ESG Guidelines: Comprehensive Guide to Environmental, Social, and Governance
Businesses are expected to do more than deliver profits; they must operate responsibly, ethically, and sustainably. This is where ESG guidelines come into play. ESG, which stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance, provides a framework for organizations to measure and report on their broader impact beyond financial performance.
ESG has emerged as a key component of how businesses develop long-term resilience, draw in investors, and gain the trust of stakeholders. This includes everything from cutting carbon emissions and guaranteeing ethical labor practices to upholding open governance structures.
As regulatory bodies, investors, and consumers place growing emphasis on ESG standards, organizations can no longer view them as optional. Instead, ESG guidelines are now a strategic necessity, shaping corporate reputation, compliance efforts, and competitive advantage.
Quick Glance
ESG guidelines define how companies should manage environmental, social, and governance responsibilities.
Global trends show stricter, more harmonized ESG regulations are on the horizon.
Vendors significantly influence ESG compliance, making vendor risk management critical.
Technology like AI and automation will drive transparency and efficiency in ESG reporting.
Auditive’s Trust Center helps organizations streamline ESG compliance with real-time monitoring and automated due diligence.
What is ESG?
ESG, short for Environmental, Social, and Governance, represents the three key dimensions that define how responsibly and sustainably a company operates. It has become a central framework for measuring a business’s long-term performance beyond financial results, highlighting how it manages risks, opportunities, and its broader impact on society.
The roots of ESG trace back to the “triple bottom line” principle: people, planet, and profit. This approach emphasizes that true success isn’t just about revenue growth but also about reducing environmental harm, fostering social responsibility, and ensuring transparent governance.
Unlike a single universal standard, ESG is built on a variety of frameworks and reporting metrics. These range from climate and carbon disclosures to diversity and inclusion programs, labor practices, and corporate governance structures. Collectively, they offer investors, regulators, and stakeholders a clear lens into how an organization aligns its operations with ethical and sustainable business practices.
What Are the Three ESG Key Factors?
The concept of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) is built on the belief that companies should be assessed not only by their financial outcomes but also by how responsibly they operate in relation to the planet, people, and internal leadership. These three pillars form the foundation of sustainable business practices, each addressing unique risks, opportunities, and long-term value creation.
1. Environmental (E)
The environmental pillar evaluates a company’s effect on the natural world and its readiness to manage climate-related risks. It goes beyond cutting emissions; it’s about building long-term sustainability and resilience.
Key focus areas include:
Climate change and carbon footprint: Greenhouse gas emissions, energy efficiency, and preparedness for climate risks like extreme weather or rising sea levels.
Water management: Responsible sourcing, usage efficiency, and wastewater treatment.
Biodiversity and land use: How operations impact ecosystems, including deforestation and raw material extraction.
Resource dependency: Reliance on non-renewable inputs such as fossil fuels or rare minerals.
Waste and pollution control: Managing hazardous waste, industrial byproducts, and plastics.
Companies that fail to address environmental concerns may face regulatory costs, supply disruptions, and reputational damage.
Also look into: Reputation Risk Management Guide
2. Social (S)
The social dimension measures how a company treats its employees, customers, and the wider community. It emphasizes human rights, labor practices, and the role of business in society.
Core aspects include:
Fair pay and labor conditions: Ensuring compliance with wage laws and ethical work environments.
Health, safety, and workforce development: Providing safe workplaces and opportunities for employee growth.
Community engagement: Supporting local communities through investments or partnerships.
Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI): Promoting representation and equal opportunity across all groups.
Customer protection: Safeguarding privacy and ensuring responsible use of personal data.
Strong social policies not only reduce risks but also strengthen brand loyalty and employee retention.
3. Governance (G)
Governance covers leadership, corporate ethics, and accountability. It ensures that decisions are made transparently and align with stakeholder interests.
Key indicators include:
Board structure and independence: Diverse boards with independent oversight drive accountability.
Executive pay: Linking compensation to performance and ensuring pay equity.
Transparency and compliance: Accurate financial reporting and adherence to regulations.
Ethics and anti-corruption: Policies to prevent bribery, fraud, and other misconduct.
