy and minimize exposure to risk:
1. Classify Your Data
Start by building a complete inventory of the data your organization holds. Classify it based on sensitivity and potential business impact; customer data, financial records, intellectual property, or internal communications may all require different levels of protection. Clear classification ensures that resources are directed where the risk is highest.
2. Restrict Access to Sensitive Data
Follow the principle of least privilege: employees should only access the data essential for their roles. Assign permissions carefully, revoke them when no longer required, and enforce strict device policies such as encryption and remote wipe capabilities. This minimizes risks tied to lost devices or compromised credentials.
3. Monitor Network Traffic
Use DLP solutions that continuously monitor traffic across emails, file transfers, and cloud platforms. Intelligent monitoring can flag suspicious activity, block unauthorized transfers, and provide valuable logs for audits or incident reports. This proactive oversight makes it easier to detect patterns and respond before a leak escalates.
4. Assess Third-Party Risks
Vendors and partners often have access to sensitive systems or data. Their weak security practices can create vulnerabilities for your business. Regularly evaluate third-party security standards and ensure they align with your organization’s compliance requirements.
Get more info: Third-party management guide
5. Conduct Regular Security Training
Employees are the first line of defense, and sometimes the weakest link. Regular training sessions help staff recognize phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and unsafe practices. Interactive methods, like phishing simulations, are especially effective in building awareness and accountability.
6. Implement a Unified Data Leak Prevention Program
In larger organizations, fragmented security measures across departments can leave dangerous gaps. A centralized DLP program ensures policies, tools, and incident responses remain consistent across the business. This reduces duplication, improves visibility, and provides stronger, organization-wide protection.
“While these practices form the foundation of strong data protection, maintaining trust also requires tools and strategies that adapt to evolving risks. That’s where partners like Auditive bring value, helping businesses unify vendor risk management and strengthen their security posture with a dedicated trust center.”
How Auditive Enhances Data Leak Prevention
Managing data leak prevention is not only about technology; it’s about creating a trusted framework where people, processes, and platforms align seamlessly. That’s where Auditive adds real value.
Auditive is designed to simplify complex security challenges by combining proactive risk management with actionable insights. Instead of leaving teams scrambling to respond after a leak, Auditive helps organizations build stronger defenses in advance. Here’s how:
Vendor Risk Management – Third-party vendors are often the weakest link in data security. Auditive provides deep visibility into your vendor ecosystem, enabling continuous monitoring and ensuring partners adhere to your compliance and data protection standards.
Trust Center – Centralize and showcase your compliance certifications, security policies, and data handling practices. By building transparency, your business not only reduces risks but also instills greater trust among stakeholders and customers.
Unified View of Risk – Rather than scattered, siloed security measures, Auditive delivers a consolidated risk picture across your entire organization, giving teams the clarity needed to prevent leaks before they happen.
Automated Monitoring & Alerts – Auditive ensures real-time monitoring of compliance and risks, enabling swift response to any activity that might indicate a potential data leak.
By integrating these capabilities, Auditive doesn’t just help with data leak prevention; it strengthens overall resilience and creates a culture of trust.
Conclusion
Data leaks are not just technical issues; they’re business-critical risks that can damage reputation, disrupt operations, and erode customer trust. Preventing them requires a structured approach that blends robust policies, secure technologies, and continuous monitoring. By investing in a clear data leak prevention strategy, businesses can reduce exposure, protect sensitive information, and strengthen trust with stakeholders.
Solutions like Auditive add a unique advantage by combining Vendor Risk Management with a centralized Trust Center. This dual approach not only helps monitor third-party vulnerabilities but also builds transparency with partners and clients. Ultimately, data protection isn’t about reacting to leaks; it’s about creating a secure, trustworthy environment where risks are minimized and business operations thrive.
FAQs
1. What is the main goal of Data Leak Prevention (DLP)?
The main goal of DLP is to ensure sensitive information, such as financial data, intellectual property, or customer records, remains secure and does not leave the organization without authorization.
2. What are common causes of data leakage?
Data leakage often stems from insider threats, human error, misconfigured cloud settings, malware attacks, or insufficient monitoring of third-party vendors.
3. How does DLP differ from traditional cybersecurity?
While traditional cybersecurity focuses on preventing external attacks, DLP specifically targets the protection of sensitive data, ensuring it isn’t exposed, stolen, or misused, whether by accident or malicious intent.
4. What role do vendors play in data leak risks?
Vendors and third-party providers can introduce vulnerabilities if they mishandle or fail to secure shared data. Strong vendor risk management is essential to close these gaps.
5. How does a Trust Center help with data leak prevention?
A Trust Center acts as a transparent hub for showcasing compliance certifications, policies, and security practices. It reassures stakeholders and customers that the organization is committed to protecting their data.