Risk Management Framework: Definition and Examples
Uncertainty is unavoidable.
From cyberattacks and supply chain disruptions to regulatory pressures and financial instability, organizations face risks at every corner. The difference between businesses that thrive and those that stumble often lies in how effectively they prepare for and respond to these risks. This is where risk frameworks play a crucial role.
A risk management framework provides a structured approach for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks while aligning them with business objectives. Rather than addressing risks reactively, it enables organizations to anticipate potential challenges, standardize responses, and build resilience. By adopting a well-defined framework, leaders can not only safeguard assets but also enhance decision-making and stakeholder confidence.
This guide breaks down the essentials of risk management frameworks, their definition, types, steps, components, and real-world benefits, while also addressing the challenges organizations face when implementing them.
Before we dive in:
A risk management framework (RMF) provides a structured way to handle risks effectively.
Key benefits include resilience, compliance, and smarter decision-making.
Common challenges: lack of expertise, resistance to change, silos, and limited resources.
Integrating vendor risk management into RMF strengthens third-party oversight.
Auditive’s Trust Center streamlines monitoring, collaboration, and automation, making your RMF a living, adaptive system.
What is the Risk Management Framework?
A risk management framework is a structured blueprint designed to help organizations systematically identify, analyze, mitigate, and monitor risks. Instead of addressing uncertainties on an ad hoc basis, risk frameworks establish consistent practices that allow businesses to respond effectively while keeping their strategic goals in focus.
At its core, a risk management framework provides:
Clarity of process – well-defined steps for recognizing and addressing different types of risks.
Alignment with business objectives – ensuring that risk strategies reinforce organizational goals rather than obstruct them.
Compliance and governance support – helping companies meet regulatory obligations and industry standards.
Decision-making confidence – enabling leaders to evaluate threats and opportunities with better information at hand.
Risks are multi-dimensional, ranging from cyber threats and financial volatility to supply chain disruptions and regulatory shifts. A effective framework equips organizations with the tools and discipline to stay ahead of this complexity. When applied effectively, risk frameworks don’t just protect against losses; they also empower companies to seize opportunities and make decisions that build long-term resilience and trust.
Importance of a Risk Management Framework
A risk management framework is more than a compliance tool, it’s a strategic safeguard that helps organizations anticipate and respond to threats before they escalate. By systematically identifying both current and potential risks, businesses gain the ability to protect their assets, reputation, and long-term sustainability.
Take cybersecurity as an example. Companies store sensitive customer data, intellectual property, and financial records across digital systems. Without a risk framework in place, they leave themselves vulnerable to:
Data Breaches – exposing sensitive information to malicious actors.
Reputation Damage – losing the trust of customers, partners, and stakeholders.
Legal Consequences – facing penalties for non-compliance with privacy and security regulations.
Financial Losses – from theft, fraud, or recovery costs.
Operational Disruptions – interruptions to business continuity caused by unmanaged threats.
In this sense, a risk management framework acts like carrying an umbrella on a cloudy day, it may not prevent the storm, but it prepares you to face it confidently. Organizations that adopt structured risk frameworks are better positioned to make informed decisions, reassure stakeholders, and balance innovation with security.
Ultimately, the importance of a risk management framework lies in its ability to transform uncertainty into manageable challenges, ensuring that risks do not derail business goals but are instead handled with foresight and resilience.
Types of Risk Management Frameworks
Organizations have access to several structured approaches when it comes to managing risks. Each framework offers unique strengths, making it suitable for different industries, business models, and compliance needs.
Below are some of the most widely adopted risk frameworks:
1. NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF)
Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, the NIST RMF is a six-step process designed primarily for U.S. government organizations. It emphasizes strong security controls, regulatory compliance, and continuous monitoring, making it ideal for businesses handling sensitive data or operating in heavily regulated environments.
Why it works: It provides a clear step-by-step approach to securing information systems while balancing compliance with operational needs.