Stakeholder engagement: Giving investors and stakeholders a voice in shaping corporate direction.
Without strong governance, even the best environmental or social programs lack credibility. Governance is the backbone that holds ESG commitments together.
Why ESG Matters?
ESG guidelines are more than just compliance requirements; they are a reflection of how prepared an organization is to meet future expectations while maintaining trust with stakeholders. Companies that embrace ESG are not only mitigating risks but also unlocking opportunities for growth, efficiency, and stronger market positioning.
Here’s why ESG truly matters:
Early Risk Identification – ESG practices help organizations detect environmental, social, and governance risks before they escalate, from regulatory changes to supply chain vulnerabilities.
Investor Appeal – Transparent ESG strategies attract investors who increasingly prioritize sustainability and ethics in their decision-making.
Operational Gains – Initiatives like energy savings, waste reduction, and responsible sourcing often translate into measurable cost efficiencies.
Governance and Accountability – Strong governance frameworks ensure regulatory alignment, ethical decision-making, and reduced compliance risks.
Brand Reputation and Loyalty – Companies committed to ESG earn greater consumer trust, foster loyalty, and stand out in competitive markets.
Read more about: Reputation Risk Management Guide
Ultimately, ESG matters because it sets the benchmark for responsible, resilient, and future-ready businesses. Organizations that treat ESG as a core strategy, not an afterthought, position themselves to thrive in an economy that values both performance and purpose.
What Are ESG Regulations?
ESG regulations are mandatory rules introduced by regulators to ensure businesses act responsibly in their environmental, social, and governance practices. Unlike voluntary efforts, these frameworks make companies legally accountable for sustainability and ethical performance.
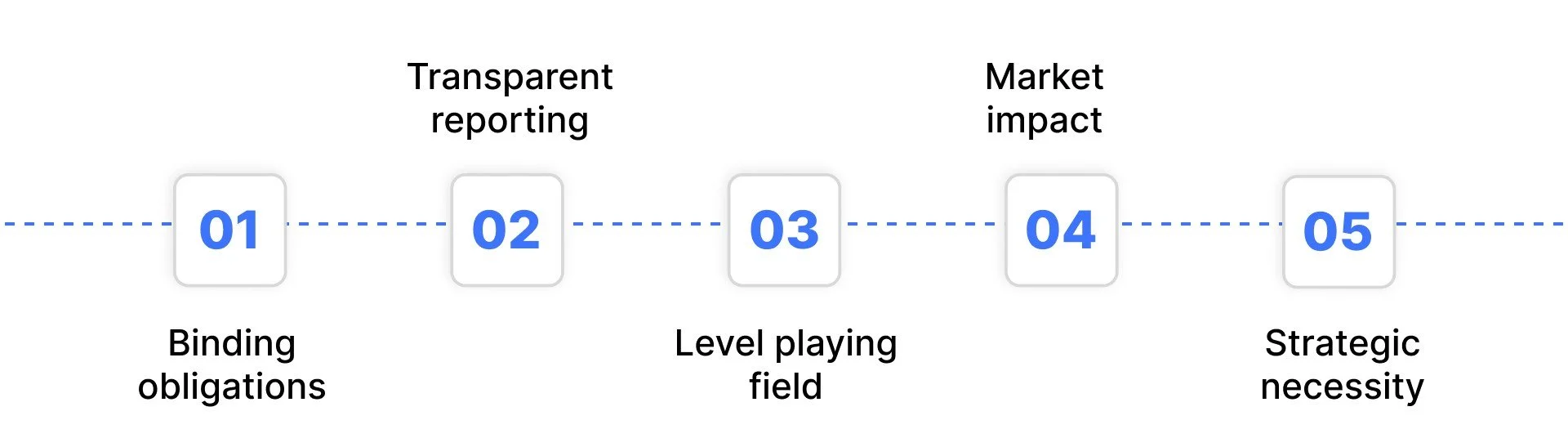
Key aspects of ESG regulations include:
Binding obligations – Companies must comply with established reporting and disclosure standards rather than optional commitments.
Transparent reporting – Requires clarity on metrics such as emissions, labor conditions, or governance structures to prevent “greenwashing.”
