Applying Successful Risk Mitigation Strategies
One unresolved risk can cost more than an entire year of prevention.
That’s not an exaggeration; IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report notes an average breach cost of $4.88 million, with operational disruptions making up a significant share of that impact. When you add the hidden losses from downtime, stalled decisions, human error, and vendor-related exposure, the case for structured risk mitigation becomes undeniable.
Organizations aren’t just trying to reduce threats; they’re trying to stay functional, adaptive, and predictable in an environment where small internal gaps can trigger large-scale failures. That’s why risk mitigation needs to move beyond theoretical frameworks and shift toward practical, evidence-driven actions that target real operational, strategic, financial, and security vulnerabilities.
This blog breaks down how to apply risk mitigation strategies that actually work.
Key Takeaways:
Risk mitigation works only when organizations have continuous visibility, not one-time assessments.
Operational, human, financial, and security risks escalate when teams rely on manual tracking.
A structured mitigation framework reduces exposure and improves decision-making.
Real-time monitoring gives leadership faster signals to act before damage occurs.
Auditive helps organizations automate oversight and improve control with data-backed insights.
Risk Mitigation: A Clear Look at What It Really Means
Risk mitigation is the discipline of identifying, analyzing, and taking decisive action to reduce or control the risks your organization may face. These risks can emerge from operational gaps, natural disasters, market volatility, vendor dependencies, technology failures, or strategic missteps.
The purpose isn’t to eliminate every risk; that’s unrealistic. The goal is to minimize the likelihood, impact, or both, so your business can operate with stability and confidence.
A risk mitigation strategy is the targeted action plan you apply once a risk is understood. Organizations typically rely on four proven approaches:
Avoidance: Removing the source of risk entirely
Reduction: Minimizing the impact or probability
Transference: Shifting risk to a third-party
Acceptance: Acknowledging the risk and preparing to absorb it
Together, these strategies help teams manage uncertainty in a structured, measurable way and maintain operational resilience.
Risk Mitigation vs. Risk Management: The Real Difference That Shapes Your Strategy
While risk mitigation sits under the broader risk management umbrella, the two aren’t interchangeable. Risk management covers the full lifecycle, identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and monitoring uncertainties across the business. It gives you a complete view of threats, dependencies, and exposure.
| Aspect | Risk Management | Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify, assess, and prioritize risks | Reduce the impact or likelihood of specific risks |
| Scope | Broad, organization-wide | Targeted, action-oriented |
| Focus | Understanding exposure | Controlling or neutralizing threats |
| Outcome | Clear risk portfolio | Practical steps that strengthen resilience |
Risk mitigation takes that mapped risk landscape and turns it into action. It focuses on reducing the likelihood or impact of specific risks through targeted controls, processes, and responses. Instead of just recognizing what could go wrong, mitigation outlines exactly how to contain or neutralize the threat before it affects operations.
With this distinction clear, we can now move into ten practical, high-impact risk mitigation strategies that strengthen resilience and support smarter decision-making.
Critical Business Risks You Must Mitigate Early
Every organization faces risks, but not all risks carry the same impact, urgency, or visibility. Understanding what threatens your operations helps you build stronger, faster, and more targeted risk mitigation strategies. Below are the core risk categories businesses must actively control:
Operational Risk, Breakdowns in internal processes, system failures, or external disruptions that slow or halt day-to-day operations.
Strategic Risk, Decisions that miss market shifts, misread customer needs, or divert resources in the wrong direction, ultimately stalling long-term growth.
Financial Risk, Market volatility, credit exposure, cyber-driven financial theft, liquidity challenges, or revenue instability that weaken financial health.
Safety Risk, Any threat that puts employees or customers at physical risk, from equipment hazards to unsafe work environments.
Security Risk, Theft, unauthorized access, or breaches affecting physical assets or sensitive information.
Human Risk, Human errors, skill gaps, internal misconduct, or sudden turnover that disrupt workflows and consistency.
Compliance Risk, Penalties, fines, or operational restrictions resulting from failure to meet regulatory or industry requirements.
Reputational Risk, Actions, incidents, or communication failures that damage customer trust and long-term brand value.
Most businesses know these risks exist, but very few have real-time visibility into how quickly they evolve.
Auditive’s ecosystem consistently highlights one gap across industries: teams track risks, but they don’t monitor them with continuous intelligence. That gap is exactly where advanced risk mitigation frameworks start proving their value.
Also read: Understanding Business Continuity and Risk Management Strategies
Types of Risk Mitigation Strategies (With Clear, Actionable Plan Examples)
Risk mitigation isn’t guesswork; it’s a structured approach to reducing exposure while strengthening operational resilience. Different situations demand different responses, and choosing the wrong strategy often leads to higher operational friction, compliance gaps, or delayed decision-making. Below are ten practical, high-precision risk mitigation strategies that help leaders act decisively.