2. COSO Framework
The COSO framework, created by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations, focuses on enterprise risk management and internal controls. It is widely used in corporate governance because it highlights transparency, accountability, and compliance with legislation.
Best suited for: Companies that prioritize regulatory alignment and want to integrate risk management with strategic objectives.
3. ISO 31000
Recognized globally, ISO 31000 sets out risk management principles and best practices for organizations of any size or sector. It revolves around risk identification, assessment, treatment, and monitoring, making it a flexible framework adaptable across industries like manufacturing, finance, and healthcare.
Why it stands out: Its adaptability fosters a risk-aware culture within organizations.
4. ITIL Framework
The ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library) framework is tailored for IT service management. It aligns IT operations with broader business goals while addressing risks such as cybersecurity threats, downtime, and service disruptions.
Who benefits most: Businesses that rely heavily on complex IT systems and prioritize efficiency and customer satisfaction.
5. PMBOK Risk Framework
The PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) framework is designed for project-based risk management. It outlines processes to identify, analyze, and respond to risks throughout the project lifecycle.
Best suited for: Industries such as construction, software development, and engineering, where delays or cost overruns can cause significant setbacks.
While these frameworks provide structure and best practices, many organizations still struggle with real-time application, monitoring, and integration across departments. This is where platforms like Auditive bring a competitive edge, enabling businesses to operationalize these frameworks with automation, continuous monitoring, and enhanced visibility.
What Are the Steps of the Risk Management Framework?
A risk management framework (RMF) provides structure to how organizations prepare for, assess, and respond to risks. However, a framework is only as strong as its implementation. Following a disciplined sequence of steps ensures that risks are consistently identified, managed, and monitored, not just during design, but throughout the entire lifecycle of your business processes.
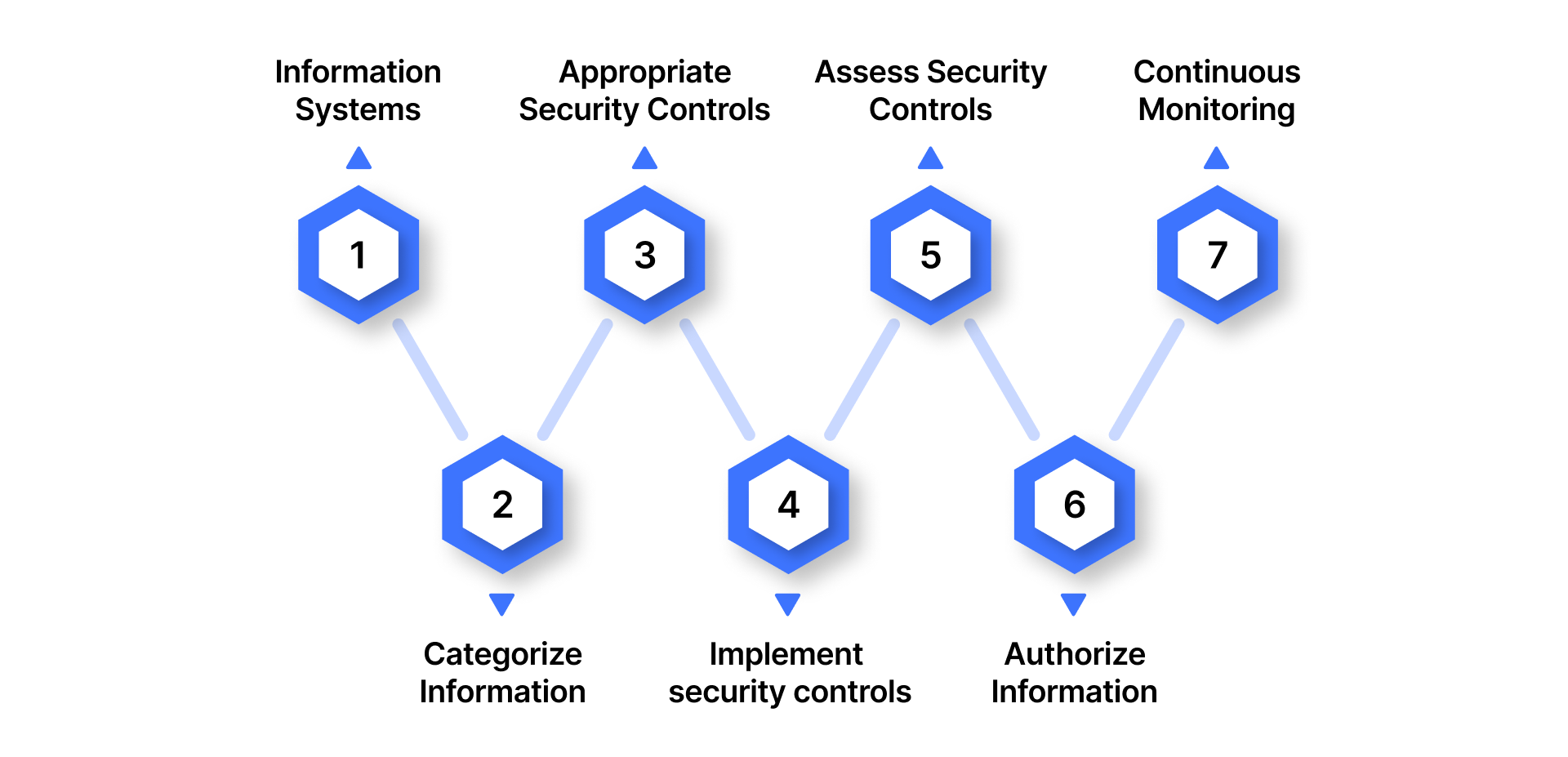
Here’s a detailed look at the seven essential steps of the RMF:
1. Prepare your information systems
This foundational stage sets the direction for the entire framework. It involves aligning risk management activities with business objectives, protecting critical assets, and embedding privacy considerations from the start. By preparing systems upfront, organizations can simplify later implementation, save resources, and establish a culture of security-first decision-making.