Level playing field – Sets universal expectations so that all businesses are assessed against the same sustainability benchmarks.
Market impact – Shapes investor decisions, consumer trust, and a company’s ability to remain competitive long-term.
Strategic necessity – ESG compliance is increasingly tied to risk management and resilience, not just regulatory approval.
Organizations looking to manage ESG regulations more effectively can use platforms like Auditive, which simplify compliance while strengthening vendor trust and accountability.
The Global Landscape of ESG Regulations
ESG regulations have taken shape differently across the world, with each region tailoring its approach to match local priorities, policy goals, and economic contexts. Understanding these variations is critical for businesses operating across borders, as compliance requires not only meeting one set of rules but also adapting to diverse frameworks simultaneously.
1. European Union (EU): Setting the global tone
The EU has established itself as a front-runner in ESG oversight, introducing some of the most comprehensive and binding measures. By creating strict classification systems and requiring extensive corporate disclosures, the EU aims to direct capital toward sustainable activities and prevent greenwashing. Its framework has influenced many other regions to follow suit, positioning Europe as the benchmark for ESG compliance.
2. United States: Shifting toward mandatory reporting
In the US, ESG oversight is evolving rapidly. Federal agencies, particularly the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), are pushing for standardized climate-related disclosures, while state-led initiatives are raising the bar for corporate accountability. Although the system is still less centralized than in Europe, businesses should prepare for greater alignment and more binding requirements in the near future.
3. United Kingdom: Building on global best practices
The UK has embedded ESG reporting firmly into corporate governance. By mandating climate-related disclosures and implementing strict sustainability requirements for financial institutions, the UK ensures businesses are transparent about both risks and opportunities. These measures align with its long-term net-zero target, reinforcing the country’s leadership in sustainable finance.
4. India: Aligning growth with sustainability
Emerging economies are also tightening their ESG focus, and India is a prime example. Mandatory reporting for top-listed companies and new national guidelines promote responsible business conduct while keeping economic development in view. These steps highlight how ESG is no longer just a developed-market concern but a universal expectation.
As these regional frameworks expand and converge, businesses face the dual challenge of ensuring compliance while staying agile enough to meet evolving demands.
This is where platforms like Auditive provide a distinct advantage, helping organizations centralize ESG reporting, simplify vendor oversight, and maintain compliance seamlessly across multiple jurisdictions.
How to Define ESG Goals
Setting effective ESG goals is about aligning sustainability commitments with your company’s core mission and business strategy. Instead of broad promises, organizations need structured objectives that drive measurable outcomes and long-term value.
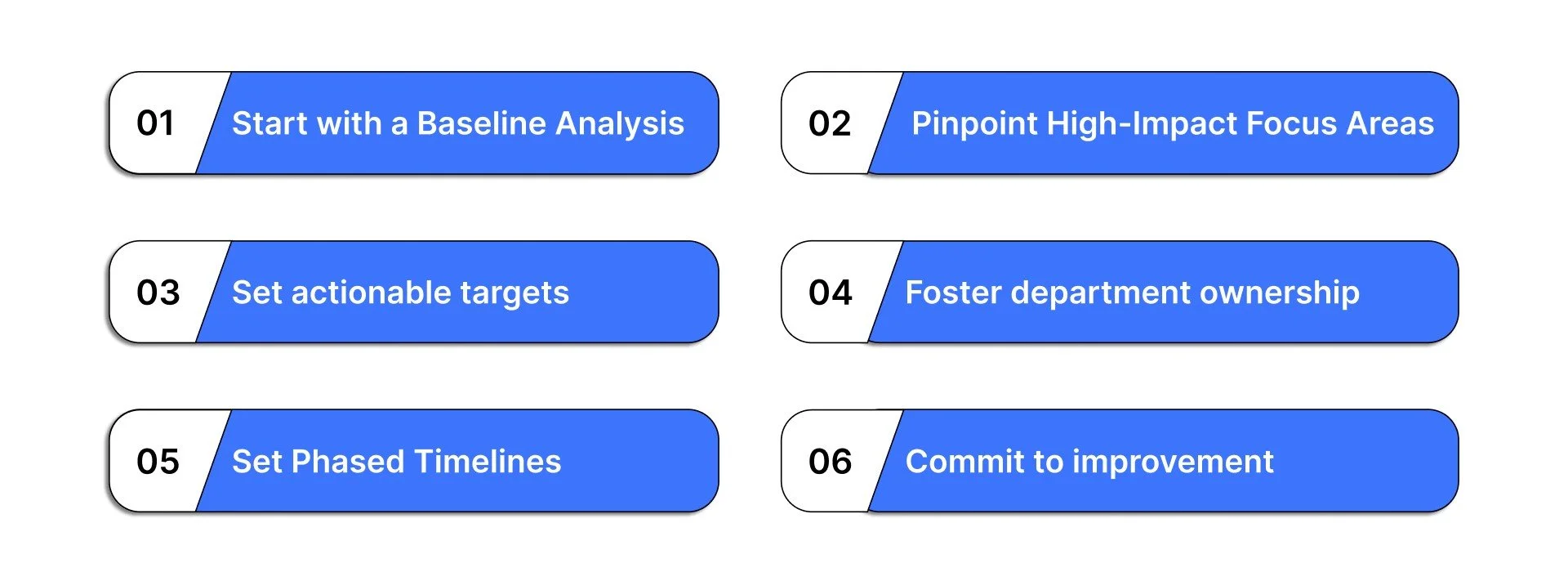