1. Challenge the Risk
Strategy: Let a manageable risk develop under observation, then act decisively if it escalates.
Example: If a storm is forecast, you may stay open initially to serve customers but shut down operations before it becomes dangerous or disruptive.
When to use: When you can predict a risk’s trajectory, and the short-term gains outweigh the potential exposure.
2. Prioritize Your Risks
Strategy: Use a risk matrix to rank overlapping risks and tackle the most critical first.
Example: A hospital in a hurricane-prone area might prioritize patient safety and critical equipment over less essential assets.
When to use: When risk resources (time, money, people) are limited, and not all risks are equally dangerous.
3. Exercise the Risk
Strategy: Run drills, simulations, or tabletop exercises to test your response plans.
Example: Fire drills measure response time and reveal bottlenecks in evacuation plans.
When to use: For high-impact but relatively predictable risks, where rehearsal can reduce real-world failure.
4. Isolate the Risk
Strategy: Partition dangerous systems or operations so that a failure in one area does not compromise everything.
Example: Expose only a public-facing server to the internet while keeping internal databases behind internal networks or firewalls.
When to use: When you cannot remove the risk entirely, but you can limit damage through segmentation.
5. Eliminate the Risk
Strategy: Remove the risky activity or component altogether.
Example: A factory stops using a toxic chemical and switches to a safer, equally effective alternative.
When to use: When the risk is too high and alternatives exist, or when the cost of mitigation is lower than the potential harm.
6. Buffer the Risk
Strategy: Add extra time, resources, or capacity to absorb potential impacts.
Example: When lifting heavy equipment, use spotters, expanded labor, and extra planning time to reduce accident risk.
When to use: For known operational risks where you can build slack into the process without prohibitive cost.
7. Quantify the Risk
Strategy: Analyze the potential upside and downside of a risk before deciding how to act.
Example: A delivery business assesses whether it’s worth continuing operations in light rain versus dangerous driving conditions.
When to use: Whenever the risk vs reward is unclear, and data can help guide a decision.
8. Monitor the Risk
Strategy: Establish tools and processes to keep an eye on how risk evolves in real time.
Example: Use a two-way communication system during civil unrest to provide updates and gather feedback from employees on the ground.
When to use: When conditions change rapidly or unpredictably and you need up-to-date intelligence.
Learn more about: Effective Continuous Risk Monitoring Practices and Techniques
9. Develop Contingency Plans
Strategy: Prepare fallback strategies in case things go wrong.
Example: Establish alternate travel routes, secondary suppliers, or emergency response plans for teams working in risky regions.
When to use: Always but especially for risks that cannot be fully mitigated or isolated.
10. Use Best Practices
Strategy: Adopt proven frameworks and industry standards.
Example: Follow OSHA or ISO safety standards rather than inventing your own safety processes from scratch.