2. Categorize information systems
Not all systems carry the same weight of risk. Categorization helps identify which systems and data are most sensitive based on regulatory requirements, financial implications, and business impact. For example, customer payment data would be categorized as high priority compared to internal administrative tools. Standards such as NIST FIPS 199 provide clear guidelines to structure this process.
3. Select appropriate security controls
Once risks are categorized, the next step is selecting the right safeguards. NIST’s extensive catalog of security controls offers a blueprint, but the selection must be tailored to the organization’s environment. For instance, a healthcare provider might emphasize HIPAA compliance controls, while a financial institution might focus more on SOX-related measures. This step ensures risks are met with the right level of protection.
4. Implement security controls
Here, planning translates into action. Controls are deployed across systems, applications, and processes to mitigate vulnerabilities. Implementation isn’t just technical, it also includes process alignment, employee awareness, and policy enforcement. The goal is to make security controls operational without disrupting business continuity.
5. Assess security controls
Controls must be tested and validated. Regular assessments measure their effectiveness against defined benchmarks and regulatory requirements. Assessments can include internal audits, penetration testing, or third-party evaluations. This ensures the controls not only exist on paper but actively reduce risk in practice.
Learn more: Third-Party Risk Management: Guidance on Achieving Compliance
6. Authorize information systems
Once controls have been assessed, senior officials or executives grant authorization for systems to operate. This step reinforces accountability and ensures that decision-makers understand the risks, controls in place, and potential implications. Authorization acts as a formal checkpoint before systems become fully operational within the framework.
7. Continuous monitoring
The final step is ongoing vigilance. Risks are dynamic, new threats emerge, compliance standards evolve, and business priorities shift. Continuous monitoring ensures that the framework adapts to these changes. This may involve automated tools for real-time alerts, periodic reviews, or reassessments to identify gaps and recalibrate controls.
When executed properly, these steps transform the RMF into more than a compliance exercise; they make it a living framework that evolves with your organization and strengthens resilience against emerging risks.