1. Start with a Baseline Analysis
Before mapping out ESG targets, organizations must first understand their current position. This assessment acts as the foundation for goal-setting and ensures focus on the right areas.
Review existing ESG policies and initiatives
Identify strengths, weaknesses, and compliance gaps
Map risks across supply chain, workforce, and operations
By establishing a baseline, companies gain a clear picture of where they stand and what needs urgent attention.
Also read: Managing Supply Chain Vulnerability
2. Pinpoint High-Impact Focus Areas
Not all ESG themes apply equally to every business. Prioritizing the areas that have the greatest relevance ensures resources are used wisely.
Environmental goals like carbon reduction or energy efficiency
Social aspects such as employee well-being, diversity, or community impact
Governance priorities like board independence or transparent reporting
This prioritization makes goals both relevant and achievable, driving stronger stakeholder engagement.
3. Create Measurable and Actionable Targets
Ambiguity undermines credibility. Goals must be precise and structured to prove accountability.
Use clear KPIs (e.g., reduce emissions by 25% within 3 years)
Ensure targets are data-driven and time-bound
Avoid vague commitments that lack evidence or tracking
Concrete goals make it easier to measure progress and build trust with regulators, investors, and customers.
4. Build Ownership Across Departments
ESG cannot be achieved in silos. Assigning responsibilities ensures accountability and consistent follow-through.
Appoint ESG leads in each department
Align individual performance metrics with ESG priorities
Promote collaboration across sustainability, finance, HR, and operations
When ESG becomes part of everyday roles, it shifts from a compliance exercise to a cultural commitment.
5. Set Phased Timelines
Breaking down big aspirations into smaller milestones ensures steady progress and avoids losing momentum.
Short-term: 1–2 years, focusing on compliance and quick wins
Medium-term: 3–5 years, integrating ESG deeper into operations
Long-term: 5+ years, achieving transformational goals like net-zero
This phased approach balances ambition with practicality, helping organizations stay on track even as external factors evolve.
6. Commit to Continuous Improvement
ESG is not static, it requires flexibility and adaptability.
Track performance through regular reporting cycles
Adjust strategies to reflect new regulations or industry benchmarks
Using technology for more accurate monitoring and insights
Continuous improvement ensures ESG goals remain meaningful and aligned with long-term business objectives.
Still, many organizations find it difficult to track whether vendors align with their ESG commitments. That’s where Auditive plays a vital role, offering real-time frameworks and automated monitoring to simplify ESG compliance and vendor alignment.
Key Components of ESG Regulations
ESG regulations are structured around a few essential elements that ensure companies adopt responsible practices while maintaining transparency with stakeholders. The most important include:
Mandatory Disclosures – Organizations are required to share measurable information on areas such as environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance integrity. This includes climate data, workforce policies, and ethical conduct.