When to use: When risks are well known and documented across industries, letting you benefit from established expertise and tools.
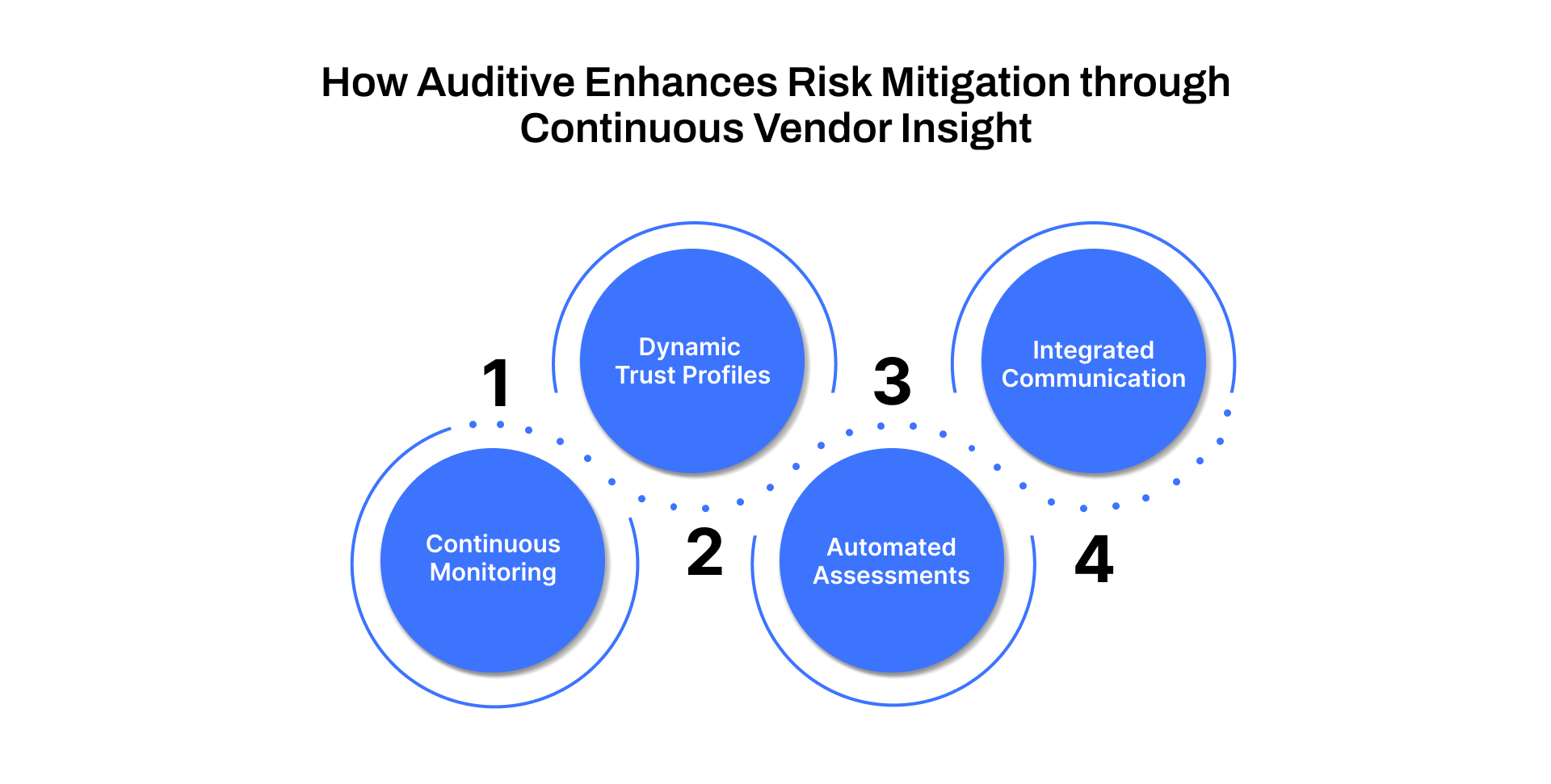
How Auditive Enhances Risk Mitigation through Continuous Vendor Insight
Mitigating third-party risk requires more than planning; you need real, up-to-date insight into how vendors are actually behaving. Auditive supports risk mitigation strategies by offering:
Continuous Monitoring: Through AuditiveX, risk signals, control changes, incident reports, certification updates, are tracked 365 days a year.
Dynamic Trust Profiles: AI-powered Trust Profiles update automatically, reflecting a vendor’s current risk posture, not just a one-time questionnaire.
Automated Assessments & Workflows: AuditiveX Plus enables you to run custom risk assessments, automate vendor reviews, and trigger risk-based workflows as issues arise.
Integrated Communication: Built-in tools help your security, procurement, and vendor teams stay aligned, respond to incidents, and adjust shared risk models in real time.
By building these capabilities into your mitigation strategy, Auditive helps you move from reactive risk response to proactive risk management, giving you visibility, agility, and accountability across your third-party ecosystem.
Final Thoughts
Strong risk mitigation isn’t about adding more controls; it’s about improving how fast you detect, interpret, and respond to operational threats. When organizations strengthen visibility across systems, decisions become clearer, incidents become preventable, and risks stop turning into costly escalations. A structured approach to mitigation doesn’t just protect the business; it ensures that teams operate with confidence, consistency, and measurable accountability.
Risk will always exist, but how you prepare for it determines how well the business performs when conditions shift.
If you want to eliminate blind spots, improve oversight, and gain real-time risk intelligence across your enterprise, schedule a demo with Auditive.
Experience how automated monitoring, clear evidence trails, and continuous analysis can transform the way your organization manages risk.
FAQs
1. Why is risk mitigation essential for business continuity?
It reduces the impact of unexpected disruptions, prevents financial and operational losses, and supports consistent, stable performance.
2. How does risk mitigation differ from risk management?
Risk management covers the full lifecycle of identifying, analyzing, and monitoring risks. Risk mitigation focuses specifically on the actions taken to reduce or eliminate those risks.
3. What is the most overlooked area of risk?
Human-driven risks, such as errors, missed updates, and inconsistent processes, often go unnoticed but cause significant operational failures.
4. Can technology improve risk mitigation outcomes?
Yes. Automated monitoring tools provide real-time visibility, early warnings, and reliable evidence that manual processes often miss.
5. How does Auditive support risk mitigation?
Auditive delivers continuous oversight, automated data validation, and clear evidence trails, enabling faster, more accurate risk detection and response.