The challenge, however, lies in execution. Many organizations struggle with silos, manual processes, and lack of real-time visibility. This is where Auditive becomes a strategic partner, automating risk tracking, simplifying compliance workflows, and ensuring your risk management framework is continuously monitored through its Trust Center and vendor risk management capabilities.
Components of a Risk Management Framework
A strong risk management framework is built on seven interconnected components that guide organizations from identifying risks to continuously improving their strategies. Each component ensures risks are addressed holistically, systematically, and in alignment with business objectives.
1. Risk Identification
The foundation of any framework starts with risk identification. This involves systematically spotting and documenting potential threats that could disrupt operations or objectives. Sources include historical data, industry benchmarks, internal assessments, and expert judgment. A thorough identification process builds a complete “risk inventory,” forming the baseline for all subsequent actions.
2. Risk Assessment and Analysis
After identifying risks, the next step is to assess and analyze their likelihood and impact. This goes beyond recognition, it measures intensity, probability, and consequences. Tools such as surveys, audits, and scenario planning help translate uncertainty into actionable insights. By doing so, organizations move from reactive decision-making to proactive preparedness.
3. Risk Mitigation
Mitigation transforms insights into action. It’s where organizations design strategies to reduce the likelihood or impact of risks. This could involve contingency planning, policy creation, or operational adjustments. Effective mitigation ensures risks don’t remain abstract, they’re countered with clear, executable responses.
4. Risk Monitoring and Reviewing
Risk is never static; it evolves with changing business conditions. Monitoring and reviewing involve continuously tracking risk profiles, assessing whether mitigation strategies are effective, and adjusting when needed. This keeps organizations agile and ensures small risks don’t snowball into larger threats.
5. Risk Communication and Reporting
Transparent communication ensures that stakeholders, from employees to regulators, understand both the risks and the strategies in place to address them. At the same time, open consultation encourages participation, bringing in diverse insights that can strengthen risk management practices. Strong communication makes risk management inclusive and credible.
Must read: Understanding Business Continuity and Risk Management Strategies
6. Governance and Compliance
Governance ensures risk management efforts align with organizational values, strategic goals, and regulatory requirements. Compliance with industry standards and laws not only minimizes exposure but also builds trust with stakeholders.
7. Continuous Improvement
No framework is complete without a commitment to continuous improvement. Lessons from past incidents, evolving regulations, and stakeholder feedback feed back into the system, ensuring that risk management practices remain relevant, efficient, and resilient over time.
Together, these seven components create a structured, adaptable framework that empowers businesses to navigate uncertainty with confidence.
While frameworks define the structure, executing them effectively requires real-time intelligence and automation. This is where solutions like Auditive step in, helping organizations transform their frameworks into actionable, technology-driven strategies for proactive risk management.
What are the Benefits of a Strong Risk Management Framework?
A strong risk management framework is more than just a defensive shield, it’s a strategic enabler that helps businesses thrive in uncertain environments. By proactively addressing risks, organizations can uncover hidden opportunities, improve efficiency, and build resilience for long-term success.
Here are the key benefits:
1. Boosts Operational Efficiency
A structured risk framework highlights inefficiencies and redundancies within processes. By clarifying potential risks, organizations can streamline workflows, optimize resource allocation, and ensure teams focus on what truly matters.
2. Strengthens Financial Performance
Proactive risk management safeguards against costly disruptions. By mitigating potential financial losses and aligning with regulatory requirements, organizations protect their bottom line while fostering sustainable growth.
3. Cultivates Trust
Transparency in handling risks reassures stakeholders, clients, and employees. Demonstrating preparedness instills confidence and strengthens relationships, reinforcing an organization’s reputation as reliable and resilient.
4. Reinforces Compliance
Non-compliance can be financially and reputationally devastating. Embedding compliance within the risk management framework ensures organizations stay aligned with evolving rules and reduces the likelihood of penalties.