Risk and Impact Assessments – Companies must actively evaluate potential risks linked to their operations and supply chains, particularly in areas such as sustainability, human rights, and corporate ethics.
Standardized Reporting Frameworks – To improve clarity and comparability across industries, businesses follow established reporting systems that align ESG information with global benchmarks.
Independent Validation – Third-party verification strengthens the reliability of ESG reporting, giving investors and regulators confidence in the accuracy of disclosures.
These components form the backbone of effective ESG compliance, ensuring organizations remain accountable while building long-term trust.
At this point, businesses often look for streamlined solutions that make ESG compliance less fragmented and more reliable, this is where platforms like Auditive provide real value.
The Future of ESG Regulations and the Role of Auditive
As ESG becomes a central pillar of global business strategy, regulations are set to grow more stringent, transparent, and standardized. Several trends are shaping this future:
Harmonization of Standards – Global initiatives, such as those by the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation, are moving toward unified ESG reporting frameworks. This reduces complexity, allowing companies to streamline compliance while enabling investors to make more consistent and reliable comparisons.
Integration into Financial Systems – ESG metrics are no longer treated as optional. Institutional investors and asset managers now embed ESG criteria directly into portfolio strategies, viewing companies with strong ESG performance as more resilient, trustworthy, and better prepared for long-term success.
Technological Advancements – Emerging technologies like AI, automation, and advanced analytics are transforming ESG reporting. These innovations improve the accuracy, speed, and transparency of data collection, verification, and reporting, helping businesses align with evolving regulations more effectively.
But keeping pace with these shifts requires more than compliance checklists; it calls for intelligent tools that provide real-time visibility and proactive risk management.
This is where Auditive adds strategic value. Through its Trust Center, Auditive empowers organizations to continuously monitor ESG compliance across their vendor ecosystem, validate supplier claims against global benchmarks, and automate due diligence. By combining transparency with scalability, Auditive transforms ESG compliance from a regulatory burden into a competitive advantage, ensuring that organizations remain compliant, accountable, and future-ready.
Conclusion
ESG guidelines are no longer optional; they are now integral to how organizations build credibility, attract investors, and ensure long-term sustainability. From harmonized regulations to AI-driven compliance tools, the ESG landscape is evolving rapidly, and businesses that take a proactive stance will stay ahead of regulatory pressures and stakeholder expectations.
To succeed, organizations must not only align with global ESG standards but also ensure that their vendor ecosystems are compliant and transparent. This is where Vendor Risk Management becomes a critical enabler. By using tools like Auditive’s Trust Center, companies can gain real-time insights, validate vendor ESG claims, and maintain continuous compliance monitoring across their supply chains.
Meeting ESG expectations is no longer about ticking boxes, it’s about showing measurable action. If you’re looking for practical ways to translate ESG commitments into operational trust, Auditive can help you bridge that gap.
ESG compliance is quickly becoming a competitive differentiator. By using Auditive, you can shift from reactive reporting to proactive ESG leadership, strengthening resilience, building investor trust, and ensuring long-term sustainability.
Book a demo today to explore how your ESG program can achieve that transformation.
FAQs
1. What are ESG guidelines?
ESG guidelines refer to standards that outline how businesses should operate responsibly across three key areas, environmental, social, and governance. They help organizations demonstrate sustainability and ethical practices to investors, regulators, and customers.
2. Why are ESG regulations becoming stricter?
With growing climate concerns, social accountability, and investor demand for transparency, governments and international bodies are pushing for standardized ESG reporting to ensure businesses meet global sustainability goals.
3. How do ESG guidelines affect vendors and suppliers?
Vendors play a direct role in ESG compliance. A supplier’s practices, such as carbon emissions, labor policies, or governance standards, can impact a company’s ESG performance, making vendor risk management essential.
4. What role does technology play in ESG compliance?
Technologies like AI, automation, and analytics improve ESG reporting accuracy and help organizations track compliance in real time, reducing errors and enhancing accountability.
5. How can Auditive help with ESG compliance?
Auditive provides real-time vendor monitoring through its Trust Center, validates supplier claims against ESG benchmarks, and automates due diligence, ensuring businesses meet evolving ESG requirements efficiently.