Also read: Guide to Effective Reputation Risk Management and Mitigation
5. Enhances Adaptability
Resilient organizations don’t just react to challenges; they evolve with them. A risk framework encourages a culture of foresight and innovative problem-solving, equipping businesses to navigate shifting markets and emerging threats with agility.
By combining efficiency, financial resilience, trust, compliance, and adaptability, a well-designed framework empowers organizations not only to withstand risks but also to use them as stepping stones toward growth.
This is also where Auditive steps in, helping businesses operationalize these benefits with advanced vendor risk management and Trust Center capabilities, ensuring risks are not just managed but turned into strategic opportunities.
Challenges in Implementing Risk Management Framework
While risk frameworks provide a structured way to manage uncertainty, organizations often face hurdles in putting them into practice. Some of the most common challenges include:
Lack of management’s support: Without strong leadership and commitment from senior management, RMF implementation can end up being a checkbox exercise rather than a meaningful risk strategy.
Limited awareness and expertise: Many teams lack deep knowledge of risk management principles or don’t have access to skilled professionals to guide adoption.
Resistance to change: Employees and even leaders may resist new processes due to fear of disruption, skepticism about benefits, or a preference for the status quo.
Siloed risk practices: Risk initiatives are often confined to isolated departments, preventing a unified, enterprise-wide risk perspective.
Integration challenges: Aligning RMF with existing workflows, technology systems, and evolving regulatory standards can prove difficult, particularly in fast-paced industries.
Resource constraints: Insufficient budget, time, or personnel can hinder the effective rollout and monitoring of the framework.
These challenges highlight why many organizations struggle to achieve maturity in their risk frameworks. The solution often lies in using modern platforms that provide automation, real-time insights, and cross-team collaboration.
This is where Auditive steps in, helping businesses overcome these roadblocks with intelligent risk monitoring and a centralized Trust Center that unifies risk practices across teams.
How Auditive Strengthens Your Risk Management Framework
Implementing a risk framework is only effective if it adapts to modern business needs. Auditive helps organizations cut through complexity by unifying risk practices under one intelligent platform.
Centralized Trust Center: Consolidates vendor and enterprise risk data, giving leadership and teams a single source of truth.
Automated Risk Monitoring: Continuously tracks compliance, vendor risk, and emerging threats, reducing the chances of oversight.
Cross-Team Visibility: Breaks down silos by enabling collaboration across departments for a holistic risk strategy.
Scalable Governance: Ensures your framework evolves with regulatory changes, business growth, and new technologies.
With Auditive, risk frameworks move beyond policy documents to become living, adaptive systems that actively safeguard business resilience and compliance.
Conclusion
A well-designed risk management framework is more than compliance; it’s a foundation for sustainable business resilience. While challenges like resource gaps, siloed practices, and resistance to change can slow adoption, the payoff is significant: greater visibility, smarter decisions, and stronger governance.
This is where solutions like Auditive add real value. By using its Trust Center and automation, organizations can strengthen their vendor risk management processes, ensure compliance, and maintain a proactive risk posture. Instead of treating risk as a reactive checklist, your business gains an integrated, adaptive system that grows alongside your strategy.
Ready to future-proof your risk management framework? Partner with Auditive and turn risk into a strategic advantage.
FAQs
1. What is a risk management framework (RMF)?
An RMF is a structured approach for identifying, assessing, responding to, and monitoring risks to improve organizational resilience and compliance.
2. Why is a risk management framework important?
It standardizes risk practices, ensures compliance with regulations, and helps businesses make informed decisions while protecting assets and reputation.
3. What are the main components of an RMF?
Core components include risk identification, analysis, evaluation, treatment, monitoring, governance, and reporting.
4. How does vendor risk management fit into an RMF?
Vendors can expose businesses to financial, operational, and compliance risks. Integrating vendor risk management into the RMF ensures third-party risks are continuously monitored and mitigated.
5. How does Auditive support RMF implementation?
Auditive provides real-time risk monitoring, automated assessments, and a centralized Trust Center, enabling organizations to unify risk practices and stay ahead of threats.